
The general formula ${{(RCO)}_{2}}O$ represents
A.An ester [CPMT $1974$; DPMT $1982$; MP PMT 1996]
B.A ketone
C.An aldehyde
D.An acid anhydride
Answer
233.1k+ views
Hint: In organic compounds the most reactive part is its functional group. There are lots of functional groups in organic chemistry. Here in this question, the given compound contains two $-CO$groups and they are connected through an oxygen atom. Therefore to recognize the function group of this compound we must have to draw the compound.
Complete answer:Generally, a functional group represents the general grouping of atoms within the molecules and that has a unique set of chemical properties. The most common examples of the functional groups are alkenes, alkynes, alcohols, ethers, amines, aldehydes, ketones, carboxylic acids, esters, anhydrides, etc
We can draw the structure of the compound ${{(RCO)}_{2}}O$ in the following way:
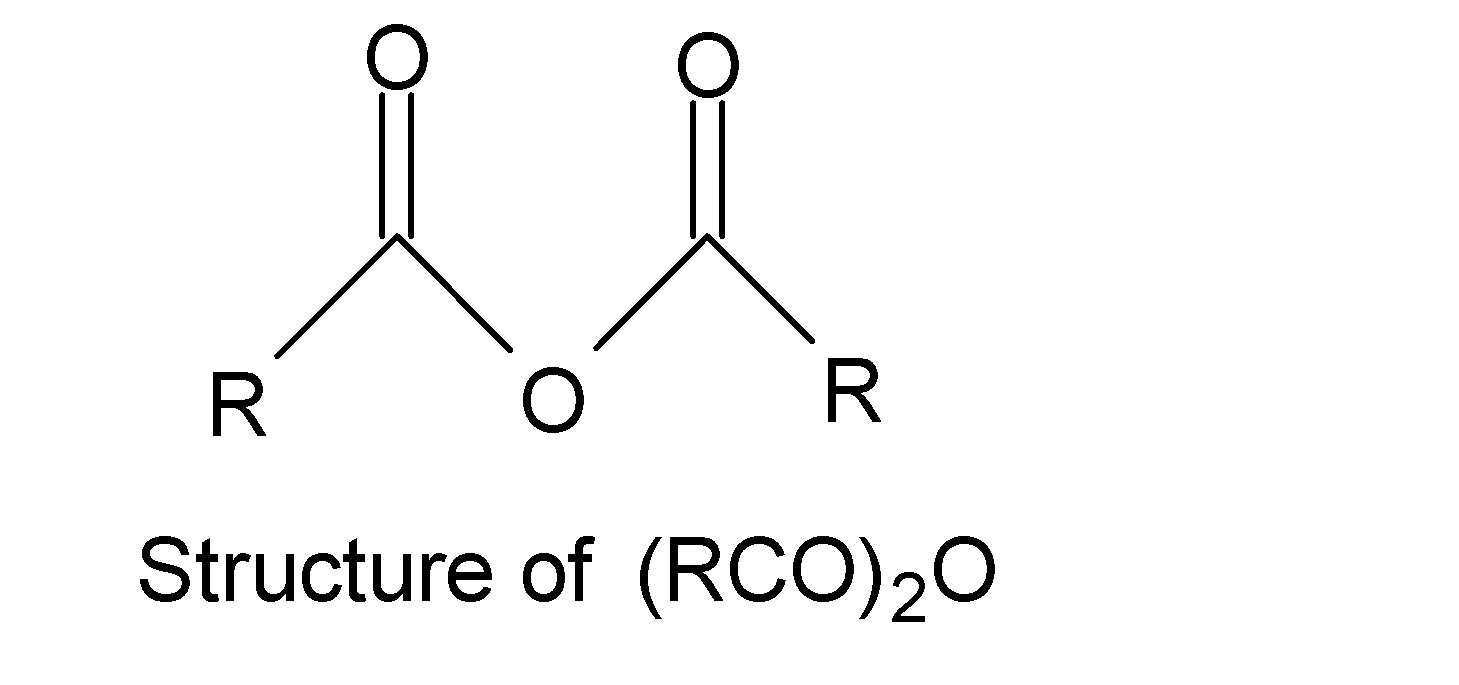
Let us check all the options to find a similar to the functional group present ${{(RCO)}_{2}}O$.
