
The maximum covalency of nitrogen is:
(A) 3
(B) 4
(C) 5
(D) 6
Answer
233.4k+ views
Hint: To find the covalency of N first see the number of valence electrons it has and then the total number of possible bonds it can form with these electrons while keeping in mind the number of electrons it can accommodate in its valence shell.
Complete step by step answer:
-First let us see what covalency is. Covalency is defined as the total number of electron pairs that an atom can share with other atoms. It can also be defined as the total number of orbitals available in the valence shell (outermost shell), whether they are empty or completely filled. We usually count the number of covalent bonds formed.
If an atom can share only 1 electron its covalency will be 1 and if an atom can share only 2 electrons its covalency will be 2.
-The maximum covalency of any element is found by counting the number of covalent and coordinate bonds that can be formed by it.
-Now about nitrogen, its atomic number is 7 and so its electronic configuration is written as: $1{s^2}2{s^2}2{p^3}$. From the electronic configuration of N atom we can see that it has two 2s electrons and three 2p valence electrons.
N atom shares its three 2p electrons with 3 H atoms to form ammonia ($N{H_3}$) molecule and completes its octet. So it cannot form any more covalent bonds. But even after sharing these 3 electrons N atom is left with its lone pair from the 2s orbital. Now ammonia donates this lone pair of electrons to form one coordinate covalent bond with a proton and forms ammonium ion ($N{H_4}^ + $).
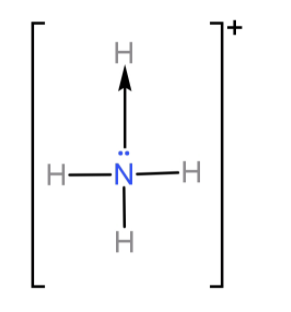
So, we have seen that N can form 4 bonds in total (3 covalent bonds and 1 co-ordinate bond). And so the covalency of N will be 4.
So, the correct option will be: (B) 4.
Note:
Even though N atom has 5 electrons in its valence shell, its covalency cannot be 5. It will be 4 only because N can accommodate a maximum of 8 electrons in its outermost shell. When its three 2p electrons bond with H the octet becomes completely filled. So, neither can any more covalent bonds be formed nor can the lone pair be broken and thus one coordinate bond can be formed. Hence, it cannot have covalency more than 4.
Complete step by step answer:
-First let us see what covalency is. Covalency is defined as the total number of electron pairs that an atom can share with other atoms. It can also be defined as the total number of orbitals available in the valence shell (outermost shell), whether they are empty or completely filled. We usually count the number of covalent bonds formed.
If an atom can share only 1 electron its covalency will be 1 and if an atom can share only 2 electrons its covalency will be 2.
-The maximum covalency of any element is found by counting the number of covalent and coordinate bonds that can be formed by it.
-Now about nitrogen, its atomic number is 7 and so its electronic configuration is written as: $1{s^2}2{s^2}2{p^3}$. From the electronic configuration of N atom we can see that it has two 2s electrons and three 2p valence electrons.
N atom shares its three 2p electrons with 3 H atoms to form ammonia ($N{H_3}$) molecule and completes its octet. So it cannot form any more covalent bonds. But even after sharing these 3 electrons N atom is left with its lone pair from the 2s orbital. Now ammonia donates this lone pair of electrons to form one coordinate covalent bond with a proton and forms ammonium ion ($N{H_4}^ + $).

So, we have seen that N can form 4 bonds in total (3 covalent bonds and 1 co-ordinate bond). And so the covalency of N will be 4.
So, the correct option will be: (B) 4.
Note:
Even though N atom has 5 electrons in its valence shell, its covalency cannot be 5. It will be 4 only because N can accommodate a maximum of 8 electrons in its outermost shell. When its three 2p electrons bond with H the octet becomes completely filled. So, neither can any more covalent bonds be formed nor can the lone pair be broken and thus one coordinate bond can be formed. Hence, it cannot have covalency more than 4.
Recently Updated Pages
JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 (January 31 Evening Shift) Question Paper with Solutions [PDF]

JEE Main 2023 January 30 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 25 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 24 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

Trending doubts
JEE Main 2026: Session 2 Registration Open, City Intimation Slip, Exam Dates, Syllabus & Eligibility

JEE Main 2026 Application Login: Direct Link, Registration, Form Fill, and Steps

Understanding the Angle of Deviation in a Prism

Hybridisation in Chemistry – Concept, Types & Applications

How to Convert a Galvanometer into an Ammeter or Voltmeter

Understanding the Electric Field of a Uniformly Charged Ring

Other Pages
JEE Advanced Marks vs Ranks 2025: Understanding Category-wise Qualifying Marks and Previous Year Cut-offs

Hydrocarbons Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 9 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Thermodynamics Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 5 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Equilibrium Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 6 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Organic Chemistry Some Basic Principles And Techniques Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 8 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

NCERT Solutions For Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 7 Redox Reactions (2025-26)




