
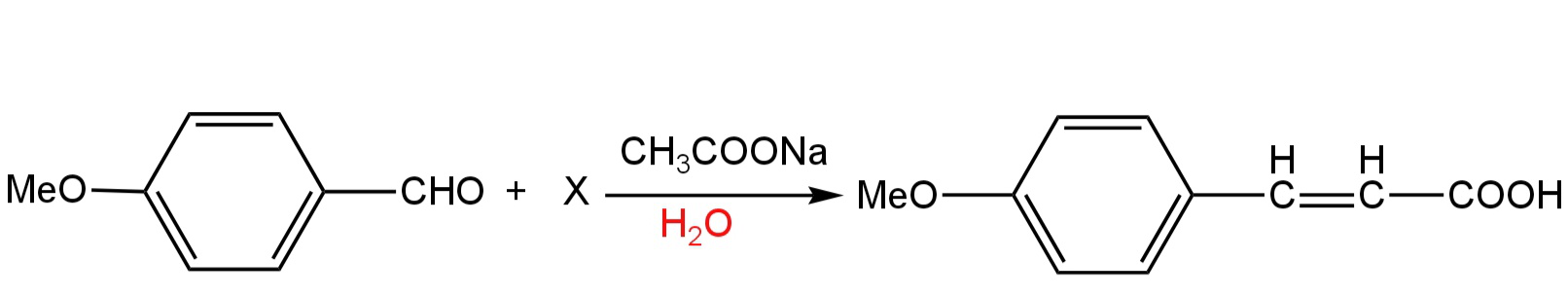
The compound (X) is
A. Acetic acid
B. Bromoacetic acid
C. Acetic anhydride
D. 2-oxo ethanoic acid
Answer
233.1k+ views
Hint: In the given reaction an α,β-unsaturated aromatic acid is formed by the reaction of an aromatic aldehyde and an acid anhydride in the presence of an alkali salt of the acid.
The alkali salt behaves as a base catalyst,
Complete step-by-step answer:
Perkin reaction is an organic chemical reaction established by William Henry Perkin, an English chemist.
This reaction produces an α,β-unsaturated aromatic acid.
This reaction's mechanism contains the reaction of aromatic aldehydes with the aliphatic acid anhydride in the presence of the alkali salt of the acid to give cinnamic acid derivatives.
In the given reaction, we have a reactant in which a methoxy group is attached to the para position of benzaldehyde.
The IUPAC name of this compound is 4-methoxy benzaldehyde.
This compound when treated with X in presence of sodium ethoxide gives α,β-unsaturated aromatic acid.
The IUPAC name of this compound is 4-methoxy cinnamic acid.
This reaction is Perkin's reaction.
So, X is acetic anhydride.
Mechanism of the reaction
The first step of the reaction involves the abstraction of α-hydrogen from acetic anhydride by the base.
Here the base is sodium ethoxide.
This leads to the formation of a nucleophile which attacks the electrophilic carbonyl carbon of 4-methoxy benzaldehyde.
The next step involves the treatment of the newly formed product with the base.
Then a molecule of water is removed from the product which is followed by hydrolysis.
4-methoxy cinnamic acid and acetic acid are formed as the product.
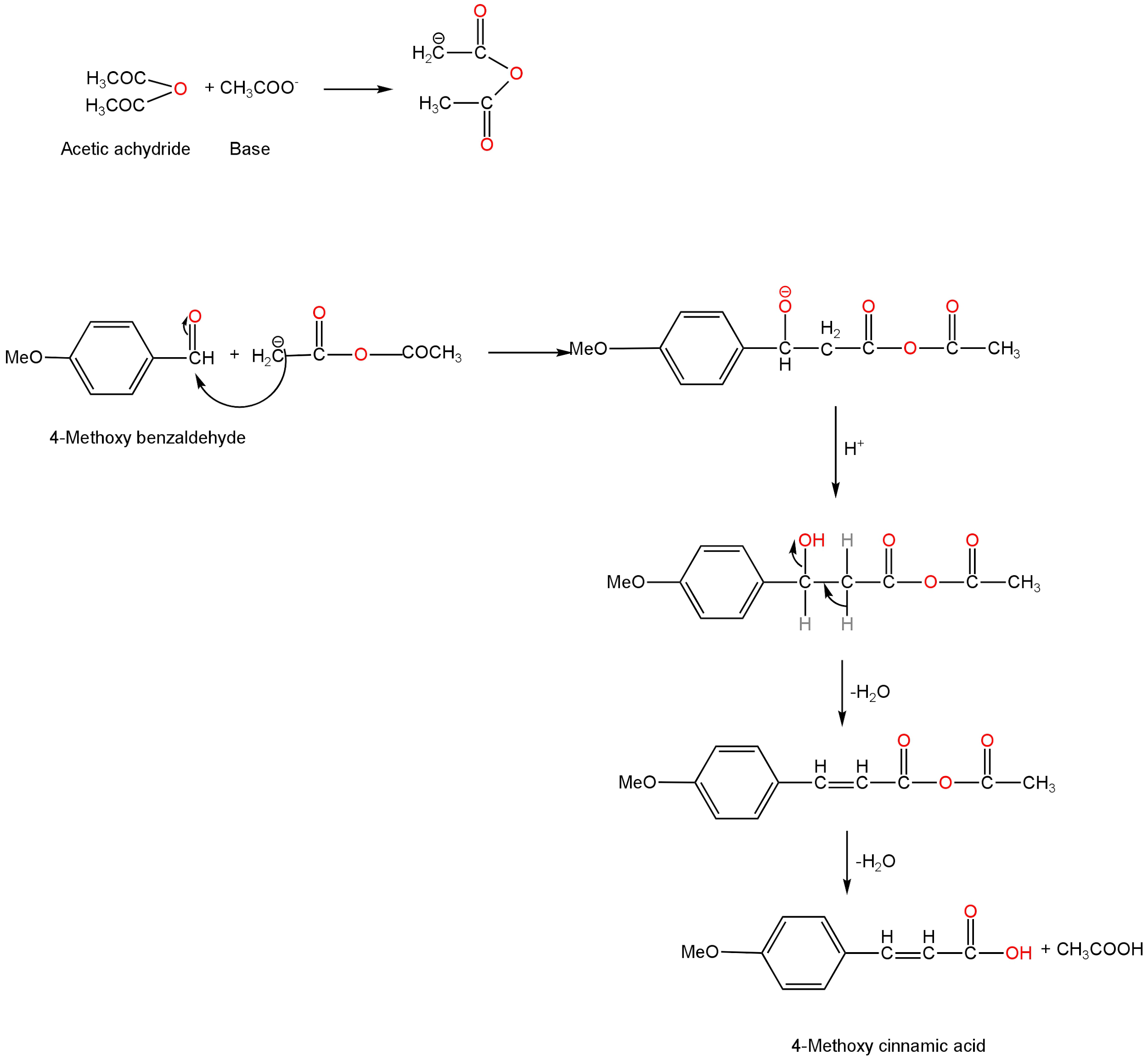
Image: Mechanism of Perkin's reaction
So, option C is correct.
Additional Information: Perkin's reaction was labelled after the name of its discoverer – William Henry Perkin.
Note: While attempting the question, one must remember the reactants used and products formed during a Perkin's reaction. An aromatic aldehyde and an aliphatic anhydride are used as the reactant. An alkali salt of an acid is used in this reaction.
The alkali salt behaves as a base catalyst,
Complete step-by-step answer:
Perkin reaction is an organic chemical reaction established by William Henry Perkin, an English chemist.
This reaction produces an α,β-unsaturated aromatic acid.
This reaction's mechanism contains the reaction of aromatic aldehydes with the aliphatic acid anhydride in the presence of the alkali salt of the acid to give cinnamic acid derivatives.
In the given reaction, we have a reactant in which a methoxy group is attached to the para position of benzaldehyde.
The IUPAC name of this compound is 4-methoxy benzaldehyde.
This compound when treated with X in presence of sodium ethoxide gives α,β-unsaturated aromatic acid.
The IUPAC name of this compound is 4-methoxy cinnamic acid.
This reaction is Perkin's reaction.
So, X is acetic anhydride.
Mechanism of the reaction
The first step of the reaction involves the abstraction of α-hydrogen from acetic anhydride by the base.
Here the base is sodium ethoxide.
This leads to the formation of a nucleophile which attacks the electrophilic carbonyl carbon of 4-methoxy benzaldehyde.
The next step involves the treatment of the newly formed product with the base.
Then a molecule of water is removed from the product which is followed by hydrolysis.
4-methoxy cinnamic acid and acetic acid are formed as the product.