Esters are the carboxylic acid derivative compound and can be derived from an acid in which at least one hydroxyl group, $-OH$group is replaced by an alkyl alkoxy group, $-0R$. A common structure of ester is shown below which $-R$denotes the alkyl or aryl group.
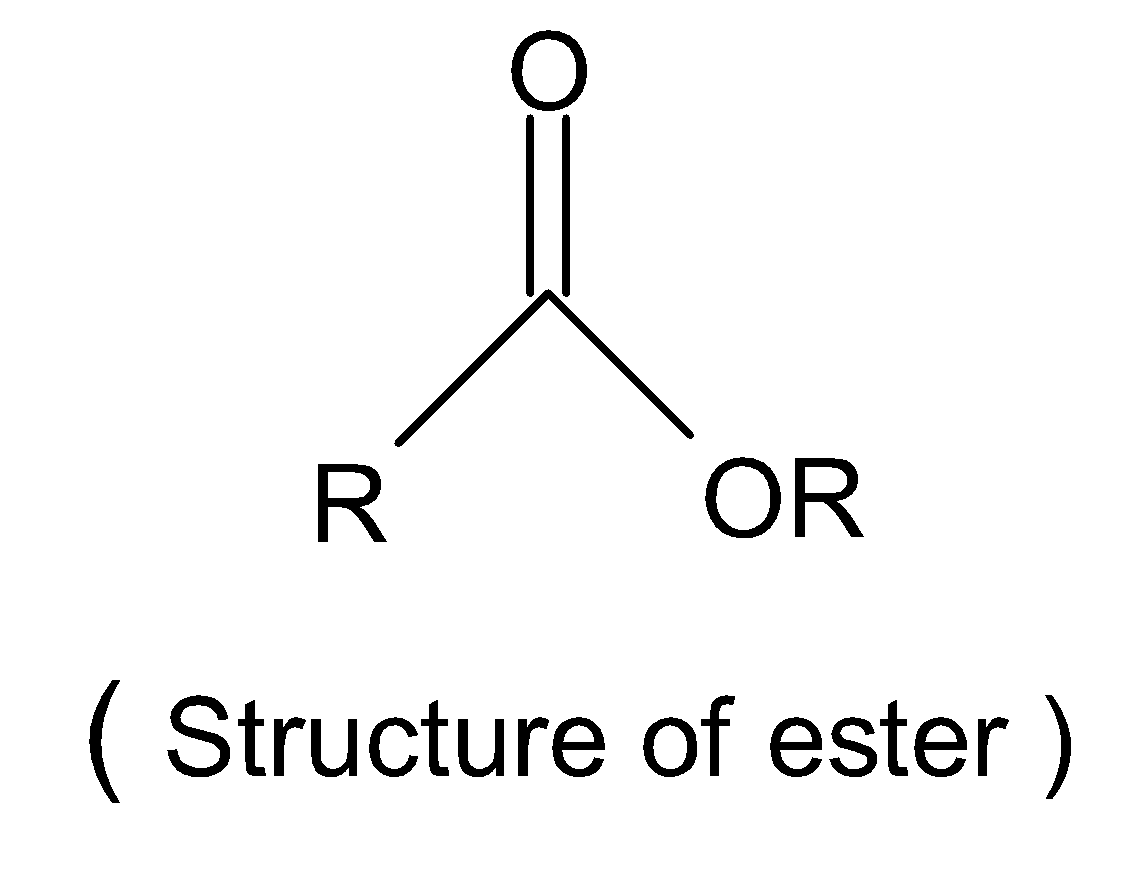
So, the given compound is not an ester.
Aldehyde and ketones are carbonyl compounds containing carbonyl functional groups, $C=O$ . In aldehyde, at least one hydrogen atom is connected to the $C=O$group but in ketone carbonyl groups are attached to two alkyl or aryl groups. Acetaldehyde and acetone are examples of aldehyde and ketone.
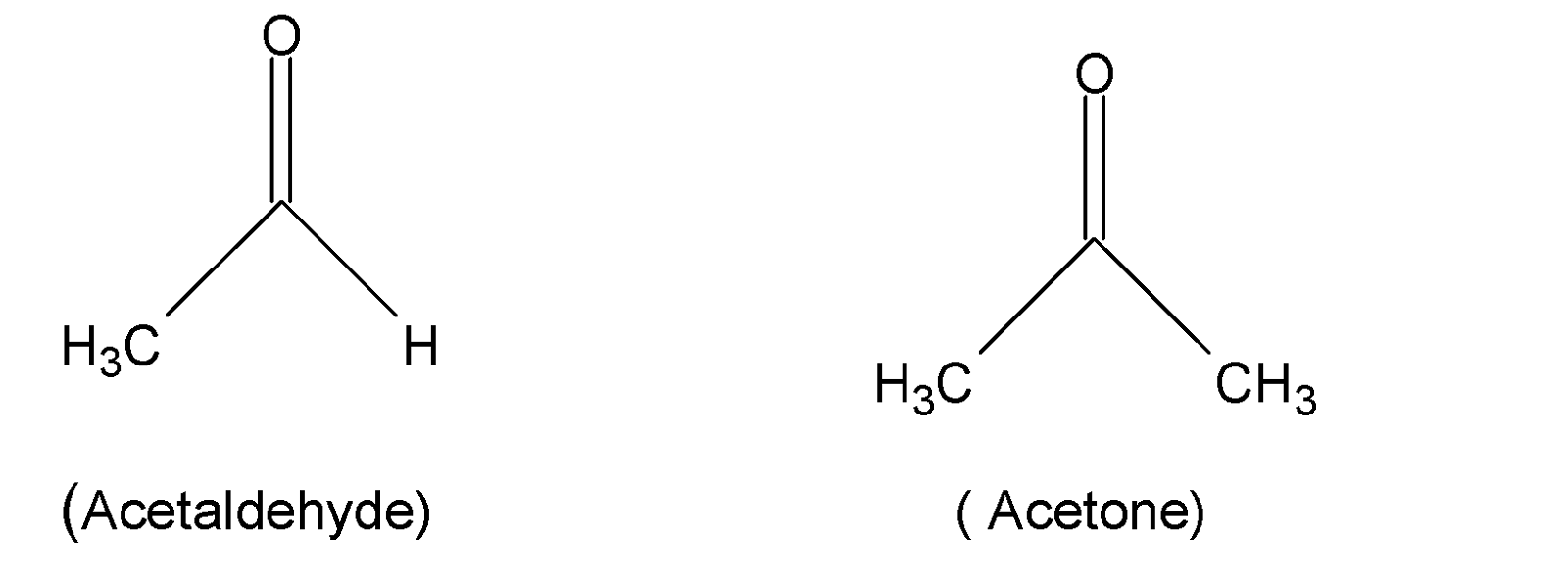
Thus, the compound ${{(RCO)}_{2}}O$ is not an aldehyde or ketone.
Finally, acid anhydride falls under the carboxylic derivative category. When two carboxylic acid groups react, acid anhydride forms by the loss of one water molecule. For example, if we combine two common carboxylic acids of chemical formula $RCOOH$where $R-$denotes an alkyl or aryl group we get an acid anhydride having the formula,${{(RCO)}_{2}}O$.
