
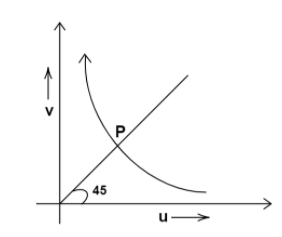
The graph shows the variation of $v$ with change in $u$ for a mirror. Points plotted above the point $P$ on the curve are for values of $v$ :
(A) Smaller than $f$
(B) Smaller that $2f$
(C) Larger than $f$
(D) Larger than $2f$
Answer
233.1k+ views
Hint: - Use the mirror formula that gives a relation $u$ , $v$ and $f$ and find an expression for $v$ in the terms of $u$ and $f$ . Then find the relation between $v$ and $u$ at the point $P$ . Take a value of $v$ greater than $u$ and find the relation between $v$ and $f$ .
Formula used:
$\dfrac{1}{f} = \dfrac{1}{v} + \dfrac{1}{u}$
Complete step-by-step solution:
Here, $u$ is the position of the object and $v$ is the position of the image with respect to the mirror. $f$ is the focal length of the mirror.
The relation between $u$ , $v$ and $f$ is given by $\dfrac{1}{f} = \dfrac{1}{v} + \dfrac{1}{u}$.
$ \Rightarrow \dfrac{1}{v} = \dfrac{1}{f} - \dfrac{1}{u}$
On further solving we get,
$\dfrac{1}{v} = \dfrac{{u - f}}{{uf}}$
$ \Rightarrow v = \dfrac{{uf}}{{u - f}}$ ....... $\left( 1 \right)$
From the graph of $v$ versus $u$ we can understand that as the object comes towards the mirror ( as we reduce the object distance), the image distance increases. This means that $v$ is inversely proportional to $u$ .
Let us analyze the relation between $u$ and $v$ at the point $P$ . In the graph, we can see that the point $P$ also lies on a line passing through the origin and making an angle of ${45^ \circ }$ with the positive x-axis.
From geometry, we know that the $x$ and $y$ coordinates of the points on a line passing through the origin and making an angle of ${45^ \circ }$ with the positive x-axis are equal.
This means that at this point $P$ , $v = u$
Now, since the $v$ is inversely proportional to $u$ and at the point $P$ , $v = u$ , the value of $v$ will be greater than the value of $u$ for the points above point $P$ .
Therefore, let $v = nu$ , where $n$ is a real number greater than one.
$u = \dfrac{v}{n}$ .
Substitute this value of $u$ in the equation $\left( 1 \right)$ .
$v = \dfrac{{\dfrac{v}{n}f}}{{\dfrac{v}{n} - f}}$
$ \Rightarrow \dfrac{v}{n} - f = \dfrac{f}{n}$
Now further solving the equation we get,
$v - nf = f$
$ \Rightarrow v = f + nf$
$ \Rightarrow v = \left( {n + 1} \right)f$
But $n \succ 1$
This means that $\left( {n + 1} \right) \succ 2$
$ \Rightarrow \left( {n + 1} \right)f \succ 2f$
This finally means that $v \succ 2f$
Therefore, the value of $v$ is larger than $2f$ for the points above the point $P$ .
So, the correct answer is option (D).
Note: As a convex mirror produces a diminished image of a far object, a driver can easily see large traffic behind him in a small mirror. In a concave mirror which is used as a shaving mirror when we hold the face closer to the mirror, an enlarged image is produced. It is easy to understand which type of mirror is used once you understood their principle of working.
Formula used:
$\dfrac{1}{f} = \dfrac{1}{v} + \dfrac{1}{u}$
Complete step-by-step solution:
Here, $u$ is the position of the object and $v$ is the position of the image with respect to the mirror. $f$ is the focal length of the mirror.
The relation between $u$ , $v$ and $f$ is given by $\dfrac{1}{f} = \dfrac{1}{v} + \dfrac{1}{u}$.
$ \Rightarrow \dfrac{1}{v} = \dfrac{1}{f} - \dfrac{1}{u}$
On further solving we get,
$\dfrac{1}{v} = \dfrac{{u - f}}{{uf}}$
$ \Rightarrow v = \dfrac{{uf}}{{u - f}}$ ....... $\left( 1 \right)$
From the graph of $v$ versus $u$ we can understand that as the object comes towards the mirror ( as we reduce the object distance), the image distance increases. This means that $v$ is inversely proportional to $u$ .
Let us analyze the relation between $u$ and $v$ at the point $P$ . In the graph, we can see that the point $P$ also lies on a line passing through the origin and making an angle of ${45^ \circ }$ with the positive x-axis.
From geometry, we know that the $x$ and $y$ coordinates of the points on a line passing through the origin and making an angle of ${45^ \circ }$ with the positive x-axis are equal.
This means that at this point $P$ , $v = u$
Now, since the $v$ is inversely proportional to $u$ and at the point $P$ , $v = u$ , the value of $v$ will be greater than the value of $u$ for the points above point $P$ .
Therefore, let $v = nu$ , where $n$ is a real number greater than one.
$u = \dfrac{v}{n}$ .
Substitute this value of $u$ in the equation $\left( 1 \right)$ .
$v = \dfrac{{\dfrac{v}{n}f}}{{\dfrac{v}{n} - f}}$
$ \Rightarrow \dfrac{v}{n} - f = \dfrac{f}{n}$
Now further solving the equation we get,
$v - nf = f$
$ \Rightarrow v = f + nf$
$ \Rightarrow v = \left( {n + 1} \right)f$
But $n \succ 1$
This means that $\left( {n + 1} \right) \succ 2$
$ \Rightarrow \left( {n + 1} \right)f \succ 2f$
This finally means that $v \succ 2f$
Therefore, the value of $v$ is larger than $2f$ for the points above the point $P$ .
So, the correct answer is option (D).
Note: As a convex mirror produces a diminished image of a far object, a driver can easily see large traffic behind him in a small mirror. In a concave mirror which is used as a shaving mirror when we hold the face closer to the mirror, an enlarged image is produced. It is easy to understand which type of mirror is used once you understood their principle of working.
Recently Updated Pages
JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 (January 31 Evening Shift) Question Paper with Solutions [PDF]

JEE Main 2023 January 30 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 25 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 24 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

Trending doubts
JEE Main 2026: Session 2 Registration Open, City Intimation Slip, Exam Dates, Syllabus & Eligibility

JEE Main 2026 Application Login: Direct Link, Registration, Form Fill, and Steps

Understanding the Angle of Deviation in a Prism

Hybridisation in Chemistry – Concept, Types & Applications

How to Convert a Galvanometer into an Ammeter or Voltmeter

Understanding Uniform Acceleration in Physics

Other Pages
JEE Advanced Marks vs Ranks 2025: Understanding Category-wise Qualifying Marks and Previous Year Cut-offs

Dual Nature of Radiation and Matter Class 12 Physics Chapter 11 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Understanding the Electric Field of a Uniformly Charged Ring

JEE Advanced Weightage 2025 Chapter-Wise for Physics, Maths and Chemistry

Derivation of Equation of Trajectory Explained for Students

Understanding Electromagnetic Waves and Their Importance