Image: Mechanism of Perkin's reaction
So, option C is correct.
Additional Information: Perkin's reaction was labelled after the name of its discoverer – William Henry Perkin.
Note: While attempting the question, one must remember the reactants used and products formed during a Perkin's reaction. An aromatic aldehyde and an aliphatic anhydride are used as the reactant. An alkali salt of an acid is used in this reaction.
Recently Updated Pages
JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 (January 31 Evening Shift) Question Paper with Solutions [PDF]

JEE Main 2023 January 30 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 25 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 24 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

Trending doubts
JEE Main 2026: Session 2 Registration Open, City Intimation Slip, Exam Dates, Syllabus & Eligibility

JEE Main 2026 Application Login: Direct Link, Registration, Form Fill, and Steps

Understanding the Angle of Deviation in a Prism

Hybridisation in Chemistry – Concept, Types & Applications

How to Convert a Galvanometer into an Ammeter or Voltmeter

Understanding the Electric Field of a Uniformly Charged Ring

Other Pages
JEE Advanced Marks vs Ranks 2025: Understanding Category-wise Qualifying Marks and Previous Year Cut-offs

NCERT Solutions For Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 1 Solutions (2025-26)

Solutions Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 1 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

NCERT Solutions For Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 4 The d and f Block Elements (2025-26)

Biomolecules Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 10 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

NCERT Solutions For Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 10 Biomolecules (2025-26)




