
The function $f\left( x \right) = \left| {px - q} \right| + r\left| x \right|$, $x \in \left( { - \infty ,\infty } \right)$ where $p > 0$, $q > 0$, $r > 0$ and it has a minimum value. Find the condition so the function has a minimum value.
A. $p \ne q$
B. $q \ne r$
C. $p \ne r$$
D. $p = q = r$
Answer
232.8k+ views
Hint: We rewrite the given function in the piecewise manner. After that, we will draw a diagram for the conditions $p = r$, $p < r$, and $p > r$. From the diagram, we will find the point where the function is minimum.
Complete step by step solution:
Given function is $f\left( x \right) = \left| {px - q} \right| + r\left| x \right|$, $x \in \left( { - \infty ,\infty } \right)$.
We know that, the absolute function$f\left( x \right) = \left| x \right|$ can be written as$f\left( x \right) = \left\{ {\begin{array}{*{20}{c}}{ - x,}&{x < 0}\\{x,}&{x \ge 0}\end{array}} \right.$.
The function $f\left( x \right)$ is a sum of two absolute functions.
Assume that, $f\left( x \right) = \left| {px - q} \right| + r\left| x \right| = g\left( x \right) + h\left( x \right)$
The piecewise from of $g\left( x \right) = \left| {px - q} \right|$ is $g\left( x \right) = \left\{ {\begin{array}{*{20}{c}}{ - \left( {px - p} \right),}&{px - p < 0}\\{px - p,}&{px - p \ge 0}\end{array}} \right.$
The piecewise form of $h\left( x \right) = r\left| x \right|$ is $h\left( x \right) = \left\{ {\begin{array}{*{20}{c}}{ - rx}&{x < 0}\\{rx}&{x \ge 0}\end{array}} \right.$
The $g\left( x \right)$function can be written is $g\left( x \right) = \left\{ {\begin{array}{*{20}{c}}{ - \left( {px - p} \right)}&{x < 0}\\{ - \left( {px - p} \right)}&{px - p < 0}\\{px - p}&{px - p \ge 0}\end{array}} \right.$.
The piecewise form of the $h\left( x \right)$is $f\left( x \right) = \left\{ {\begin{array}{*{20}{c}}{ - \left( {px - q} \right) - rx}&{x < 0}\\{ - \left( {px - q} \right) + rx}&{0 < x < \dfrac{q}{p}}\\{px - q + rx}&{x > 0}\end{array}} \right.$
$ = \left\{ {\begin{array}{*{20}{c}}{ - \left( {p + r} \right)x + q}&{x < 0}\\{\left( {p - r} \right)x + q}&{0 < x < \dfrac{q}{p}}\\{\left( {p + r} \right)x - q}&{x > 0}\end{array}} \right.$
Given that, $p > 0$, $q > 0$, $r > 0$.
So, the slope of $ - \left( {p + r} \right)x + q$ must be negative.
The slope of $\left( {p + r} \right)x - q$must be positive.
But we cannot predict the slope of $\left( {p - r} \right)x + q$.
Case I:
When $p > r$, then the slope of $\left( {p - r} \right)x + q$ is positive.
So, the graph will be
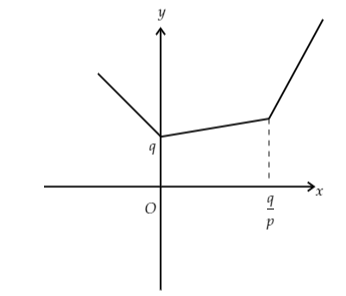
Image: Graph of function when r>p
The function $f\left( x \right)$ has a minimum point at $x = 0$.
Case II:
When $p = r$, then the slope of $\left( {p - r} \right)x + q$ is zero.
So, the graph will be
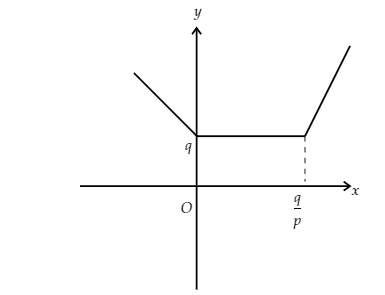
Image: Graph of function when r=p
The $f\left( x \right)$ has an infinite number of minimum points.
Case III:
When $p < r$, then the slope of $\left( {p - r} \right)x + q$ is negative.
So, the graph will be
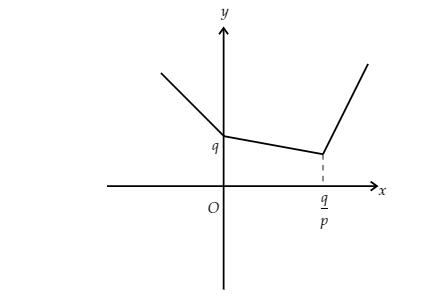
Image: Graph of function when rThe function has a minimum point at $x = \dfrac{q}{p}$.
Thus, the function has a minimum point when$p < r$ and $p > r$. This implies the function has a minimum point $p \ne r$.
Option ‘C’ is correct
Note: The maximum value is the highest point or value that a function can achieve in a graph; it is also referred to as the global maxima while the other peaks is referred to as local maxima. The same concept applies to the minimum value; the lowest value of a function for a graph is known as the global minima, while the other lower valleys are known as local minima.
Complete step by step solution:
Given function is $f\left( x \right) = \left| {px - q} \right| + r\left| x \right|$, $x \in \left( { - \infty ,\infty } \right)$.
We know that, the absolute function$f\left( x \right) = \left| x \right|$ can be written as$f\left( x \right) = \left\{ {\begin{array}{*{20}{c}}{ - x,}&{x < 0}\\{x,}&{x \ge 0}\end{array}} \right.$.
The function $f\left( x \right)$ is a sum of two absolute functions.
Assume that, $f\left( x \right) = \left| {px - q} \right| + r\left| x \right| = g\left( x \right) + h\left( x \right)$
The piecewise from of $g\left( x \right) = \left| {px - q} \right|$ is $g\left( x \right) = \left\{ {\begin{array}{*{20}{c}}{ - \left( {px - p} \right),}&{px - p < 0}\\{px - p,}&{px - p \ge 0}\end{array}} \right.$
The piecewise form of $h\left( x \right) = r\left| x \right|$ is $h\left( x \right) = \left\{ {\begin{array}{*{20}{c}}{ - rx}&{x < 0}\\{rx}&{x \ge 0}\end{array}} \right.$
The $g\left( x \right)$function can be written is $g\left( x \right) = \left\{ {\begin{array}{*{20}{c}}{ - \left( {px - p} \right)}&{x < 0}\\{ - \left( {px - p} \right)}&{px - p < 0}\\{px - p}&{px - p \ge 0}\end{array}} \right.$.
The piecewise form of the $h\left( x \right)$is $f\left( x \right) = \left\{ {\begin{array}{*{20}{c}}{ - \left( {px - q} \right) - rx}&{x < 0}\\{ - \left( {px - q} \right) + rx}&{0 < x < \dfrac{q}{p}}\\{px - q + rx}&{x > 0}\end{array}} \right.$
$ = \left\{ {\begin{array}{*{20}{c}}{ - \left( {p + r} \right)x + q}&{x < 0}\\{\left( {p - r} \right)x + q}&{0 < x < \dfrac{q}{p}}\\{\left( {p + r} \right)x - q}&{x > 0}\end{array}} \right.$
Given that, $p > 0$, $q > 0$, $r > 0$.
So, the slope of $ - \left( {p + r} \right)x + q$ must be negative.
The slope of $\left( {p + r} \right)x - q$must be positive.
But we cannot predict the slope of $\left( {p - r} \right)x + q$.
Case I:
When $p > r$, then the slope of $\left( {p - r} \right)x + q$ is positive.
So, the graph will be

