
The negative part of the addenda adds on to the carbon atom linked with the least number of hydrogen atoms. This statement is called
A. Thiele’s principle
B. Bayer’s strain theory
C. Markovnikov’s rule
D. Peroxide effect
Answer
233.1k+ views
Hint: In a hydrogenation process, alkenes react with hydrogen molecules in presence of a metal catalyst, thus hydrogen molecules are added to the double bond of alkene in such a way that each carbon atom is bonded with one hydrogen atom. This is an example of electrophilic addition reactions.
Complete Step by Step Answer:
When a hydrogen halide reacts with asymmetric alkenes the product formed by this electrophilic addition reaction is mainly governed by Markovnikov’s rule.
According to Markovnikov’s rule when hydrogen halide or protic acid reacts with asymmetric alkenes, the positive part of the reagent is added to the carbon atom attached with a higher number of hydrogen atoms while the negative part of addenda adds to the carbon atom linked with least number of hydrogen atoms. This electrophilic addition reaction is regioselective in nature which means one product is formed with a higher percentage as a major product while another one with a lower percentage is the minor product.
For example, propene reacts with hydrogen bromide to form $2-bromopropane$ the major product and $1-bromopropane$ the minor product. Here negative bromide ion $B{{r}^{-}}$gets attached to the carbon with the least number of hydrogen atoms and the positive ${{H}^{+}}$ion is linked with carbon with a higher number of hydrogen atoms and hence gives the $2-bromopropane$ major product according to Markovnikoff’s rule.
Thus,option (C) is correct.
Note: The overall reaction mechanism will be changed when a peroxide is present in the reaction medium. Alkene reacts with protic acid in presence of peroxide according to anti-Markovnikov’s rule. Here the overall regi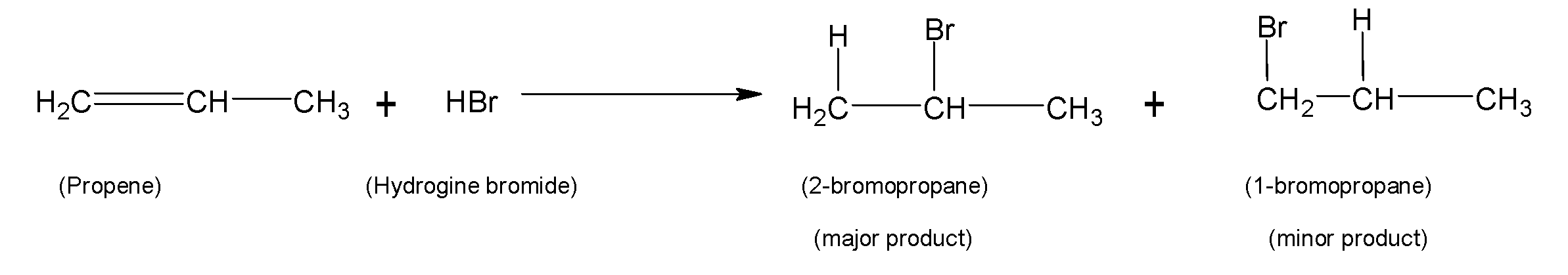 oselectivity will be changed as compared to Markovnikov’s rule.
oselectivity will be changed as compared to Markovnikov’s rule.
Complete Step by Step Answer:
When a hydrogen halide reacts with asymmetric alkenes the product formed by this electrophilic addition reaction is mainly governed by Markovnikov’s rule.
According to Markovnikov’s rule when hydrogen halide or protic acid reacts with asymmetric alkenes, the positive part of the reagent is added to the carbon atom attached with a higher number of hydrogen atoms while the negative part of addenda adds to the carbon atom linked with least number of hydrogen atoms. This electrophilic addition reaction is regioselective in nature which means one product is formed with a higher percentage as a major product while another one with a lower percentage is the minor product.
For example, propene reacts with hydrogen bromide to form $2-bromopropane$ the major product and $1-bromopropane$ the minor product. Here negative bromide ion $B{{r}^{-}}$gets attached to the carbon with the least number of hydrogen atoms and the positive ${{H}^{+}}$ion is linked with carbon with a higher number of hydrogen atoms and hence gives the $2-bromopropane$ major product according to Markovnikoff’s rule.
Thus,option (C) is correct.
Note: The overall reaction mechanism will be changed when a peroxide is present in the reaction medium. Alkene reacts with protic acid in presence of peroxide according to anti-Markovnikov’s rule. Here the overall regi
 oselectivity will be changed as compared to Markovnikov’s rule.
oselectivity will be changed as compared to Markovnikov’s rule.Recently Updated Pages
JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 (January 31 Evening Shift) Question Paper with Solutions [PDF]

JEE Main 2023 January 30 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 25 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 24 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

Trending doubts
JEE Main 2026: Session 2 Registration Open, City Intimation Slip, Exam Dates, Syllabus & Eligibility

JEE Main 2026 Application Login: Direct Link, Registration, Form Fill, and Steps

JEE Main Marking Scheme 2026- Paper-Wise Marks Distribution and Negative Marking Details

Understanding the Angle of Deviation in a Prism

Hybridisation in Chemistry – Concept, Types & Applications

How to Convert a Galvanometer into an Ammeter or Voltmeter

Other Pages
JEE Advanced Marks vs Ranks 2025: Understanding Category-wise Qualifying Marks and Previous Year Cut-offs

Hydrocarbons Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 9 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Thermodynamics Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 5 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Equilibrium Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 6 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Organic Chemistry Some Basic Principles And Techniques Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 8 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

NCERT Solutions For Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 7 Redox Reactions (2025-26)




