
The Lewis structure of \[C{H_3}COOH\] as shown below is incorrect. Draw the correct Lewis structure of acetic acid.
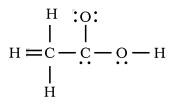
Answer
233.1k+ views
Hint: A Lewis structure of a compound or an isolated atom is the simplified method of representation of the valence shell electrons of the molecule of the compound or of the isolated atom. It is used to represent the arrangement of electrons around each individual atom of a molecule. Bonding electrons are represented as a line between the two atoms while electrons not participating in the bond formation are shown as dots.
Complete Step by Step Solution:
As given in the question, the chemical formula of the compound is \[C{H_3}COOH\] and its common name is acetic acid.
The given Lewis structure in the diagram is:-
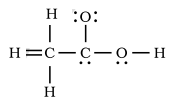
Image - The incorrect Lewis structure of Acetic acid provided in the question.
From the above diagram, a few incorrect details are marked out in the diagram below.
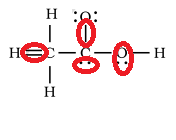
Image - The incorrect Lewis structure of Acetic acid with the mistakes marked out.
A) Here, the first mistake is the double bonding representation between Carbon and hydrogen atoms. A hydrogen atom has a single electron in its outermost shell, hence only one electron can participate in the bond formation. So, there must be a single bond instead of the double bond shown in the figure.
B) There is a single bond representation between the oxygen atom and the carbon atom. Oxygen has the atomic number of 8. Two of its electron are present in the inner shell while the rest of 6 electrons are found in the outermost shell. Here, there must be a double bond representing covalent bonding between the second carbon atom’s two electrons and two electrons of the Oxygen atom. The remaining two pairs of electrons which do not participate in the bond formation must remain the same.
C) Lone pair representation of the carbon atom is incorrect. Carbon has only four electrons in the outermost shell i.e. its E.C is 2,4. Hence after four of its electrons are involved in bond formation, there won’t be any remaining lone pair.
D) Oxygen is shown to have a single lone pair of electrons. As already mentioned above, oxygen has six electrons in its valence shell, hence after two of its electrons participate in bond formation, the remaining four electrons must be represented as two lone pairs of electrons.
After making all the necessary corrections, as mentioned above, the final Lewis dot structure of Acetic acid is:-
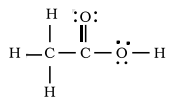
Image - The correct Lewis dot structure of Acetic acid.
Note: Lewis structures are not used to represent the geometry of molecules. It also refrains from explaining the cause of the bond formation and the nature of sharing of electrons between the atoms. It is the simplest and most limited theory on the electronic structure.
Complete Step by Step Solution:
As given in the question, the chemical formula of the compound is \[C{H_3}COOH\] and its common name is acetic acid.
The given Lewis structure in the diagram is:-
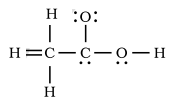
Image - The incorrect Lewis structure of Acetic acid provided in the question.
From the above diagram, a few incorrect details are marked out in the diagram below.

Image - The incorrect Lewis structure of Acetic acid with the mistakes marked out.
A) Here, the first mistake is the double bonding representation between Carbon and hydrogen atoms. A hydrogen atom has a single electron in its outermost shell, hence only one electron can participate in the bond formation. So, there must be a single bond instead of the double bond shown in the figure.
B) There is a single bond representation between the oxygen atom and the carbon atom. Oxygen has the atomic number of 8. Two of its electron are present in the inner shell while the rest of 6 electrons are found in the outermost shell. Here, there must be a double bond representing covalent bonding between the second carbon atom’s two electrons and two electrons of the Oxygen atom. The remaining two pairs of electrons which do not participate in the bond formation must remain the same.
C) Lone pair representation of the carbon atom is incorrect. Carbon has only four electrons in the outermost shell i.e. its E.C is 2,4. Hence after four of its electrons are involved in bond formation, there won’t be any remaining lone pair.
D) Oxygen is shown to have a single lone pair of electrons. As already mentioned above, oxygen has six electrons in its valence shell, hence after two of its electrons participate in bond formation, the remaining four electrons must be represented as two lone pairs of electrons.
After making all the necessary corrections, as mentioned above, the final Lewis dot structure of Acetic acid is:-
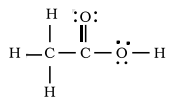
Image - The correct Lewis dot structure of Acetic acid.
Note: Lewis structures are not used to represent the geometry of molecules. It also refrains from explaining the cause of the bond formation and the nature of sharing of electrons between the atoms. It is the simplest and most limited theory on the electronic structure.
Recently Updated Pages
JEE Main 2026 Session 2 Registration Open, Exam Dates, Syllabus & Eligibility

JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 (January 31 Evening Shift) Question Paper with Solutions [PDF]

JEE Main 2023 January 30 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 25 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

Trending doubts
Understanding Average and RMS Value in Electrical Circuits

Ideal and Non-Ideal Solutions Explained for Class 12 Chemistry

Understanding Atomic Structure for Beginners

Understanding Elastic Collisions in Two Dimensions

For pure water A pH increases while pOH decreases with class 11 chemistry JEE_Main

Which of the following is most stable A Sn2+ B Ge2+ class 11 chemistry JEE_Main

Other Pages
NCERT Solutions For Class 11 Chemistry in Hindi Chapter 8 Redox Reactions (2025-26)

An ideal gas is at pressure P and temperature T in class 11 chemistry JEE_Main

In Carius method of estimation of halogens 015g of class 11 chemistry JEE_Main

Understanding Collisions: Types and Examples for Students

NCERT Solutions For Class 11 Chemistry in Hindi Chapter 1 Some Basic Concepts of Chemistry (2025-26)

Happy New Year Wishes 2026 – 100+ Messages, Quotes, Shayari, Images & Status in All Languages




