
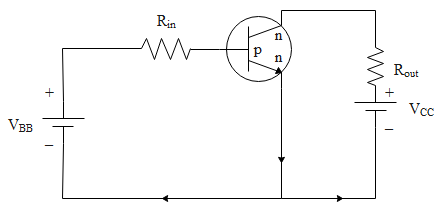
The given transistor operates in saturation region then what should be the value of ${{V}_{BB}}$: (${{\text{V}}_{\text{CE}}}\text{= 0}$, ${{R}_{out}}=200\Omega$, ${{R}_{in}}=100K\Omega$, ${{\text{V}}_{\text{CC}}}\text{= 3 volt }$, ${{\text{V}}_{\text{BE}}}\text{= 0}\text{.7 volt }$, ${{\text{V}}_{\text{CE}}}\text{= 0}$, $\beta =200$).
(A) 4.1 volt
(B) 7.5 volt
(C) 8.2 volt
(D) 6.8 volt
Answer
232.8k+ views
Hint We know that the Saturation region is one in which both Emitter Base and Base Collector junctions of the transistor are forward biased. In this region high currents flow through the transistor, as both junctions of the transistor are forward biased and bulk resistance offered is very much less. The region between cut off and saturation is known as active region. In the active region, collector-base junction remains reverse biased while base-emitter junction remains forward biased. Consequently, the transistor will function normally in this region. Based on this concept we have to answer this question.
Complete step by step answer
A transistor is a semiconductor device used to amplify or switch electronic signals and electrical power. It is composed of semiconductor material usually with at least three terminals for connection to an external circuit.
We can further say that the name transistor is derived from “transfer resistor” it means that the resistance is changed. It is a solid-state device which is made up of silicon and germanium. Hence the function of a transistor is to change the resistance for various applications using its specifications.
We know that,
It is known that the expression as:
$\mathrm{V}_{\mathrm{CE}}=\mathrm{V}_{\mathrm{CC}}-\mathrm{I}_{\mathrm{C}} \mathrm{R}_{\mathrm{O}}$
We can say that a diode is called a diode because it has two distinct electrodes (i.e. terminals), called the anode and the cathode. A diode is electrically asymmetric because current can flow freely from the anode to the cathode, but not in the other direction.
Put the values in the above expression to get that:
$0=3-\mathrm{I}_{\mathrm{C}} \times 200$
So, the value is obtained:
$\mathrm{I}_{\mathrm{C}}=\dfrac{3}{200}=15 \mathrm{mA}$
It can be said that the transistor consists of two PN diodes connected back to back. It has three terminals namely emitter, base and collector. The basic idea behind a transistor is that it lets you control the flow of current through one channel by varying the intensity of a much smaller current that's flowing through a second channel.
We know the value is given as:
$\beta=200$
We can say that a transistor is a semiconductor device used to amplify or switch electronic signals and electrical power. It is composed of semiconductor material usually with at least three terminals for connection to an external circuit.
The formula is given as:
$\beta=\dfrac{\mathrm{I}_{\mathrm{C}}}{\mathrm{I}_{\mathrm{B}}}$
So, the value is given as:
$\mathrm{I}_{\mathrm{B}}=\dfrac{\mathrm{I}_{\mathrm{C}}}{\mathrm{I}_{\beta}}=\dfrac{15 \mathrm{mA}}{200}=75 \mu \mathrm{A}$
The expression to find the voltage is given as:
$\mathrm{V}_{\mathrm{BE}}=\mathrm{V}_{\mathrm{BB}}-\mathrm{I}_{\mathrm{B}} \mathrm{R}_{\mathrm{in}}$
The value is given as:
$\mathrm{V}_{\mathrm{BB}}=0.7+75 \times 10-6 \times 100 \times 10^{3}$
The value is obtained as:
$\mathrm{V}_{\mathrm{BB}}=0.7+7.5=8.2 \mathrm{volt}$
So, the value of $\mathrm{V}_{\mathrm{BB}}$ is 8.2 volt.
Hence, C is the correct option.
Note: We know that saturation is the on mode of a transistor. A transistor in saturation mode acts like a short circuit between collector and emitter. In saturation mode both of the "diodes" in the transistor are forward biased. Saturation means holding as much moisture as possible. When you water your houseplants, you may soak them until the soil around each plant reaches saturation. The noun saturation means the act of completely soaking something until it's absorbed as much water as it can. The voltage between the collector and emitter terminals under conditions of base current or base-emitter voltage beyond which the collector current remains essentially constant as the base current or voltage is increased.
Complete step by step answer
