
The shape of ${{\text{O}}_{\text{2}}}{{\text{F}}_{\text{2}}}$is similar to:
(A) ${{\text{C}}_{\text{2}}}{{\text{F}}_{\text{2}}}$
(B) ${{\text{O}}_{\text{2}}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}$
(C) ${{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}{{\text{F}}_{\text{2}}}$
(D) ${{\text{C}}_{\text{2}}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}$
Answer
232.8k+ views
Hint: The bonding in the oxygen in dioxygen difluoride is different than the usual. This is particularly because of the very short distance between $\text{O-O}$ the bond and a long-distance along with the $\text{O-F}$bond. Thus the two $\text{O-F}$ bonds are arranged in the two planes perpendicular to each other. Such that the ${{\text{O}}_{\text{2}}}{{\text{F}}_{\text{2}}}$ exhibit open book structure.
Complete step by step solution:
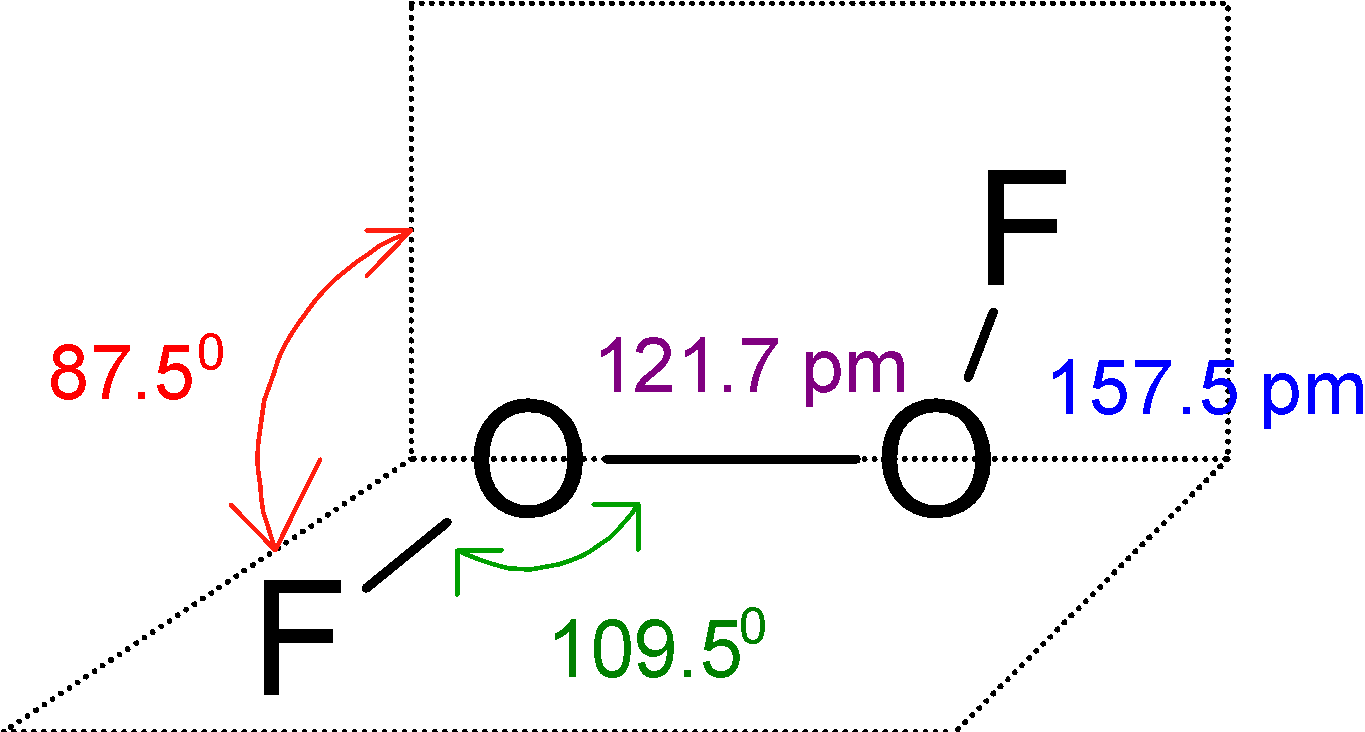
The ${{\text{O}}_{\text{2}}}{{\text{F}}_{\text{2}}}$has a large dihedral angle that approaches $\text{9}{{\text{0}}^{\text{0}}}\text{C}$ and has ${{\text{C}}_{\text{2}}}$ an axis of symmetry.
The VSEPR theory is used to decide the geometry of${{\text{O}}_{\text{2}}}{{\text{F}}_{\text{2}}}$.
The two oxygen atoms are bonded by the peroxide linkage. Each oxygen atom is bonded to a fluorine atom. The Lewis dot structure for the ${{\text{O}}_{\text{2}}}{{\text{F}}_{\text{2}}}$is as follows:
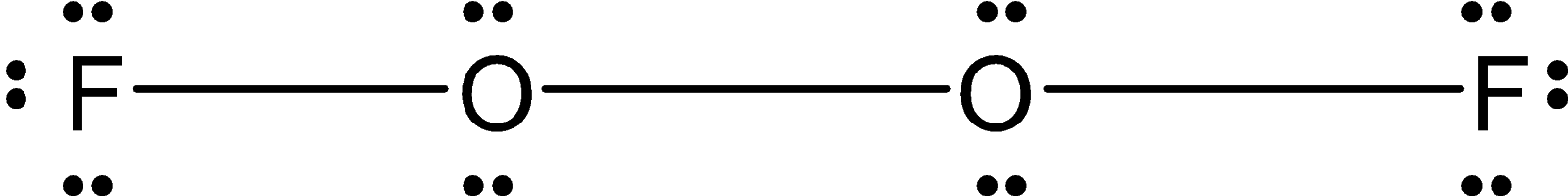
This ${{\text{O}}_{\text{2}}}{{\text{F}}_{\text{2}}}$ is an open book type structure. Since the oxygen has the two-electron pair the structure cannot be linear but it is like the fluorine atom is in a different plane. The structure is as follows:
Let's have a look at the option.
In ${{\text{C}}_{\text{2}}}{{\text{F}}_{\text{2}}}$ , the two carbon atoms are forming a covalent bond and each carbon is bonded to the two fluorine atom. the structure of the ${{\text{C}}_{\text{2}}}{{\text{F}}_{\text{2}}}$ is as shown below:
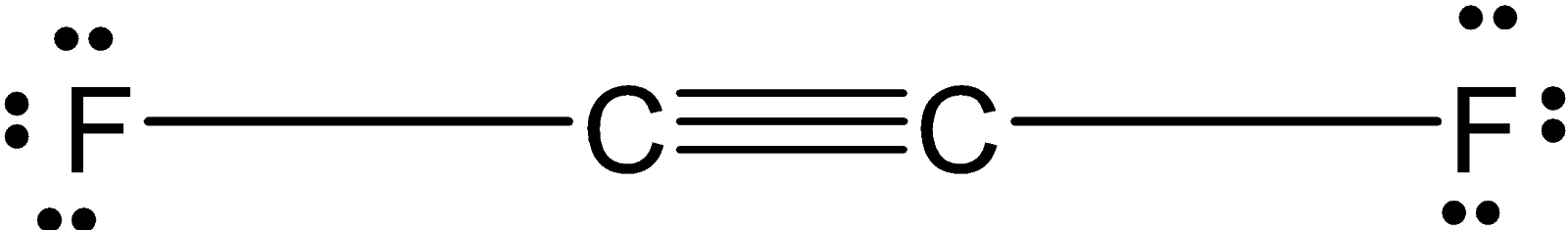
The two carbon atoms share the three bonds. Since the carbon is a $\text{sp}$ hybridized. The ${{\text{C}}_{\text{2}}}{{\text{F}}_{\text{2}}}$ have a linear structure.
Hydrogen peroxide ${{\text{O}}_{\text{2}}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}$ is a nonplanar molecule. Two oxygen are bonded with each other forming a peroxide bond. Each oxygen atom is bonded to the hydrogen atom. Since each oxygen has two lone pairs of electrons on it. The structure is not planar. Instead of that, it is non-planar when two hydrogen atoms are in a different plane. It has an open book structure as shown below.
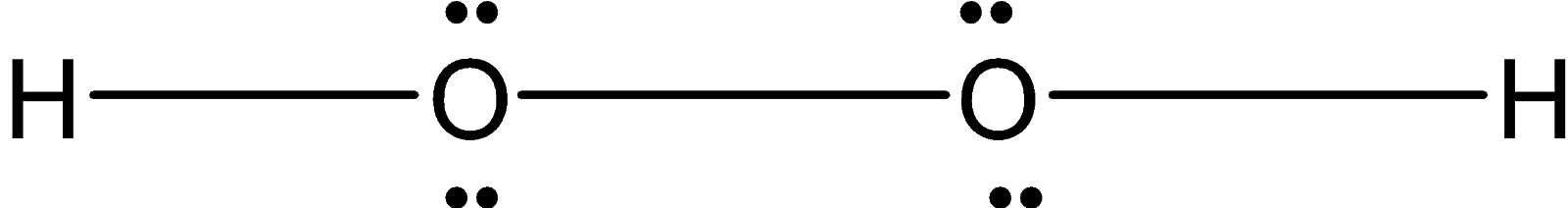
The ${{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}{{\text{F}}_{\text{2}}}$ is a dimer of $\text{HF}$. Since the $\text{HF}$ is linear molecule the dimer ${{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}{{\text{F}}_{\text{2}}}$ is also a linear molecule.