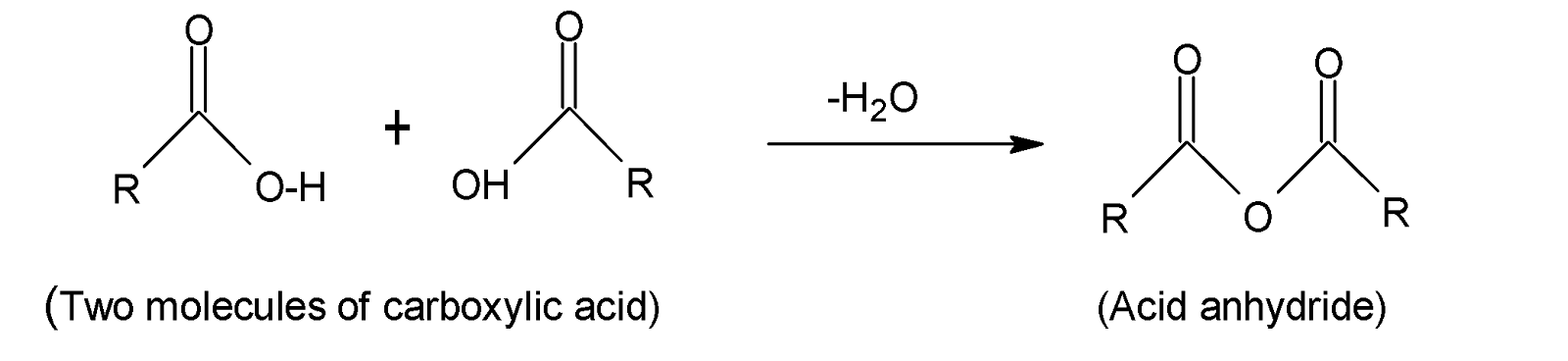
Therefore the formula ${{(RCO)}_{2}}O$ represents an acid anhydride.
Thus, option (D) is correct.
Note: To deal with any problem in chemistry, especially in organic chemistry we need to learn how to recognize certain patterns in molecular structures and reactions. One of the most important of those basic patterns is the recognition of functional groups. By learning this we will reach one step closer to identifying possible reactions.
Complete answer:Generally, a functional group represents the general grouping of atoms within the molecules and that has a unique set of chemical properties. The most common examples of the functional groups are alkenes, alkynes, alcohols, ethers, amines, aldehydes, ketones, carboxylic acids, esters, anhydrides, etc
We can draw the structure of the compound ${{(RCO)}_{2}}O$ in the following way:

