
The product formed by heating a mixture of ammonium chloride and potassium cyanate is
A.\[{{\rm{N}}_{\rm{2}}}{\rm{O}}\]
B.\[{\rm{N}}{{\rm{H}}_{\rm{3}}}\]
C.\[{\rm{C}}{{\rm{H}}_{\rm{3}}}{\rm{N}}{{\rm{H}}_{\rm{2}}}\]
D.\[{{\rm{H}}_{\rm{2}}}{\rm{NCON}}{{\rm{H}}_{\rm{2}}}\]
Answer
233.1k+ views
Hint: The treatment of ammonium chloride with potassium cyanate gives ammonium cyanate. Ammonium cyanate under the action of heat forms urea.
Complete Step by Step Solution:
When a mixture of ammonium chloride and potassium cyanate is heated, they form ammonium cyanate.
The chemical formula of ammonium cyanate is
NH4CNO.
The reaction happens as follows:
\[{\rm{N}}{{\rm{H}}_{\rm{4}}}{\rm{Cl + KCNO}} \to {\rm{N}}{{\rm{H}}_{\rm{4}}}{\rm{CNO}}\]
Ammonium cyanate is a salt which occurs only as a weak intermediate.
Ammonium cyanate breaks down to ammonia and cyanic acid.
The chemical formula for cyanic acid is HOCN.
Ammonia and cyanic acid together form urea.
This is a reversible reaction.
This reaction is called Wohler's synthesis.
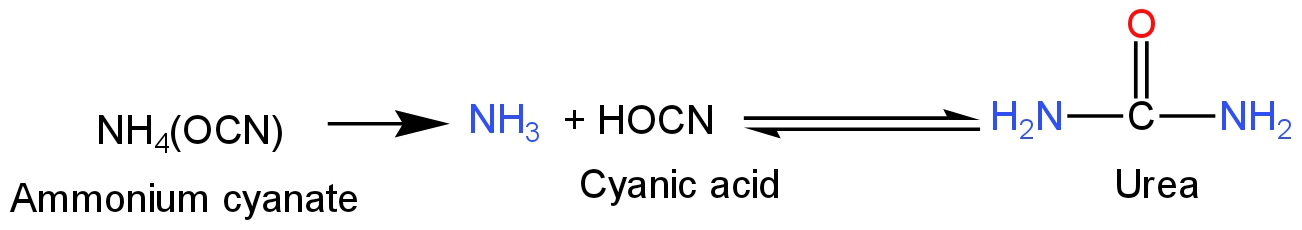
Image: Formation of urea
Out of the given options, option D is the chemical formula of urea.
So, option D is correct.
Additional Information: The Wöhler synthesis is the transformation of ammonium cyanate into urea. This chemical reaction was depicted in 1828 by Friedrich Wohler. It is frequently referred to as the beginning step of modern organic chemistry. Around 1780 chemists began to differentiate between organic compounds collected from
plants and animals and inorganic compounds readied from mineral sources. Berzelius, a Swedish chemist formulated that a ‘vital force’ was credible for the building of organic compounds. However, this belief was dismissed in 1828 when F. Wohler synthesise an organic compound, urea from an inorganic compound, ammonium cyanate.
There are different chemical names for urea like diaminomethanal, carbamide, carbonyl diamide, etc., but urea is the preferred IUPAC name.
Note: While attending to the question, one must have an idea about Wohler's synthesis reaction. The chemical formula of urea must be kept in mind while going through the given options.
Complete Step by Step Solution:
When a mixture of ammonium chloride and potassium cyanate is heated, they form ammonium cyanate.
The chemical formula of ammonium cyanate is
NH4CNO.
The reaction happens as follows:
\[{\rm{N}}{{\rm{H}}_{\rm{4}}}{\rm{Cl + KCNO}} \to {\rm{N}}{{\rm{H}}_{\rm{4}}}{\rm{CNO}}\]
Ammonium cyanate is a salt which occurs only as a weak intermediate.
Ammonium cyanate breaks down to ammonia and cyanic acid.
The chemical formula for cyanic acid is HOCN.
Ammonia and cyanic acid together form urea.
This is a reversible reaction.
This reaction is called Wohler's synthesis.

Image: Formation of urea
Out of the given options, option D is the chemical formula of urea.
So, option D is correct.
Additional Information: The Wöhler synthesis is the transformation of ammonium cyanate into urea. This chemical reaction was depicted in 1828 by Friedrich Wohler. It is frequently referred to as the beginning step of modern organic chemistry. Around 1780 chemists began to differentiate between organic compounds collected from
plants and animals and inorganic compounds readied from mineral sources. Berzelius, a Swedish chemist formulated that a ‘vital force’ was credible for the building of organic compounds. However, this belief was dismissed in 1828 when F. Wohler synthesise an organic compound, urea from an inorganic compound, ammonium cyanate.
There are different chemical names for urea like diaminomethanal, carbamide, carbonyl diamide, etc., but urea is the preferred IUPAC name.
Note: While attending to the question, one must have an idea about Wohler's synthesis reaction. The chemical formula of urea must be kept in mind while going through the given options.
Recently Updated Pages
JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 (January 31 Evening Shift) Question Paper with Solutions [PDF]

JEE Main 2023 January 30 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 25 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 24 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

Trending doubts
JEE Main 2026: Session 2 Registration Open, City Intimation Slip, Exam Dates, Syllabus & Eligibility

JEE Main 2026 Application Login: Direct Link, Registration, Form Fill, and Steps

Understanding the Angle of Deviation in a Prism

Hybridisation in Chemistry – Concept, Types & Applications

How to Convert a Galvanometer into an Ammeter or Voltmeter

Understanding the Electric Field of a Uniformly Charged Ring

Other Pages
JEE Advanced Marks vs Ranks 2025: Understanding Category-wise Qualifying Marks and Previous Year Cut-offs

NCERT Solutions For Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 1 Solutions (2025-26)

Solutions Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 1 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

NCERT Solutions For Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 4 The d and f Block Elements (2025-26)

Biomolecules Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 10 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

NCERT Solutions For Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 10 Biomolecules (2025-26)




