
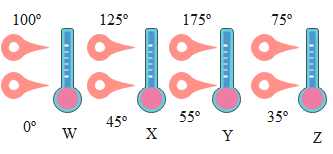
The diagram shows four thermometers labelled W, X, Y, Z. The freezing and boiling points of water are marked on them. Rank the thermometers according to the size of the degree on their scales, smallest to largest.
Answer
232.8k+ views
Hint: We know that temperature (sometimes called thermodynamic temperature) is a measure of the average kinetic energy of the particles in a system. Adding heat to a system causes its temperature to rise. Temperature is a measure of the average kinetic energy of the particles in an object. Thermal energy is the total energy an object has due to the internal motions of its particles. The temperature is related to the average kinetic energy not the total kinetic energy. There are three temperature scales in use today, Fahrenheit, Celsius and Kelvin. Fahrenheit temperature scale is a scale based on 32 for the freezing point of water and 212 for the boiling point of water, the interval between the two being divided into 180 parts.
Complete step by step answer
From the Diagram
For $\mathrm{W}$;
Difference between two Extreme Temperature:$100^{\circ}-0^{\circ}=100^{\circ} \mathrm{W}$
For X:-
Difference between two extreme temperature
$=125^{\circ}-45^{\circ}$
$=80^{\circ} \mathrm{X}$
For Y :-
Difference between two extreme temperature
$175^{\circ}-55^{\circ}$
$=120^{\circ} \mathrm{Y}$
Where as for Z:-
Difference between extreme temperature
$=75^{\circ}-35^{\circ}$
$=40^{\circ} \mathrm{Z}$
Hence from this we get:-
$\mathrm{T}_{\mathrm{Z}}>\mathrm{T}_{\mathrm{X}}>\mathrm{T}_{\mathrm{W}}>\mathrm{T}_{\mathrm{Y}}$
Note: We know that temperature is a physical quantity that expresses hot and cold. It is the manifestation of thermal energy, present in all matter, which is the source of the occurrence of heat, a flow of energy, when a body is in contact with another that is colder. Temperature is measured with a thermometer. Thermometer is an instrument used to measure temperature, especially one in which a thin column of liquid, such as mercury, expands and contracts within a graduated sealed tube. These liquid thermometers are based on the principle of thermal expansion. When a substance gets hotter, it expands to a greater volume. Nearly all substances exhibit this behaviour of thermal expansion. It is the basis of the design and operation of thermometers.
Complete step by step answer
From the Diagram
For $\mathrm{W}$;
Difference between two Extreme Temperature:$100^{\circ}-0^{\circ}=100^{\circ} \mathrm{W}$
For X:-
Difference between two extreme temperature
$=125^{\circ}-45^{\circ}$
$=80^{\circ} \mathrm{X}$
For Y :-
Difference between two extreme temperature
$175^{\circ}-55^{\circ}$
$=120^{\circ} \mathrm{Y}$
Where as for Z:-
Difference between extreme temperature
$=75^{\circ}-35^{\circ}$
$=40^{\circ} \mathrm{Z}$
Hence from this we get:-
$\mathrm{T}_{\mathrm{Z}}>\mathrm{T}_{\mathrm{X}}>\mathrm{T}_{\mathrm{W}}>\mathrm{T}_{\mathrm{Y}}$
Note: We know that temperature is a physical quantity that expresses hot and cold. It is the manifestation of thermal energy, present in all matter, which is the source of the occurrence of heat, a flow of energy, when a body is in contact with another that is colder. Temperature is measured with a thermometer. Thermometer is an instrument used to measure temperature, especially one in which a thin column of liquid, such as mercury, expands and contracts within a graduated sealed tube. These liquid thermometers are based on the principle of thermal expansion. When a substance gets hotter, it expands to a greater volume. Nearly all substances exhibit this behaviour of thermal expansion. It is the basis of the design and operation of thermometers.
Recently Updated Pages
JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 (January 31 Evening Shift) Question Paper with Solutions [PDF]

JEE Main 2023 January 30 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 25 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 24 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

Trending doubts
JEE Main 2026: Session 2 Registration Open, City Intimation Slip, Exam Dates, Syllabus & Eligibility

JEE Main 2026 Application Login: Direct Link, Registration, Form Fill, and Steps

Understanding the Angle of Deviation in a Prism

Hybridisation in Chemistry – Concept, Types & Applications

How to Convert a Galvanometer into an Ammeter or Voltmeter

Understanding Uniform Acceleration in Physics

Other Pages
JEE Advanced Marks vs Ranks 2025: Understanding Category-wise Qualifying Marks and Previous Year Cut-offs

Laws of Motion Class 11 Physics Chapter 4 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Waves Class 11 Physics Chapter 14 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Mechanical Properties of Fluids Class 11 Physics Chapter 9 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Thermodynamics Class 11 Physics Chapter 11 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Units And Measurements Class 11 Physics Chapter 1 CBSE Notes - 2025-26