The ${{\text{C}}_{\text{2}}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}$ is a linear molecule. Here carbon is a $\text{sp}$ hybridized.
Therefore, hydrogen peroxide ${{\text{O}}_{\text{2}}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}$ has a similar shape ${{\text{O}}_{\text{2}}}{{\text{F}}_{\text{2}}}$.
Hence, (B) is the correct option.
Note: In general cases, the oxygen exhibits the $-2$ oxidation state. The peroxides like hydrogen peroxide have an unusual oxidation state of oxygen. The compound is electrically neutral. Thus oxidation state of oxygen is:
$\begin{align}
& \text{2(+1) + 2(x) = 0} \\
& \text{+2 = }-\text{2 x} \\
& \therefore \text{O}\text{.S}\text{.of oxygen = }-\frac{2}{2}=\text{ }-1 \\
\end{align}$
Therefore, the oxidation state of oxygen in hydrogen peroxide is $\text{ }-1\text{ }$.
The lone pairs on oxygen restricts the linear structure of hydrogen peroxide or ${{\text{O}}_{\text{2}}}{{\text{F}}_{\text{2}}}$ and the structure is open book structure.
Complete step by step solution:
The ${{\text{O}}_{\text{2}}}{{\text{F}}_{\text{2}}}$has a large dihedral angle that approaches $\text{9}{{\text{0}}^{\text{0}}}\text{C}$ and has ${{\text{C}}_{\text{2}}}$ an axis of symmetry.
The VSEPR theory is used to decide the geometry of${{\text{O}}_{\text{2}}}{{\text{F}}_{\text{2}}}$.
The two oxygen atoms are bonded by the peroxide linkage. Each oxygen atom is bonded to a fluorine atom. The Lewis dot structure for the ${{\text{O}}_{\text{2}}}{{\text{F}}_{\text{2}}}$is as follows:
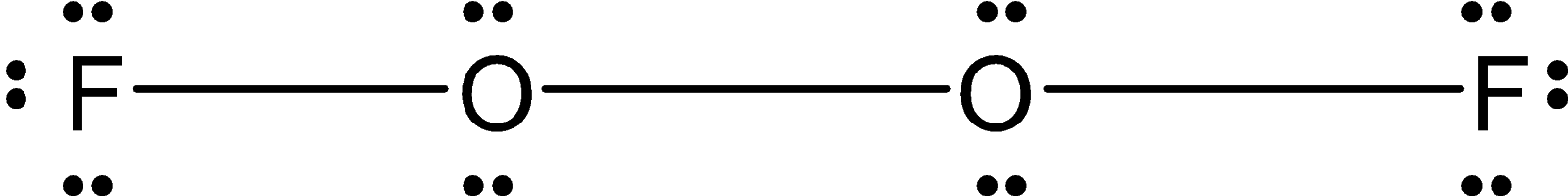
This ${{\text{O}}_{\text{2}}}{{\text{F}}_{\text{2}}}$ is an open book type structure. Since the oxygen has the two-electron pair the structure cannot be linear but it is like the fluorine atom is in a different plane. The structure is as follows:

Let's have a look at the option.
In ${{\text{C}}_{\text{2}}}{{\text{F}}_{\text{2}}}$ , the two carbon atoms are forming a covalent bond and each carbon is bonded to the two fluorine atom. the structure of the ${{\text{C}}_{\text{2}}}{{\text{F}}_{\text{2}}}$ is as shown below:
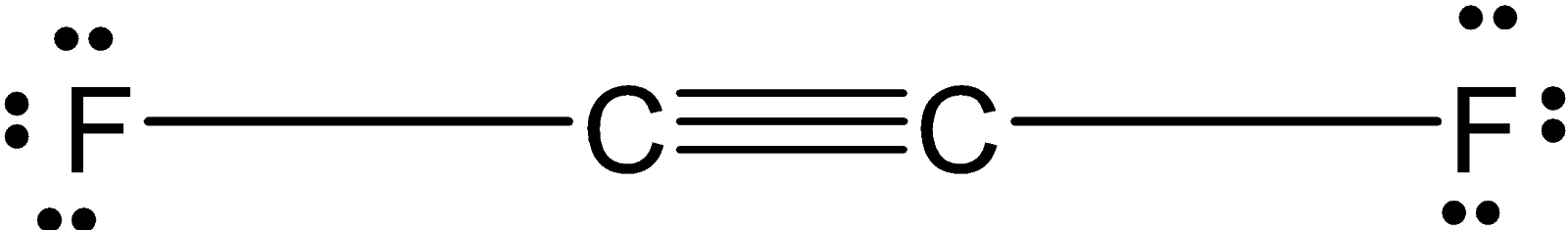
The two carbon atoms share the three bonds. Since the carbon is a $\text{sp}$ hybridized. The ${{\text{C}}_{\text{2}}}{{\text{F}}_{\text{2}}}$ have a linear structure.
Hydrogen peroxide ${{\text{O}}_{\text{2}}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}$ is a nonplanar molecule. Two oxygen are bonded with each other forming a peroxide bond. Each oxygen atom is bonded to the hydrogen atom. Since each oxygen has two lone pairs of electrons on it. The structure is not planar. Instead of that, it is non-planar when two hydrogen atoms are in a different plane. It has an open book structure as shown below.
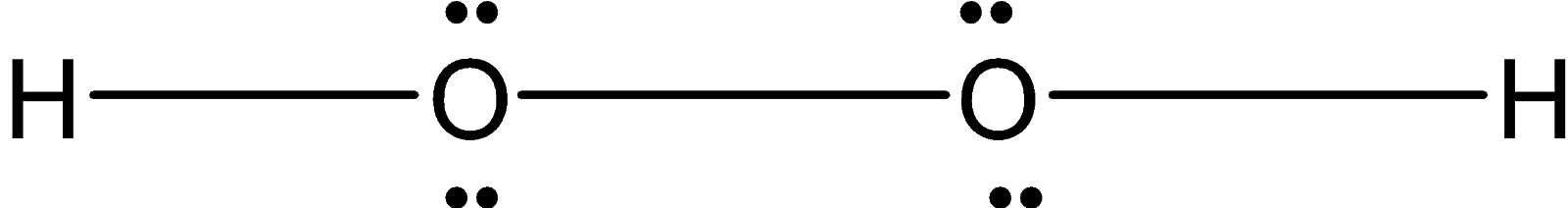
The ${{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}{{\text{F}}_{\text{2}}}$ is a dimer of $\text{HF}$. Since the $\text{HF}$ is linear molecule the dimer ${{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}{{\text{F}}_{\text{2}}}$ is also a linear molecule.