Let us check all the options to find a similar to the functional group present ${{(RCO)}_{2}}O$.
Esters are the carboxylic acid derivative compound and can be derived from an acid in which at least one hydroxyl group, $-OH$group is replaced by an alkyl alkoxy group, $-0R$. A common structure of ester is shown below which $-R$denotes the alkyl or aryl group.

So, the given compound is not an ester.
Aldehyde and ketones are carbonyl compounds containing carbonyl functional groups, $C=O$ . In aldehyde, at least one hydrogen atom is connected to the $C=O$group but in ketone carbonyl groups are attached to two alkyl or aryl groups. Acetaldehyde and acetone are examples of aldehyde and ketone.

Thus, the compound ${{(RCO)}_{2}}O$ is not an aldehyde or ketone.
Finally, acid anhydride falls under the carboxylic derivative category. When two carboxylic acid groups react, acid anhydride forms by the loss of one water molecule. For example, if we combine two common carboxylic acids of chemical formula $RCOOH$where $R-$denotes an alkyl or aryl group we get an acid anhydride having the formula,${{(RCO)}_{2}}O$.

Therefore the formula ${{(RCO)}_{2}}O$ represents an acid anhydride.
Thus, option (D) is correct.
Note: To deal with any problem in chemistry, especially in organic chemistry we need to learn how to recognize certain patterns in molecular structures and reactions. One of the most important of those basic patterns is the recognition of functional groups. By learning this we will reach one step closer to identifying possible reactions.
Recently Updated Pages
JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 (January 31 Evening Shift) Question Paper with Solutions [PDF]

JEE Main 2023 January 30 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 25 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 24 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

Trending doubts
JEE Main 2026: Session 2 Registration Open, City Intimation Slip, Exam Dates, Syllabus & Eligibility

JEE Main 2026 Application Login: Direct Link, Registration, Form Fill, and Steps

Understanding the Angle of Deviation in a Prism

Hybridisation in Chemistry – Concept, Types & Applications

How to Convert a Galvanometer into an Ammeter or Voltmeter

Understanding the Electric Field of a Uniformly Charged Ring

Other Pages
JEE Advanced Marks vs Ranks 2025: Understanding Category-wise Qualifying Marks and Previous Year Cut-offs

NCERT Solutions For Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 1 Solutions (2025-26)

Solutions Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 1 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

NCERT Solutions For Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 4 The d and f Block Elements (2025-26)

Biomolecules Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 10 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

NCERT Solutions For Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 10 Biomolecules (2025-26)




