
The lower surface of a cube is fixed. On its upper surface, force is applied at an angle of ${30^0}$ from its surface. The change will be in its:
(A) Shape
(B) Size
(C) Volume
(D) Both shape and size
Answer
233.1k+ views
Hint: Here force is applied only on the upper surface at a certain angle as given in the question above but the lower surface of the cube is fixed and it is asked what type of change is caused by this force in the cube. Force applied here will be normal stress and shear stress which will cause compression in the cube.
Complete answer:
According to the question, the force is applied on the upper surface and the lower surface is fixed. The applied force is at an angle of $30^{\circ}$.
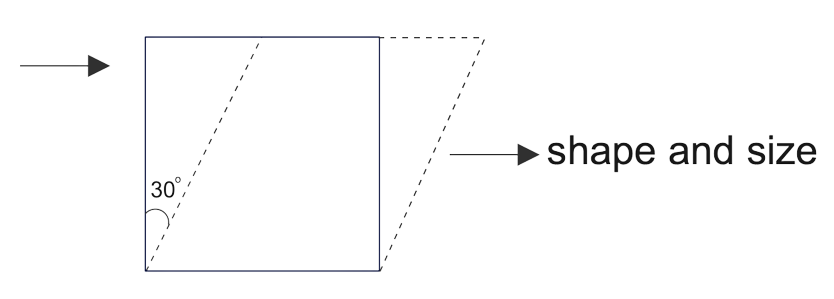
When a force is applied to the cube, it moves parallel to the surface and compresses. As a result, its size will change.
Since the force direction is asymmetric, the compression will be asymmetric. As a result, its shape will change.
Therefore, we can say that when a force is applied, shear stress and normal stress act on the cube, compressing it. As a result, both shape and size have changed.
Normal stress, as the name implies, occurs when the direction of the deforming force is perpendicular to the cross-sectional area of the body. Shearing stress or tangential stress is the stress encountered by an object when the direction of the deforming force or external force is parallel to the cross-sectional area. This causes a change in the shape of the body.
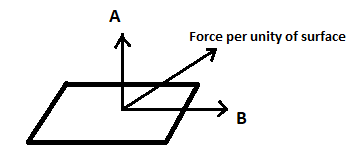
In the above diagram, A represents normal stress acting on the surface whereas B represents shearing stress acting on the surface parallel to the cross-sectional area.
The correct option is (D).
Note: Whatever stress is applied, it only deforms the shape, not the volume. When stress is applied to an object, the molecules simply deform; no reaction occurs to increase the size of the molecules, and no external atoms or molecules are added, so there is only deformation. So, it is to be noted that volume will not change in the given question.
Complete answer:
According to the question, the force is applied on the upper surface and the lower surface is fixed. The applied force is at an angle of $30^{\circ}$.

When a force is applied to the cube, it moves parallel to the surface and compresses. As a result, its size will change.
Since the force direction is asymmetric, the compression will be asymmetric. As a result, its shape will change.
Therefore, we can say that when a force is applied, shear stress and normal stress act on the cube, compressing it. As a result, both shape and size have changed.
Normal stress, as the name implies, occurs when the direction of the deforming force is perpendicular to the cross-sectional area of the body. Shearing stress or tangential stress is the stress encountered by an object when the direction of the deforming force or external force is parallel to the cross-sectional area. This causes a change in the shape of the body.

In the above diagram, A represents normal stress acting on the surface whereas B represents shearing stress acting on the surface parallel to the cross-sectional area.
The correct option is (D).
Note: Whatever stress is applied, it only deforms the shape, not the volume. When stress is applied to an object, the molecules simply deform; no reaction occurs to increase the size of the molecules, and no external atoms or molecules are added, so there is only deformation. So, it is to be noted that volume will not change in the given question.
Recently Updated Pages
Dimensions of Charge: Dimensional Formula, Derivation, SI Units & Examples

How to Calculate Moment of Inertia: Step-by-Step Guide & Formulas

Circuit Switching vs Packet Switching: Key Differences Explained

Dimensions of Pressure in Physics: Formula, Derivation & SI Unit

JEE General Topics in Chemistry Important Concepts and Tips

JEE Extractive Metallurgy Important Concepts and Tips for Exam Preparation

Trending doubts
JEE Main 2026 Application Login: Direct Link, Registration, Form Fill, and Steps

JEE Main Marking Scheme 2026- Paper-Wise Marks Distribution and Negative Marking Details

Understanding Uniform Acceleration in Physics

Understanding How a Current Loop Acts as a Magnetic Dipole

Understanding Average and RMS Value in Electrical Circuits

Understanding Collisions: Types and Examples for Students

Other Pages
JEE Advanced Weightage 2025 Chapter-Wise for Physics, Maths and Chemistry

NCERT Solutions For Class 11 Physics Chapter 10 Thermal Properties of Matter (2025-26)

Ideal and Non-Ideal Solutions Explained for Class 12 Chemistry

JEE Main Participating Colleges 2026 - A Complete List of Top Colleges

Understanding Atomic Structure for Beginners

NCERT Solutions For Class 11 Physics Chapter 12 Kinetic Theory (2025-26)




