
The components required to make a simple series circuit to light a bulb are:
(A) Wires and cell
(B) Cell and Switch
(C) Bulb and wires
(D) Both B and C
Answer
240.9k+ views
Hint: To answer this question we should be having an idea about the various elements that are required to make a simple circuit. Among the elements we should be knowing which are the essential ones and which are the ones without which also the circuit can work. The more the number of components the more will be the complexity. So from the name it is known that a simple circuit will be having only the important components.
Complete step by step answer:
The components that are required to make a simple series circuit to light a bulb are the following:
1. Cells: The cells are required to make the current flow in the circuit. So without them the circuit will not be functional.
2. Switch: A switch is required to keep a control on the current flow in the circuit.
3. Bulbs: Since we are making a simple series circuit to light a bulb, we need to use bulbs in the circuit.
4. Wires: Wires are required to connect the various components that are present in the circuit.
Hence we can say that the components required to make a simple series circuit to light a bulb are cell, switch, bulb and wires. So both option B and C are the answer.
Hence option D is correct.
The diagram of a simple series circuit is given below:
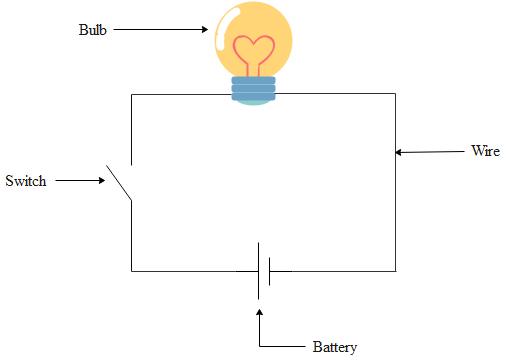
Note: In the answer, we have come across the term series circuit. This series circuit is defined as a circuit which consists of one resistor or even we can have more than one resistor. But the flow of electricity will be confined to only one path in the circuit. The electrons will flow from one end of the circuit to the other and there will be no branches in the circuit.
Complete step by step answer:
The components that are required to make a simple series circuit to light a bulb are the following:
1. Cells: The cells are required to make the current flow in the circuit. So without them the circuit will not be functional.
2. Switch: A switch is required to keep a control on the current flow in the circuit.
3. Bulbs: Since we are making a simple series circuit to light a bulb, we need to use bulbs in the circuit.
4. Wires: Wires are required to connect the various components that are present in the circuit.
Hence we can say that the components required to make a simple series circuit to light a bulb are cell, switch, bulb and wires. So both option B and C are the answer.
Hence option D is correct.
The diagram of a simple series circuit is given below:

Note: In the answer, we have come across the term series circuit. This series circuit is defined as a circuit which consists of one resistor or even we can have more than one resistor. But the flow of electricity will be confined to only one path in the circuit. The electrons will flow from one end of the circuit to the other and there will be no branches in the circuit.
Recently Updated Pages
JEE Main 2025-26 Mock Tests: Free Practice Papers & Solutions

JEE Main 2025-26 Experimental Skills Mock Test – Free Practice

JEE Main 2025-26 Electronic Devices Mock Test: Free Practice Online

JEE Main 2025-26 Atoms and Nuclei Mock Test – Free Practice Online

JEE Main 2025-26: Magnetic Effects of Current & Magnetism Mock Test

JEE Main Mock Test 2025: Properties of Solids and Liquids

Trending doubts
JEE Main 2026: Session 1 Results Out and Session 2 Registration Open, City Intimation Slip, Exam Dates, Syllabus & Eligibility

Ideal and Non-Ideal Solutions Explained for Class 12 Chemistry

JEE Main Participating Colleges 2026 - A Complete List of Top Colleges

Clemmensen and Wolff Kishner Reductions Explained for JEE & NEET

Degree of Dissociation: Meaning, Formula, Calculation & Uses

Understanding the Angle of Deviation in a Prism

Other Pages
CBSE Class 12 Physics Question Paper 2026: Download SET-wise PDF with Answer Key & Analysis

JEE Advanced Marks vs Ranks 2025: Understanding Category-wise Qualifying Marks and Previous Year Cut-offs

JEE Advanced 2026 - Exam Date (Released), Syllabus, Registration, Eligibility, Preparation, and More

CBSE Class 12 Physics Question Paper Set 3 (55/1/3) 2025 – PDF, Solutions & Analysis

CBSE Class 12 Physics Set 2 (55/2/2) 2025 Question Paper & Solutions

Dual Nature of Radiation and Matter Class 12 Physics Chapter 11 CBSE Notes - 2025-26




