
The compound X in the reaction is
\[{\rm{X}} \overset{CH_{3}MgI}{\rightarrow}{\rm{Y}} \overset{Hydrolysis}{\rightarrow} {\rm{Mg(OH)I}} + {\rm{C}}{{\rm{H}}_{\rm{3}}}{\rm{COOH}}\]
A. HCHO
B. \[{\rm{C}}{{\rm{H}}_{\rm{3}}}{\rm{CHO}}\]
C. \[{\left( {{\rm{C}}{{\rm{H}}_{\rm{3}}}} \right)_2}{\rm{CO}}\]
D. \[{\rm{C}}{{\rm{O}}_{\rm{2}}}\]
Answer
233.1k+ views
Hint: Grignard reagent belongs to the class of organometallic compound. Its chemical formula is \[{\rm{R}} - {\rm{Mg}} - {\rm{X}}\] , where, R is for an alkyl group, Mg is for magnesium atom and X is for any halogen atom such as bromine, chlorine etc.
Complete step by step answer:
Let's understand the reaction of a Grignard reagent with Carbon dioxide. A Grignard reagent, when undergoing a reaction with carbon dioxide, then undergoes hydrolysis to give the product of carboxylic acid.
Let's understand the reaction mechanism of the reaction in detail. The first step is breaking of C-Mg bond and attack of C- at the carbon atom of carbon dioxide. In the step, the carboxylate ion forms. Then, when the carboxylate ion undergoes a reaction with water, the formation of carboxylic acid occurs.
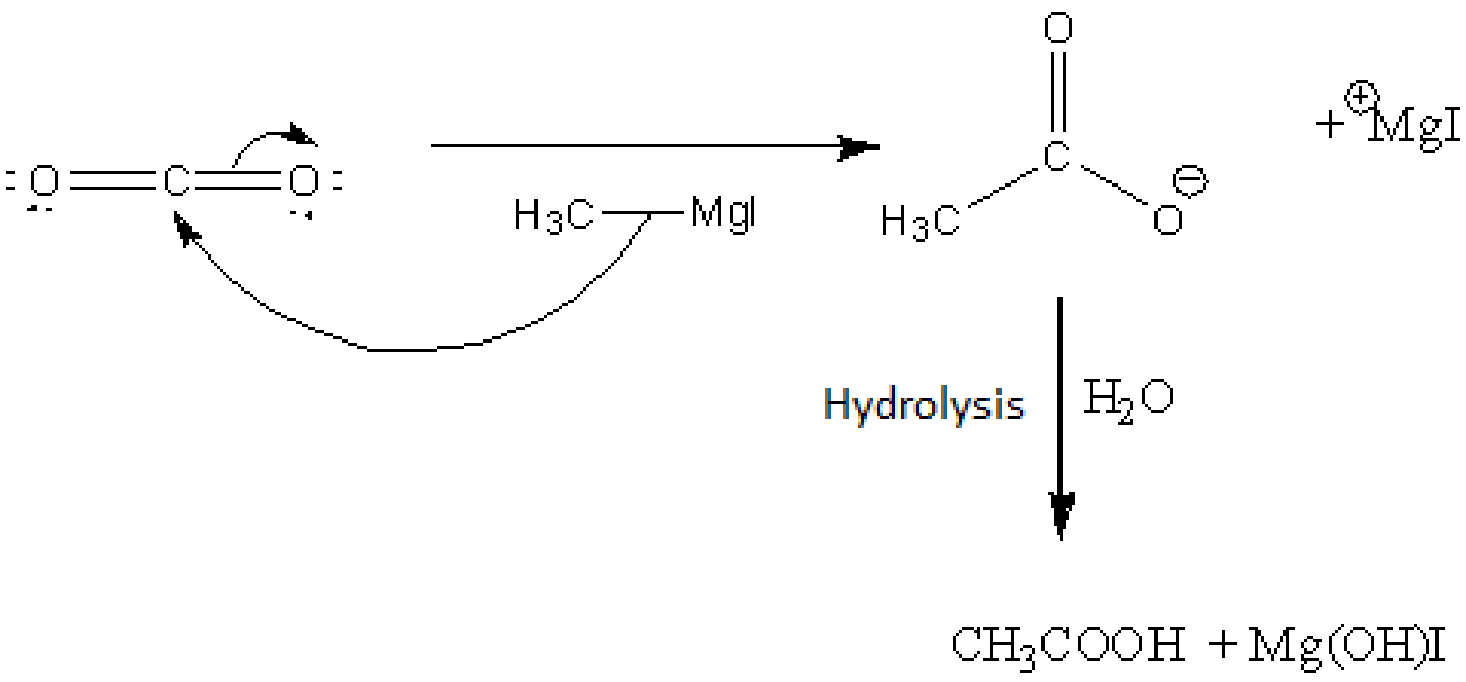
Image: Grignard reagent undergoes reaction with Carbon dioxide
Therefore, X is carbon dioxide. Hence, option B is the right answer.
Additional Information:
The preparation of the Grignard reagent is done from the reaction of magnesium and alkyl halide in the presence of ether (dry). Some of the reactions are,
(1)The reaction of aldehydes with Grignard reagent gives the product secondary alcohol.
(2)The reaction of ketones with Grignard reagent gives the product of tertiary alcohol.
(3)The reaction of esters with Grignard reagent gives the product of tertiary alcohol.
Note: The use of Grignard reagent to prepare chemo catalyst which is used in the chemical and pharmaceutical industries is very useful. In the agronomic industry, the development of eco-friendly products from Grignard reagents that possess soil-enriching properties results in a good market for Grignard reagents.
Complete step by step answer:
Let's understand the reaction of a Grignard reagent with Carbon dioxide. A Grignard reagent, when undergoing a reaction with carbon dioxide, then undergoes hydrolysis to give the product of carboxylic acid.
Let's understand the reaction mechanism of the reaction in detail. The first step is breaking of C-Mg bond and attack of C- at the carbon atom of carbon dioxide. In the step, the carboxylate ion forms. Then, when the carboxylate ion undergoes a reaction with water, the formation of carboxylic acid occurs.

