
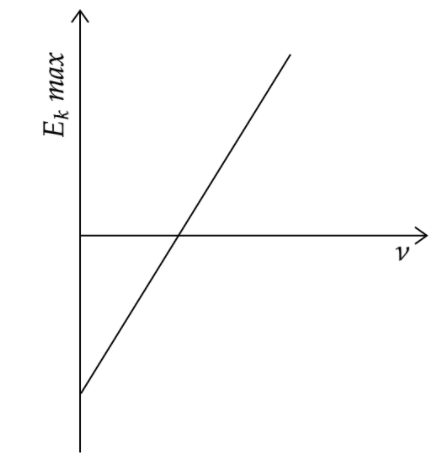
The maximum kinetic energy of the emitted frequency \[\nu \] of incident radiation is plotted as shown in the fig. This graph helps us in determining the following physical quantities:
(This question has multiple correct options)
A) Work function of the cathode metal
B) Threshold frequency
C) Planck’s constant
D) Charge on an electron
Answer
232.8k+ views
Hint: Before analysing the given graph, we should discuss in brief about the photoelectric effect. The photoelectric effect is the emission of electrons when electromagnetic radiation, such as light, hits a material. Electrons emitted in this manner are called photoelectrons. In classical electromagnetic theory, the photoelectric effect would be attributed to the transfer of energy from the continuous light waves to an electron.
Formula Used:
\[{{E}_{k}}\max =h\nu -W\]
Complete step by step solution:
The Einstein’s equation for photoelectric effect is given by \[{E_k}_max =h\nu -W\] where \[{{E}_{k}}\max \] is the maximum kinetic energy of the photoelectron, \[h\] is the Planck’s constant, \[\nu \] is the frequency of the incident light and \[W\] is the work function of the metal. Since \[{{E}_{k}}\max \] is plotted along the y-axis and \[\nu \] is plotted along the x-axis, we can write the equation of the graphical line as \[y=hx-W\].
Comparing the above equation with the standard equation for a straight line \[y=mx+c\] , we can say that the slope of the line is given by \[h\] , that is the Planck’s constant, the intercept on the y-axis is given by \[W\] or the work function of the metal and the intercept on the x-axis gives the threshold frequency needed for photoelectron emission.
Now, we can analyse the options and say that options (A), (B) and (C) are the correct answers or the graph of the photoelectric effect helps in the determination of the Work function of the cathode metal, the threshold frequency and the Planck’s constant.
Note: It is a universally known fact that the slope of the graphical curve of the photoelectric effect gives the value of the Planck’s constant. So sometimes students only choose the option of the Planck’s constant and they move forward. It is, therefore, always advised to check all the possible options as sometimes multiple options are correct and the examiner doesn’t mention this fact to check the wit of the students.
Formula Used:
\[{{E}_{k}}\max =h\nu -W\]
Complete step by step solution:
The Einstein’s equation for photoelectric effect is given by \[{E_k}_max =h\nu -W\] where \[{{E}_{k}}\max \] is the maximum kinetic energy of the photoelectron, \[h\] is the Planck’s constant, \[\nu \] is the frequency of the incident light and \[W\] is the work function of the metal. Since \[{{E}_{k}}\max \] is plotted along the y-axis and \[\nu \] is plotted along the x-axis, we can write the equation of the graphical line as \[y=hx-W\].
Comparing the above equation with the standard equation for a straight line \[y=mx+c\] , we can say that the slope of the line is given by \[h\] , that is the Planck’s constant, the intercept on the y-axis is given by \[W\] or the work function of the metal and the intercept on the x-axis gives the threshold frequency needed for photoelectron emission.
Now, we can analyse the options and say that options (A), (B) and (C) are the correct answers or the graph of the photoelectric effect helps in the determination of the Work function of the cathode metal, the threshold frequency and the Planck’s constant.
Note: It is a universally known fact that the slope of the graphical curve of the photoelectric effect gives the value of the Planck’s constant. So sometimes students only choose the option of the Planck’s constant and they move forward. It is, therefore, always advised to check all the possible options as sometimes multiple options are correct and the examiner doesn’t mention this fact to check the wit of the students.
Recently Updated Pages
JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 (January 31 Evening Shift) Question Paper with Solutions [PDF]

JEE Main 2023 January 30 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 25 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 24 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

Trending doubts
JEE Main 2026: Session 2 Registration Open, City Intimation Slip, Exam Dates, Syllabus & Eligibility

JEE Main 2026 Application Login: Direct Link, Registration, Form Fill, and Steps

Understanding the Angle of Deviation in a Prism

Hybridisation in Chemistry – Concept, Types & Applications

How to Convert a Galvanometer into an Ammeter or Voltmeter

Understanding Uniform Acceleration in Physics

Other Pages
JEE Advanced Marks vs Ranks 2025: Understanding Category-wise Qualifying Marks and Previous Year Cut-offs

Dual Nature of Radiation and Matter Class 12 Physics Chapter 11 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Understanding the Electric Field of a Uniformly Charged Ring

JEE Advanced Weightage 2025 Chapter-Wise for Physics, Maths and Chemistry

Derivation of Equation of Trajectory Explained for Students

Understanding Electromagnetic Waves and Their Importance