The ${{\text{C}}_{\text{2}}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}$ is a linear molecule. Here carbon is a $\text{sp}$ hybridized.
Therefore, hydrogen peroxide ${{\text{O}}_{\text{2}}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}$ has a similar shape ${{\text{O}}_{\text{2}}}{{\text{F}}_{\text{2}}}$.
Hence, (B) is the correct option.
Note: In general cases, the oxygen exhibits the $-2$ oxidation state. The peroxides like hydrogen peroxide have an unusual oxidation state of oxygen. The compound is electrically neutral. Thus oxidation state of oxygen is:
$\begin{align}
& \text{2(+1) + 2(x) = 0} \\
& \text{+2 = }-\text{2 x} \\
& \therefore \text{O}\text{.S}\text{.of oxygen = }-\frac{2}{2}=\text{ }-1 \\
\end{align}$
Therefore, the oxidation state of oxygen in hydrogen peroxide is $\text{ }-1\text{ }$.
The lone pairs on oxygen restricts the linear structure of hydrogen peroxide or ${{\text{O}}_{\text{2}}}{{\text{F}}_{\text{2}}}$ and the structure is open book structure.
Recently Updated Pages
JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 (January 31 Evening Shift) Question Paper with Solutions [PDF]

JEE Main 2023 January 30 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 25 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 24 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

Trending doubts
JEE Main 2026: Session 2 Registration Open, City Intimation Slip, Exam Dates, Syllabus & Eligibility

JEE Main 2026 Application Login: Direct Link, Registration, Form Fill, and Steps

Understanding the Angle of Deviation in a Prism

Hybridisation in Chemistry – Concept, Types & Applications

How to Convert a Galvanometer into an Ammeter or Voltmeter

Understanding the Electric Field of a Uniformly Charged Ring

Other Pages
JEE Advanced Marks vs Ranks 2025: Understanding Category-wise Qualifying Marks and Previous Year Cut-offs

Hydrocarbons Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 9 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Thermodynamics Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 5 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Equilibrium Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 6 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Organic Chemistry Some Basic Principles And Techniques Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 8 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

NCERT Solutions For Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 7 Redox Reactions (2025-26)




