
The figure shows a circuit that contains four identical resistors with resistance R = 2.0 Ω. Two identical inductors with inductance L = 2.0 mH and an ideal battery with emf E = 9.V. The current ‘i’ just after the switch ‘s’ is closed will be
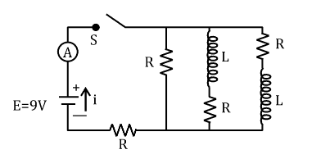
A. 9A
B. 3.0 A
C. 2.25 A
D. 3.37 A
Answer
233.1k+ views
Hint: At the instant when the switch is closed, it is derived from basic concepts that the inductor behaves like a resistance of infinite value. Based on the above inference the circuit can be redrawn to analyse its behavior just as the switch is closed.
Formula used:
Basic form of Ohm’s Law assuming ideal conditions is written below
\[V = I \times R\] ………… (1)
Where, V= Voltage across a resistive element in Volts
I= Current through the resistive element in Amperes
R= Resistance offered to the flow of current by the element in Ohms
Complete answer:
Here, after redrawing the circuit to represent the state just after the switch is closed. The inductor is assumed to be a resistance of infinite value.
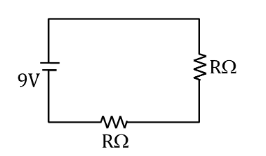
Image: Circuit just after switch is closed
Data given:
R= 2.0 ohm
L= 2mH (milli Henry)
E=9 V
Putting the values given above and using Ohm’s Law (1) for the circuit drawn above (2), we can write ,
\[\dfrac{V}{I} = R\]
\[R = \]\[2 + 2 = 4\] Ohm
Here, The equivalent resistance is added because the resistances given are in series.
\[I = \dfrac{V}{R} = \dfrac{9}{4} = 2.25\] Amperes
Hence, the current just after the switch is closed is 2.25 Amperes.
The correct answer is C.
Note: This problem deals with transient state analysis. During the transient state there is a change in the variables or process, but this stage is temporary and finally the system reaches a steady state. As the circuit is in a transient state just after the switch is closed, the inductor behaves as open circuit. Students often make a common mistake to solve the given question. They used a second loop to solve. Here we need to use the first loop.
Formula used:
Basic form of Ohm’s Law assuming ideal conditions is written below
\[V = I \times R\] ………… (1)
Where, V= Voltage across a resistive element in Volts
I= Current through the resistive element in Amperes
R= Resistance offered to the flow of current by the element in Ohms
Complete answer:
Here, after redrawing the circuit to represent the state just after the switch is closed. The inductor is assumed to be a resistance of infinite value.

Image: Circuit just after switch is closed
Data given:
R= 2.0 ohm
L= 2mH (milli Henry)
E=9 V
Putting the values given above and using Ohm’s Law (1) for the circuit drawn above (2), we can write ,
\[\dfrac{V}{I} = R\]
\[R = \]\[2 + 2 = 4\] Ohm
Here, The equivalent resistance is added because the resistances given are in series.
\[I = \dfrac{V}{R} = \dfrac{9}{4} = 2.25\] Amperes
Hence, the current just after the switch is closed is 2.25 Amperes.
The correct answer is C.
Note: This problem deals with transient state analysis. During the transient state there is a change in the variables or process, but this stage is temporary and finally the system reaches a steady state. As the circuit is in a transient state just after the switch is closed, the inductor behaves as open circuit. Students often make a common mistake to solve the given question. They used a second loop to solve. Here we need to use the first loop.
Recently Updated Pages
JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 (January 31 Evening Shift) Question Paper with Solutions [PDF]

JEE Main 2023 January 30 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 25 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 24 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

Trending doubts
JEE Main 2026: Session 2 Registration Open, City Intimation Slip, Exam Dates, Syllabus & Eligibility

JEE Main 2026 Application Login: Direct Link, Registration, Form Fill, and Steps

Understanding the Angle of Deviation in a Prism

Hybridisation in Chemistry – Concept, Types & Applications

How to Convert a Galvanometer into an Ammeter or Voltmeter

Understanding Uniform Acceleration in Physics

Other Pages
JEE Advanced Marks vs Ranks 2025: Understanding Category-wise Qualifying Marks and Previous Year Cut-offs

Dual Nature of Radiation and Matter Class 12 Physics Chapter 11 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Understanding the Electric Field of a Uniformly Charged Ring

JEE Advanced Weightage 2025 Chapter-Wise for Physics, Maths and Chemistry

Derivation of Equation of Trajectory Explained for Students

Understanding Electromagnetic Waves and Their Importance




