
The function(s) of salt bridge in a cell is/are
A. It maintains standard electrode potential of cell constant which depends on several factors.
B. It completes the electrical circuit.
C. It departs both the solutions from each other.
D. It maintains the electrical neutrality of both electrolytic solutions.
Answer
240.3k+ views
Hint: A salt bridge is a chemical junction that connects the anodic and cathodic compartments in a cell or electrolytic solution thereby completing the circuit. It prevents the cell from taking its reaction to equilibrium and balances the charges in both the solutions.
Complete step-by-step answer:
A salt bridge is a device that is used in a galvanic cell for connecting its oxidation and reduction half cells where a weak electrolyte is used. It usually consists of a strong electrolyte which is further made up of ions such as KCl. These are generally used in a galvanic cell such as a voltaic cell or Daniel cell.
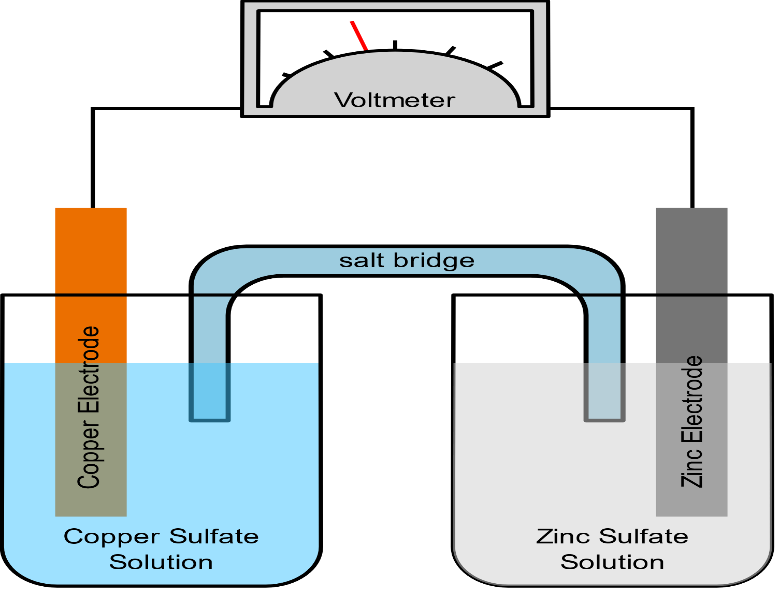
The main function of a salt bridge is to maintain the electrical neutrality of both electrolytic solutions within the internal circuit. It basically helps in preventing the accumulation of positive and negative charges around the respective electrolytic electrodes and further allowing a smooth reaction to occur. It also provides continual flow of electrons. However, the purpose of a salt bridge is not just to move electrons from the electrolyte rather to maintain charge balance because the electrons move from one-half cell to the other.
Salt bridge avoids the diffusion or mechanical flow of solution from one-half cell to another. It minimizes the liquid-liquid junction potential which arises between two solutions when they are in contact with each other. In short, it acts as an electrical contact between two half cells.
Hence, the correct options are (A), (B), (C) and (D).
Note: If there is no salt bridge in the cell, then the anodic and cathodic half cells will be joined only from one side and the electrical circuit will remain incomplete. There occurs a further accumulation of negative charge in one solution and positive in another.
Complete step-by-step answer:
A salt bridge is a device that is used in a galvanic cell for connecting its oxidation and reduction half cells where a weak electrolyte is used. It usually consists of a strong electrolyte which is further made up of ions such as KCl. These are generally used in a galvanic cell such as a voltaic cell or Daniel cell.

The main function of a salt bridge is to maintain the electrical neutrality of both electrolytic solutions within the internal circuit. It basically helps in preventing the accumulation of positive and negative charges around the respective electrolytic electrodes and further allowing a smooth reaction to occur. It also provides continual flow of electrons. However, the purpose of a salt bridge is not just to move electrons from the electrolyte rather to maintain charge balance because the electrons move from one-half cell to the other.
Salt bridge avoids the diffusion or mechanical flow of solution from one-half cell to another. It minimizes the liquid-liquid junction potential which arises between two solutions when they are in contact with each other. In short, it acts as an electrical contact between two half cells.
Hence, the correct options are (A), (B), (C) and (D).
Note: If there is no salt bridge in the cell, then the anodic and cathodic half cells will be joined only from one side and the electrical circuit will remain incomplete. There occurs a further accumulation of negative charge in one solution and positive in another.
Recently Updated Pages
Know The Difference Between Fluid And Liquid

Difference Between Crystalline and Amorphous Solid: Table & Examples

Types of Solutions in Chemistry: Explained Simply

Hess Law of Constant Heat Summation: Definition, Formula & Applications

Disproportionation Reaction: Definition, Example & JEE Guide

JEE Extractive Metallurgy Important Concepts and Tips for Exam Preparation

Trending doubts
JEE Main 2026: Session 1 Results Out and Session 2 Registration Open, City Intimation Slip, Exam Dates, Syllabus & Eligibility

Ideal and Non-Ideal Solutions Explained for Class 12 Chemistry

JEE Main Participating Colleges 2026 - A Complete List of Top Colleges

Clemmensen and Wolff Kishner Reductions Explained for JEE & NEET

Degree of Dissociation: Meaning, Formula, Calculation & Uses

Understanding the Angle of Deviation in a Prism

Other Pages
JEE Advanced Marks vs Ranks 2025: Understanding Category-wise Qualifying Marks and Previous Year Cut-offs

JEE Advanced 2026 - Exam Date (Released), Syllabus, Registration, Eligibility, Preparation, and More

CBSE Notes Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 9 - Hydrocarbons - 2025-26

CBSE Notes Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 5 - Thermodynamics - 2025-26

CBSE Notes Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 6 - Equilibrium - 2025-26

Inductive Effect and Its Role in Acidic Strength




