
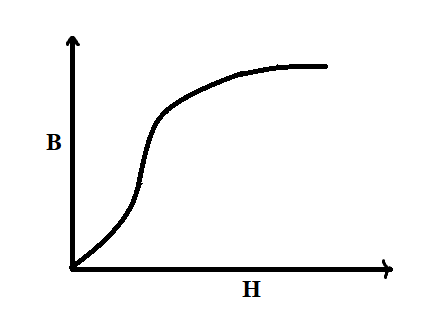
The figure represents the $B - H$ curve for commercial iron. As $H$ is increased, permeability.
A) Increases and becomes constant.
B) Increases, reaches a maximum and then decreases
C) Decrease continuously till it becomes very small
D) Decreases and then increases
Answer
232.8k+ views
Hint: The $B - H$ curve characterises the magnetic properties of an element or an alloy. $B$ denotes the magnetic flux density and H represents the magnetic field strength. The curve shows how commercial iron responds to magnetisation. Commercial iron is the form of iron containing carbon and other impurities in small amounts.
Complete step by step solution:
The $B - H$ curve is used to study the magnetic properties of a material. Elements show different behaviour under magnetisation. The magnetic flux density, which is the number of magnetic field lines through a unit area is represented on the $Y$ axis of the graph using $B$ and the strength of the magnetic field is given on the $X$ axis denoted by $H$.
Magnetic strength of an electromagnet depends on the type of material of the core, the number of turns of the coil and the current flowing through the coil. We can increase the magnetic strength by increasing the current or the number of turns in the coil or both.
The ratio of magnetic induction to magnetic intensity is called magnetic permeability and is denoted by $\mu $. The magnetic permeability can be used to measure a material’s resistance to the magnetic field. The formula for permeability is given by
$\mu = \dfrac{B}{H}$
We know that iron is a ferromagnetic material. Materials like iron do not have a constant permeability. The permeability increases with increase in magnetic field, after reaching a maximum value it will start decreasing.
Therefore, the answer is: Option (B), Increases, reaches a maximum and then decreases.
Note: Permeability is inversely proportional to magnetic field strength. The permeability of free space ${\mu _0}$ is a constant. But the relative permeability ${\mu _r}$ is not a constant. It is a function of magnetic field intensity. In ferromagnetic materials the ratio of flux density to field strength is not constant, it varies with the flux density. The curve plotted with flux density against field strength is called the magnetization curves or magnetic hysteresis curves. This helps in studying the magnetic behaviour of different materials. The relative permeability is the ratio of permeability through a medium and the permeability through a vacuum. It is expressed as ${\mu _r} = \dfrac{\mu }{{{\mu _0}}}$.
Complete step by step solution:
The $B - H$ curve is used to study the magnetic properties of a material. Elements show different behaviour under magnetisation. The magnetic flux density, which is the number of magnetic field lines through a unit area is represented on the $Y$ axis of the graph using $B$ and the strength of the magnetic field is given on the $X$ axis denoted by $H$.
Magnetic strength of an electromagnet depends on the type of material of the core, the number of turns of the coil and the current flowing through the coil. We can increase the magnetic strength by increasing the current or the number of turns in the coil or both.
The ratio of magnetic induction to magnetic intensity is called magnetic permeability and is denoted by $\mu $. The magnetic permeability can be used to measure a material’s resistance to the magnetic field. The formula for permeability is given by
$\mu = \dfrac{B}{H}$
We know that iron is a ferromagnetic material. Materials like iron do not have a constant permeability. The permeability increases with increase in magnetic field, after reaching a maximum value it will start decreasing.
Therefore, the answer is: Option (B), Increases, reaches a maximum and then decreases.
Note: Permeability is inversely proportional to magnetic field strength. The permeability of free space ${\mu _0}$ is a constant. But the relative permeability ${\mu _r}$ is not a constant. It is a function of magnetic field intensity. In ferromagnetic materials the ratio of flux density to field strength is not constant, it varies with the flux density. The curve plotted with flux density against field strength is called the magnetization curves or magnetic hysteresis curves. This helps in studying the magnetic behaviour of different materials. The relative permeability is the ratio of permeability through a medium and the permeability through a vacuum. It is expressed as ${\mu _r} = \dfrac{\mu }{{{\mu _0}}}$.
Recently Updated Pages
JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 (January 31 Evening Shift) Question Paper with Solutions [PDF]

JEE Main 2023 January 30 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 25 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 24 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

Trending doubts
JEE Main 2026: Session 2 Registration Open, City Intimation Slip, Exam Dates, Syllabus & Eligibility

JEE Main 2026 Application Login: Direct Link, Registration, Form Fill, and Steps

Understanding the Angle of Deviation in a Prism

Hybridisation in Chemistry – Concept, Types & Applications

How to Convert a Galvanometer into an Ammeter or Voltmeter

Understanding Uniform Acceleration in Physics

Other Pages
JEE Advanced Marks vs Ranks 2025: Understanding Category-wise Qualifying Marks and Previous Year Cut-offs

Dual Nature of Radiation and Matter Class 12 Physics Chapter 11 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Understanding the Electric Field of a Uniformly Charged Ring

JEE Advanced Weightage 2025 Chapter-Wise for Physics, Maths and Chemistry

Derivation of Equation of Trajectory Explained for Students

Understanding Electromagnetic Waves and Their Importance




