
The correct statement on the isomerism associated with the following complex ions is:
(a) ${{\left[ Ni{{\left( {{H}_{2}}O \right)}_{5}}N{{H}_{3}} \right]}^{2+}}$
(b) ${{\left[ Ni{{\left( {{H}_{2}}O \right)}_{4}}{{\left( N{{H}_{3}} \right)}_{2}} \right]}^{2+}}$
(c) ${{\left[ Ni{{\left( {{H}_{2}}O \right)}_{3}}{{\left( N{{H}_{3}} \right)}_{3}} \right]}^{2+}}$
(A) Both (a) and (b) show geometrical isomerism.
(B) (b) shows geometrical isomerism and (c) shows optical isomerism.
(C) (a) shows geometrical isomerism and (b) shows optical isomerism.
(D) Both (b) and (c) show geometrical isomerism.
Answer
243k+ views
Hint: Recollect the concept of coordination chemistry. Think about what is optical isomerism and what is geometrical isomerism. Draw the structures of the given three complexes and try to identify the isomerism present in them. Then choose the most suitable option as an answer.
Complete step by step solution:
- Stereoisomerism is the phenomena in which atoms have a different spatial arrangement. It is classified into two types: Optical isomerism and Geometrical isomerism.
- In optical isomerism, the two isomers are non-superimposable mirror images of each other. So, the point of contact between the metal and the ligands remains the same.
- In geometrical isomerism, the two isomers will have different arrangements of ligands around the central metal atom. This involves cis- and trans- isomers.
- Let’s draw the structure of the given coordination complexes.
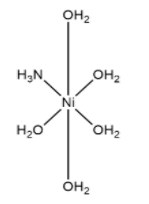
(a) ${{\left[ Ni{{\left( {{H}_{2}}O \right)}_{5}}N{{H}_{3}} \right]}^{2+}}$
(b) ${{\left[ Ni{{\left( {{H}_{2}}O \right)}_{4}}{{\left( N{{H}_{3}} \right)}_{2}} \right]}^{2+}}$
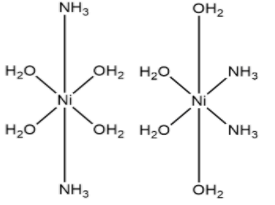
This complex shows geometrical isomerism and has trans and cis isomers which are shown above respectively.
(c) ${{\left[ Ni{{\left( {{H}_{2}}O \right)}_{3}}{{\left( N{{H}_{3}} \right)}_{3}} \right]}^{2+}}$
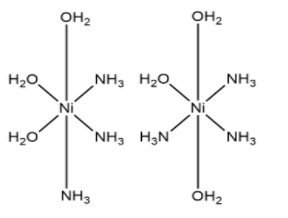
- This complex has facial and meridional, fac and mer isomers which are shown above. Therefore, this complex also shows geometrical isomerism.
- Therefore, the complexes (b) ${{\left[ Ni{{\left( {{H}_{2}}O \right)}_{4}}{{\left( N{{H}_{3}} \right)}_{2}} \right]}^{2+}}$ and (c) ${{\left[ Ni{{\left( {{H}_{2}}O \right)}_{3}}{{\left( N{{H}_{3}} \right)}_{3}} \right]}^{2+}}$ show geometrical isomerism.
Therefore, the correct answer is option (D).
Note: Remember fac isomer is the one in which ligands two ligands are in plane with metal and one ligand is out of plane. mer-isomer is the one in which three ligands and metal are in the same plane. cis-isomer is the one in which same ligands are adjacent to each other and trans isomer is the one in which same ligands are exactly opposite to each other.
Complete step by step solution:
- Stereoisomerism is the phenomena in which atoms have a different spatial arrangement. It is classified into two types: Optical isomerism and Geometrical isomerism.
- In optical isomerism, the two isomers are non-superimposable mirror images of each other. So, the point of contact between the metal and the ligands remains the same.
- In geometrical isomerism, the two isomers will have different arrangements of ligands around the central metal atom. This involves cis- and trans- isomers.
- Let’s draw the structure of the given coordination complexes.
(a) ${{\left[ Ni{{\left( {{H}_{2}}O \right)}_{5}}N{{H}_{3}} \right]}^{2+}}$

(b) ${{\left[ Ni{{\left( {{H}_{2}}O \right)}_{4}}{{\left( N{{H}_{3}} \right)}_{2}} \right]}^{2+}}$

This complex shows geometrical isomerism and has trans and cis isomers which are shown above respectively.
(c) ${{\left[ Ni{{\left( {{H}_{2}}O \right)}_{3}}{{\left( N{{H}_{3}} \right)}_{3}} \right]}^{2+}}$

- This complex has facial and meridional, fac and mer isomers which are shown above. Therefore, this complex also shows geometrical isomerism.
- Therefore, the complexes (b) ${{\left[ Ni{{\left( {{H}_{2}}O \right)}_{4}}{{\left( N{{H}_{3}} \right)}_{2}} \right]}^{2+}}$ and (c) ${{\left[ Ni{{\left( {{H}_{2}}O \right)}_{3}}{{\left( N{{H}_{3}} \right)}_{3}} \right]}^{2+}}$ show geometrical isomerism.
Therefore, the correct answer is option (D).
Note: Remember fac isomer is the one in which ligands two ligands are in plane with metal and one ligand is out of plane. mer-isomer is the one in which three ligands and metal are in the same plane. cis-isomer is the one in which same ligands are adjacent to each other and trans isomer is the one in which same ligands are exactly opposite to each other.
Recently Updated Pages
JEE Main 2026 Session 2 City Intimation Slip & Exam Date: Expected Date, Download Link

JEE Main 2026 Session 2 Application Form: Reopened Registration, Dates & Fees

JEE Main 2026 Session 2 Registration (Reopened): Last Date, Fees, Link & Process

WBJEE 2026 Registration Started: Important Dates Eligibility Syllabus Exam Pattern

Know The Difference Between Fluid And Liquid

Difference Between Crystalline and Amorphous Solid: Table & Examples

Trending doubts
JEE Main 2026: Session 1 Results Out and Session 2 Registration Open, City Intimation Slip, Exam Dates, Syllabus & Eligibility

Ideal and Non-Ideal Solutions Explained for Class 12 Chemistry

Understanding the Angle of Deviation in a Prism

Understanding Differential Equations: A Complete Guide

Hybridisation in Chemistry – Concept, Types & Applications

Understanding the Electric Field of a Uniformly Charged Ring

Other Pages
JEE Advanced Marks vs Ranks 2025: Understanding Category-wise Qualifying Marks and Previous Year Cut-offs

JEE Advanced 2026 - Exam Date (Released), Syllabus, Registration, Eligibility, Preparation, and More

CBSE Notes Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 9 - Hydrocarbons - 2025-26

CBSE Notes Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 5 - Thermodynamics - 2025-26

CBSE Notes Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 6 - Equilibrium - 2025-26

CBSE Notes Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 8 - Organic Chemistry Some Basic Principles And Techniques - 2025-26