Image: Grignard reagent undergoes reaction with Carbon dioxide
Therefore, X is carbon dioxide. Hence, option B is the right answer.
Additional Information:
The preparation of the Grignard reagent is done from the reaction of magnesium and alkyl halide in the presence of ether (dry). Some of the reactions are,
(1)The reaction of aldehydes with Grignard reagent gives the product secondary alcohol.
(2)The reaction of ketones with Grignard reagent gives the product of tertiary alcohol.
(3)The reaction of esters with Grignard reagent gives the product of tertiary alcohol.
Note: The use of Grignard reagent to prepare chemo catalyst which is used in the chemical and pharmaceutical industries is very useful. In the agronomic industry, the development of eco-friendly products from Grignard reagents that possess soil-enriching properties results in a good market for Grignard reagents.
Recently Updated Pages
JEE Main 2026 Session 2 Registration Open, Exam Dates, Syllabus & Eligibility

JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 (January 31 Evening Shift) Question Paper with Solutions [PDF]

JEE Main 2023 January 30 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 25 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

Trending doubts
JEE Main Marking Scheme 2026- Paper-Wise Marks Distribution and Negative Marking Details

Understanding Average and RMS Value in Electrical Circuits

Understanding Collisions: Types and Examples for Students

Ideal and Non-Ideal Solutions Explained for Class 12 Chemistry

Understanding Atomic Structure for Beginners

AssertionIn electrolytic refining of metal impure metal class 12 chemistry JEE_Main

Other Pages
JEE Advanced Weightage 2025 Chapter-Wise for Physics, Maths and Chemistry

NCERT Solutions For Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 2 Solutions Hindi Medium (2025-26)

CBSE Class 12 Chemistry Set 1 56/2/1 2025: Question Paper, Answers & Analysis

CBSE Class 12 Chemistry Question Paper Set 3 2025 with Answers

Inductive Effect and Its Role in Acidic Strength

Degree of Dissociation: Meaning, Formula, Calculation & Uses




