
The given lens is broken into four parts rearranged as shown. If the initial focal length is f, then after rearrangement the equivalent focal length is
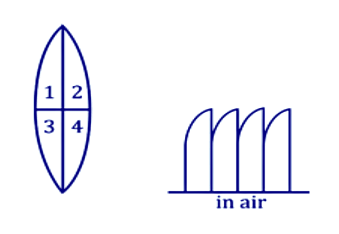
A. f
B. $\dfrac{f}{2} \\ $
C. $\dfrac{f}{4} \\ $
D. 4f
Answer
232.8k+ views
Hint: In this question we will use the concept of effects on focal length when a lens is cut longitudinally (along the principal axis) as well as when its cut transversely (perpendicular to the principal axis). When a lens is cut transversely the focal length remains the same but when it is cut vertically, the focal length gets doubled.
Complete step by step solution:
Let us assume the focal length is cut transversely first. There will be no change in focal length and the focal length of part 1+2 and part 3+4 will be equal to f.
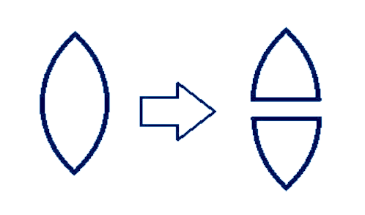
Now, the cut is made longitudinally onto the two parts of the lens and we get 4 parts. Now the focal length of each part is equal to 2f after the vertical cut.
Now 4 lenses of 2f focal length are kept in line. Therefore, the equivalent focal length
$\dfrac{1}{{{f}_{eq}}}=\dfrac{1}{2f}+\dfrac{1}{2f}+\dfrac{1}{2f}+\dfrac{1}{2f}$
$\Rightarrow \dfrac{1}{{{f}_{eq}}}=\dfrac{4}{2f}$
$\Rightarrow \dfrac{1}{{{f}_{eq}}}=\dfrac{2}{f}$
$\therefore {{f}_{eq}}=\dfrac{f}{2}$
Hence, the correct answer is B.
Additional Information: The extent of convergence a lens creates determines its focal length. Convex lenses have two refractive surfaces: one through which light enters and one through which light exits. However, after being divided in half, it turns into a plano-concave lens, and as a result, the radius of curvature of the planar portion is infinite. As a result, convergence doesn't occur at the planar region, increasing effective focal length.
Note: A convex lens could be thought of as two plano-convex lenses with a combined focal length of f. We get the effective focal length f/2 when,
$\dfrac{1}{f}=\dfrac{1}{{{f}_{1}}}+\dfrac{1}{{{f}_{2}}}$
In the other case, if the convex lens's focal length is f, the plano-convex lens' focal length should be 2f.
Complete step by step solution:
Let us assume the focal length is cut transversely first. There will be no change in focal length and the focal length of part 1+2 and part 3+4 will be equal to f.

Now, the cut is made longitudinally onto the two parts of the lens and we get 4 parts. Now the focal length of each part is equal to 2f after the vertical cut.
Now 4 lenses of 2f focal length are kept in line. Therefore, the equivalent focal length
$\dfrac{1}{{{f}_{eq}}}=\dfrac{1}{2f}+\dfrac{1}{2f}+\dfrac{1}{2f}+\dfrac{1}{2f}$
$\Rightarrow \dfrac{1}{{{f}_{eq}}}=\dfrac{4}{2f}$
$\Rightarrow \dfrac{1}{{{f}_{eq}}}=\dfrac{2}{f}$
$\therefore {{f}_{eq}}=\dfrac{f}{2}$
Hence, the correct answer is B.
Additional Information: The extent of convergence a lens creates determines its focal length. Convex lenses have two refractive surfaces: one through which light enters and one through which light exits. However, after being divided in half, it turns into a plano-concave lens, and as a result, the radius of curvature of the planar portion is infinite. As a result, convergence doesn't occur at the planar region, increasing effective focal length.
Note: A convex lens could be thought of as two plano-convex lenses with a combined focal length of f. We get the effective focal length f/2 when,
$\dfrac{1}{f}=\dfrac{1}{{{f}_{1}}}+\dfrac{1}{{{f}_{2}}}$
In the other case, if the convex lens's focal length is f, the plano-convex lens' focal length should be 2f.
Recently Updated Pages
JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 (January 31 Evening Shift) Question Paper with Solutions [PDF]

JEE Main 2023 January 30 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 25 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 24 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

Trending doubts
JEE Main 2026: Session 2 Registration Open, City Intimation Slip, Exam Dates, Syllabus & Eligibility

JEE Main 2026 Application Login: Direct Link, Registration, Form Fill, and Steps

JEE Main Marking Scheme 2026- Paper-Wise Marks Distribution and Negative Marking Details

Understanding the Angle of Deviation in a Prism

Hybridisation in Chemistry – Concept, Types & Applications

How to Convert a Galvanometer into an Ammeter or Voltmeter

Other Pages
JEE Advanced Marks vs Ranks 2025: Understanding Category-wise Qualifying Marks and Previous Year Cut-offs

Dual Nature of Radiation and Matter Class 12 Physics Chapter 11 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Understanding Uniform Acceleration in Physics

Understanding the Electric Field of a Uniformly Charged Ring

JEE Advanced Weightage 2025 Chapter-Wise for Physics, Maths and Chemistry

Derivation of Equation of Trajectory Explained for Students




