
Thiol group is present in:
A. cystine
B. cysteine
C. methionine
D. cytosine
Answer
243.3k+ views
Hint:
Thiol group is –SH. The amino acid containing thiol group is a triprotic acid with three ionizable functional groups including a carboxylic acid, an amino, and a sulfhydryl group and is polar and non – charged.
Complete step by step answer:
Thiol is any organosulfur compound of the form R−SH, where R can be an alkyl or aryl group. Structure :
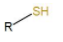
The –SH functional group is referred to as either a thiol group or a sulfanyl group.
In Thiols sulphur takes the place of oxygen in the hydroxyl group (-OH) of an alcohol.
In this question we are required to identify the compound containing thiol , among the options we can see that only cysteine contains the thiol (-SH) group.
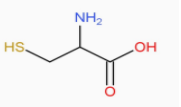
Cysteine symbol - Cys it is a polar , non- charged semi - essential proteinogenic amino acid with the formula $H{{O}_{2}}CCH(N{{H}_{2}})C{{H}_{2}}SH$.
As we can see in the diagram the thiol side chain in cysteine often participates in enzymatic reactions, as a nucleophile.
It is observed that the thiol on oxidation gives disulfide derivative cystine, which serves an important structural role in many proteins.
According to the new R/S system , based on the atomic numbers of atoms near the asymmetric carbon, we can say that cysteine shows R-chirality because sulphur is the second neighbour to the asymmetric carbon.
Cysteine shows amphoteric character in its monomeric form; it means that it can react both as an acid as well as a base.
As previously stated Cysteine is a semi – essential amino acid but for individuals with certain metabolic diseases or who suffer from malabsorption syndromes it is important.
So, the correct option is (B).
Note:
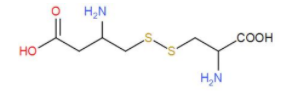
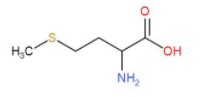
Methionine and cystine are both sulphur containing amino acids but (–SH) thiol group is not present and cystine is formed by joining two cysteine molecules together while cytosine does not have any sulphur. For better understanding study the diagrams:
Cystine -
Methionine –
Cytosine –
Thiol group is –SH. The amino acid containing thiol group is a triprotic acid with three ionizable functional groups including a carboxylic acid, an amino, and a sulfhydryl group and is polar and non – charged.
Complete step by step answer:
Thiol is any organosulfur compound of the form R−SH, where R can be an alkyl or aryl group. Structure :

The –SH functional group is referred to as either a thiol group or a sulfanyl group.
In Thiols sulphur takes the place of oxygen in the hydroxyl group (-OH) of an alcohol.
In this question we are required to identify the compound containing thiol , among the options we can see that only cysteine contains the thiol (-SH) group.

Cysteine symbol - Cys it is a polar , non- charged semi - essential proteinogenic amino acid with the formula $H{{O}_{2}}CCH(N{{H}_{2}})C{{H}_{2}}SH$.
As we can see in the diagram the thiol side chain in cysteine often participates in enzymatic reactions, as a nucleophile.
It is observed that the thiol on oxidation gives disulfide derivative cystine, which serves an important structural role in many proteins.
According to the new R/S system , based on the atomic numbers of atoms near the asymmetric carbon, we can say that cysteine shows R-chirality because sulphur is the second neighbour to the asymmetric carbon.
Cysteine shows amphoteric character in its monomeric form; it means that it can react both as an acid as well as a base.
As previously stated Cysteine is a semi – essential amino acid but for individuals with certain metabolic diseases or who suffer from malabsorption syndromes it is important.
So, the correct option is (B).
Note:
Methionine and cystine are both sulphur containing amino acids but (–SH) thiol group is not present and cystine is formed by joining two cysteine molecules together while cytosine does not have any sulphur. For better understanding study the diagrams:
Cystine -

Methionine –

Cytosine –

Recently Updated Pages
JEE Main 2026 Session 2 City Intimation Slip & Exam Date: Expected Date, Download Link

JEE Main 2026 Session 2 Application Form: Reopened Registration, Dates & Fees

JEE Main 2026 Session 2 Registration (Reopened): Last Date, Fees, Link & Process

WBJEE 2026 Registration Started: Important Dates Eligibility Syllabus Exam Pattern

Types of Solutions in Chemistry: Explained Simply

JEE Main Mock Test 2025-26: Principles Related To Practical

Trending doubts
JEE Main 2026: Session 1 Results Out and Session 2 Registration Open, City Intimation Slip, Exam Dates, Syllabus & Eligibility

Ideal and Non-Ideal Solutions Explained for Class 12 Chemistry

Understanding the Angle of Deviation in a Prism

Understanding Differential Equations: A Complete Guide

Hybridisation in Chemistry – Concept, Types & Applications

Understanding the Electric Field of a Uniformly Charged Ring

Other Pages
CBSE Class 12 Chemistry Question Paper 2026 PDF Download (All Sets) with Answer Key

NCERT Solutions For Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 10 Biomolecules - 2025-26

NCERT Solutions For Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 4 The D And F Block Elements - 2025-26

JEE Advanced Marks vs Ranks 2025: Understanding Category-wise Qualifying Marks and Previous Year Cut-offs

NCERT Solutions For Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 2 Electrochemistry - 2025-26

NCERT Solutions For Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 1 Solutions - 2025-26