A transistor is a semiconductor device used to amplify or switch electronic signals and electrical power. It is composed of semiconductor material usually with at least three terminals for connection to an external circuit.
We can further say that the name transistor is derived from “transfer resistor” it means that the resistance is changed. It is a solid-state device which is made up of silicon and germanium. Hence the function of a transistor is to change the resistance for various applications using its specifications.
We know that,
It is known that the expression as:
$\mathrm{V}_{\mathrm{CE}}=\mathrm{V}_{\mathrm{CC}}-\mathrm{I}_{\mathrm{C}} \mathrm{R}_{\mathrm{O}}$
We can say that a diode is called a diode because it has two distinct electrodes (i.e. terminals), called the anode and the cathode. A diode is electrically asymmetric because current can flow freely from the anode to the cathode, but not in the other direction.
Put the values in the above expression to get that:
$0=3-\mathrm{I}_{\mathrm{C}} \times 200$
So, the value is obtained:
$\mathrm{I}_{\mathrm{C}}=\dfrac{3}{200}=15 \mathrm{mA}$
It can be said that the transistor consists of two PN diodes connected back to back. It has three terminals namely emitter, base and collector. The basic idea behind a transistor is that it lets you control the flow of current through one channel by varying the intensity of a much smaller current that's flowing through a second channel.
We know the value is given as:
$\beta=200$
We can say that a transistor is a semiconductor device used to amplify or switch electronic signals and electrical power. It is composed of semiconductor material usually with at least three terminals for connection to an external circuit.
The formula is given as:
$\beta=\dfrac{\mathrm{I}_{\mathrm{C}}}{\mathrm{I}_{\mathrm{B}}}$
So, the value is given as:
$\mathrm{I}_{\mathrm{B}}=\dfrac{\mathrm{I}_{\mathrm{C}}}{\mathrm{I}_{\beta}}=\dfrac{15 \mathrm{mA}}{200}=75 \mu \mathrm{A}$
The expression to find the voltage is given as:
$\mathrm{V}_{\mathrm{BE}}=\mathrm{V}_{\mathrm{BB}}-\mathrm{I}_{\mathrm{B}} \mathrm{R}_{\mathrm{in}}$
The value is given as:
$\mathrm{V}_{\mathrm{BB}}=0.7+75 \times 10-6 \times 100 \times 10^{3}$
The value is obtained as:
$\mathrm{V}_{\mathrm{BB}}=0.7+7.5=8.2 \mathrm{volt}$
So, the value of $\mathrm{V}_{\mathrm{BB}}$ is 8.2 volt.
Hence, C is the correct option.
Note: We know that saturation is the on mode of a transistor. A transistor in saturation mode acts like a short circuit between collector and emitter. In saturation mode both of the "diodes" in the transistor are forward biased. Saturation means holding as much moisture as possible. When you water your houseplants, you may soak them until the soil around each plant reaches saturation. The noun saturation means the act of completely soaking something until it's absorbed as much water as it can. The voltage between the collector and emitter terminals under conditions of base current or base-emitter voltage beyond which the collector current remains essentially constant as the base current or voltage is increased.
Recently Updated Pages
JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 (January 31 Evening Shift) Question Paper with Solutions [PDF]

JEE Main 2023 January 30 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 25 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 24 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

Trending doubts
JEE Main 2026: Session 2 Registration Open, City Intimation Slip, Exam Dates, Syllabus & Eligibility

JEE Main 2026 Application Login: Direct Link, Registration, Form Fill, and Steps

Understanding the Angle of Deviation in a Prism

Hybridisation in Chemistry – Concept, Types & Applications

How to Convert a Galvanometer into an Ammeter or Voltmeter

Understanding Uniform Acceleration in Physics

Other Pages
JEE Advanced Marks vs Ranks 2025: Understanding Category-wise Qualifying Marks and Previous Year Cut-offs

Dual Nature of Radiation and Matter Class 12 Physics Chapter 11 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Understanding the Electric Field of a Uniformly Charged Ring

JEE Advanced Weightage 2025 Chapter-Wise for Physics, Maths and Chemistry

Derivation of Equation of Trajectory Explained for Students

Understanding Electromagnetic Waves and Their Importance