Image: Graph of function when r>p
The function $f\left( x \right)$ has a minimum point at $x = 0$.
Case II:
When $p = r$, then the slope of $\left( {p - r} \right)x + q$ is zero.
So, the graph will be

Image: Graph of function when r=p
The $f\left( x \right)$ has an infinite number of minimum points.
Case III:
When $p < r$, then the slope of $\left( {p - r} \right)x + q$ is negative.
So, the graph will be

Image: Graph of function when r
Thus, the function has a minimum point when$p < r$ and $p > r$. This implies the function has a minimum point $p \ne r$.
Option ‘C’ is correct
Note: The maximum value is the highest point or value that a function can achieve in a graph; it is also referred to as the global maxima while the other peaks is referred to as local maxima. The same concept applies to the minimum value; the lowest value of a function for a graph is known as the global minima, while the other lower valleys are known as local minima.
Recently Updated Pages
The area of an expanding rectangle is increasing at class 12 maths JEE_Main

If y xxx cdots infty then find dfracdydx A yxy 1 B class 12 maths JEE_Main

Area vs Volume: Key Differences Explained for Students

Mutually Exclusive vs Independent Events: Key Differences Explained

Geometry of Complex Numbers Explained

JEE General Topics in Chemistry Important Concepts and Tips

Trending doubts
JEE Main 2026: Admit Card Out, City Intimation Slip, Exam Dates, Syllabus & Eligibility

JEE Main 2026 Application Login: Direct Link, Registration, Form Fill, and Steps

JEE Main Marking Scheme 2026- Paper-Wise Marks Distribution and Negative Marking Details

Understanding the Angle of Deviation in a Prism

Hybridisation in Chemistry – Concept, Types & Applications

How to Convert a Galvanometer into an Ammeter or Voltmeter

Other Pages
JEE Advanced Marks vs Ranks 2025: Understanding Category-wise Qualifying Marks and Previous Year Cut-offs

Understanding the Electric Field of a Uniformly Charged Ring

Derivation of Equation of Trajectory Explained for Students

Understanding Electromagnetic Waves and Their Importance

Inductive Effect and Its Role in Acidic Strength

JEE Advanced Weightage 2025 Chapter-Wise for Physics, Maths and Chemistry




