
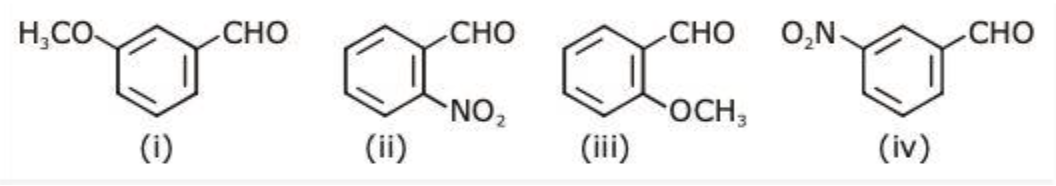
The increasing order of the following compounds towards $HCN$ addition is:
(a) \[\left( {iii} \right){\text{ }} < {\text{ }}\left( i \right){\text{ }} < {\text{ }}\left( {iv} \right){\text{ }} < {\text{ }}\left( {ii} \right)\]
(b) \[\left( {iii} \right){\text{ }} < {\text{ }}\left( {iv} \right){\text{ }} < {\text{ }}\left( i \right){\text{ }} < {\text{ }}\left( {ii} \right)\]
(c) \[\left( i \right){\text{ }} < {\text{ }}\left( {iii} \right){\text{ }} < {\text{ }}\left( {iv} \right){\text{ }} < {\text{ }}\left( {ii} \right)\]
(d) \[\left( {iii} \right){\text{ }} < {\text{ }}\left( {iv} \right){\text{ }} < {\text{ }}\left( {ii} \right){\text{ }} < {\text{ }}\left( i \right)\]
Answer
233.4k+ views
Hint: Nucleophile means nucleus loving. These are those species that attack electron deficient compounds. On the other hand, an electrophile is electron loving that attacks electron rich compounds. Electron withdrawing groups tend to withdraw the electron density towards itself, making the benzene ring electron deficient and susceptible to attack by the nucleophile.
Complete Step by Step Solution:
All the four compounds have benzaldehyde groups with different groups attached at ortho or meta positions. The effect of various groups attached determines the order of addition of$HCN$.
$C{N^{ - 1}}$Is the nucleophile so addition of nucleophile is favoured with an electron deficient compound.
$N{O_2}$ shows –M effect (withdrawing of electron density through pie bonds) only at the ortho position. But when $N{O_2}$group is attached at meta position, it no more shows resonance but withdraws electron density through sigma bond due to the fact that $N$of $N{O_2}$ is more electronegative than \[C\]of benzene ring. Hence, $N{O_2}$ at meta position shows –I effect.
Similarly \[OC{H_3}\]is an electron releasing group and donates the lone pair present on oxygen thus showing + M effect when attached at ortho position. \[OC{H_3}\] attached at meta position shows –I effect and not +I. This is because oxygen is more electronegative than carbon of benzene ring and withdrawing of electron density takes place through sigma bond. \[OC{H_3}\] at ortho position is least susceptible towards $HCN$ addition.
Mesomeric effect is stronger than inductive effect. Hence –M effect leads to stronger withdrawal of electrons than –I effect. Hence, $N{O_2}$at ortho is more electron withdrawing in nature.
Thus, order of electron withdrawing nature of groups is same as order towards $HCN$ addition
-M>-I>+M
-I effect of $N{O_2}$ is stronger than \[OC{H_3}\]
Hence the overall order is (a) (iii) < (i) < (iv) < (ii).
Note: Nucleophile is itself an electron rich species and usually carries a lone pair or negative charge. Positively charged species are generally called the electrophile. Inductive effect operates through sigma bonds and is dependent on electronegativity. Thus, inductive effect is observed at both meta and ortho position but mesomeric effect is only observed at ortho (and para).
Complete Step by Step Solution:
All the four compounds have benzaldehyde groups with different groups attached at ortho or meta positions. The effect of various groups attached determines the order of addition of$HCN$.
$C{N^{ - 1}}$Is the nucleophile so addition of nucleophile is favoured with an electron deficient compound.
$N{O_2}$ shows –M effect (withdrawing of electron density through pie bonds) only at the ortho position. But when $N{O_2}$group is attached at meta position, it no more shows resonance but withdraws electron density through sigma bond due to the fact that $N$of $N{O_2}$ is more electronegative than \[C\]of benzene ring. Hence, $N{O_2}$ at meta position shows –I effect.
Similarly \[OC{H_3}\]is an electron releasing group and donates the lone pair present on oxygen thus showing + M effect when attached at ortho position. \[OC{H_3}\] attached at meta position shows –I effect and not +I. This is because oxygen is more electronegative than carbon of benzene ring and withdrawing of electron density takes place through sigma bond. \[OC{H_3}\] at ortho position is least susceptible towards $HCN$ addition.
Mesomeric effect is stronger than inductive effect. Hence –M effect leads to stronger withdrawal of electrons than –I effect. Hence, $N{O_2}$at ortho is more electron withdrawing in nature.
Thus, order of electron withdrawing nature of groups is same as order towards $HCN$ addition
-M>-I>+M
-I effect of $N{O_2}$ is stronger than \[OC{H_3}\]
Hence the overall order is (a) (iii) < (i) < (iv) < (ii).
Note: Nucleophile is itself an electron rich species and usually carries a lone pair or negative charge. Positively charged species are generally called the electrophile. Inductive effect operates through sigma bonds and is dependent on electronegativity. Thus, inductive effect is observed at both meta and ortho position but mesomeric effect is only observed at ortho (and para).
Recently Updated Pages
JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 (January 31 Evening Shift) Question Paper with Solutions [PDF]

JEE Main 2023 January 30 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 25 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 24 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

Trending doubts
JEE Main 2026: Session 2 Registration Open, City Intimation Slip, Exam Dates, Syllabus & Eligibility

JEE Main 2026 Application Login: Direct Link, Registration, Form Fill, and Steps

JEE Main Marking Scheme 2026- Paper-Wise Marks Distribution and Negative Marking Details

Understanding the Angle of Deviation in a Prism

Hybridisation in Chemistry – Concept, Types & Applications

How to Convert a Galvanometer into an Ammeter or Voltmeter

Other Pages
JEE Advanced Marks vs Ranks 2025: Understanding Category-wise Qualifying Marks and Previous Year Cut-offs

Hydrocarbons Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 9 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Thermodynamics Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 5 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Equilibrium Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 6 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Organic Chemistry Some Basic Principles And Techniques Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 8 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

NCERT Solutions For Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 7 Redox Reactions (2025-26)




