
What will be the change in the resistance of a circuit consisting of five identical conductors if two similar conductors are added as shown by the dashed line in figure.
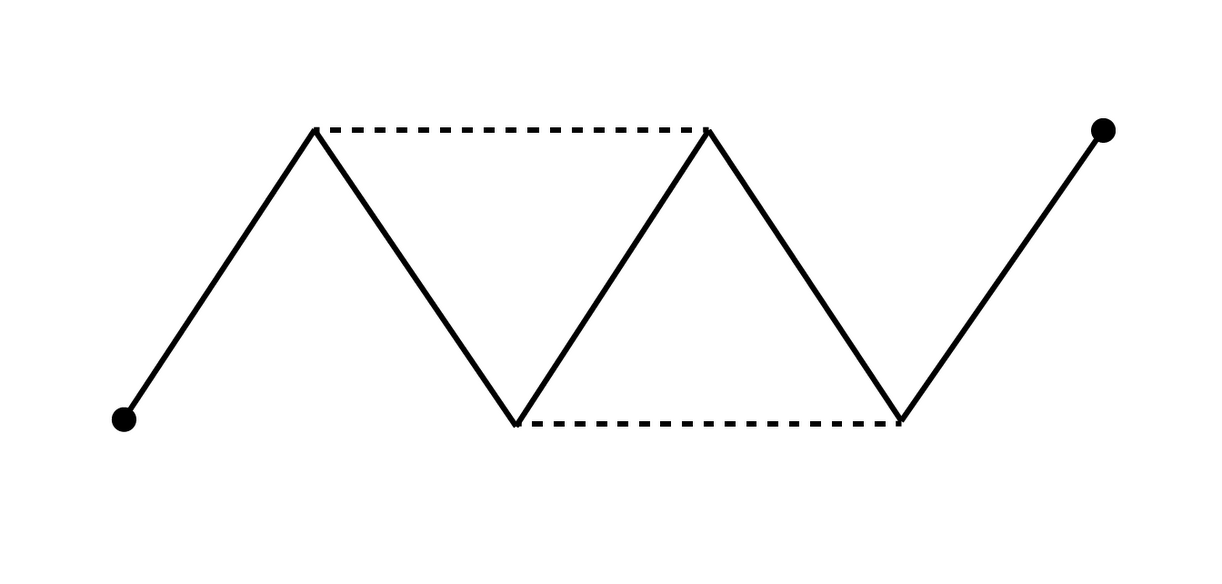
A) Becomes 1/5 times
B) Becomes 3/5 times
C) Becomes 2/5 times
D) Becomes 1/2 times
Answer
233.1k+ views
Hint:The problem is from the current electricity part of physics. We can apply the concept of resistance here. Use the equation for effective resistance in parallel and series combinations. The equivalent resistance is a single resistance which can replace all the component resistances in a circuit in such a manner that the current in the circuit remains unchanged.
Complete answer:
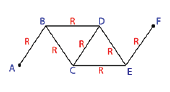
Let R represent each conductor's resistor. The five resistors are connected in series before adding two more conductors.
The equivalent resistance of the system will be, ${R_E} = R + R + R + R + R = 5R$
By adding two conductors, a balanced Wheatstone bridge circuit will be created in BCDE. The equivalent resistance of the system will be, ${R_E} = R$.
Now total equivalent resistance of the new system will be, ${R_E} = R + R + R = 3R$
The ratio between new equivalent resistance to previous equivalent resistance is given below.
\[\dfrac{{{R_{NEW}}}}{{{R_{OLD}}}} = \dfrac{{3R}}{{5R}} = \dfrac{3}{5}\]
The resistance becomes 3/5 times of the initial resistance.
Hence, the correct option is Option (B).
Note: A conductor's electrical resistance is affected by the following parameters: The conductor's cross-sectional area, the conductor's length, the conductor's material and the conducting material's temperature. Electrical resistance is inversely proportional to the cross-sectional area and directly proportional to the conductor's length. While solving this question pay close attention to circuits and terminals in which these resistances are connected and apply the concepts of parallel combination and series combination of resistance accordingly.
Complete answer:

Let R represent each conductor's resistor. The five resistors are connected in series before adding two more conductors.
The equivalent resistance of the system will be, ${R_E} = R + R + R + R + R = 5R$
By adding two conductors, a balanced Wheatstone bridge circuit will be created in BCDE. The equivalent resistance of the system will be, ${R_E} = R$.
Now total equivalent resistance of the new system will be, ${R_E} = R + R + R = 3R$
The ratio between new equivalent resistance to previous equivalent resistance is given below.
\[\dfrac{{{R_{NEW}}}}{{{R_{OLD}}}} = \dfrac{{3R}}{{5R}} = \dfrac{3}{5}\]
The resistance becomes 3/5 times of the initial resistance.
Hence, the correct option is Option (B).
Note: A conductor's electrical resistance is affected by the following parameters: The conductor's cross-sectional area, the conductor's length, the conductor's material and the conducting material's temperature. Electrical resistance is inversely proportional to the cross-sectional area and directly proportional to the conductor's length. While solving this question pay close attention to circuits and terminals in which these resistances are connected and apply the concepts of parallel combination and series combination of resistance accordingly.
Recently Updated Pages
JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 (January 31 Evening Shift) Question Paper with Solutions [PDF]

JEE Main 2023 January 30 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 25 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 24 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

Trending doubts
JEE Main 2026: Session 2 Registration Open, City Intimation Slip, Exam Dates, Syllabus & Eligibility

JEE Main 2026 Application Login: Direct Link, Registration, Form Fill, and Steps

Understanding the Angle of Deviation in a Prism

Hybridisation in Chemistry – Concept, Types & Applications

How to Convert a Galvanometer into an Ammeter or Voltmeter

Understanding Uniform Acceleration in Physics

Other Pages
JEE Advanced Marks vs Ranks 2025: Understanding Category-wise Qualifying Marks and Previous Year Cut-offs

Dual Nature of Radiation and Matter Class 12 Physics Chapter 11 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Understanding the Electric Field of a Uniformly Charged Ring

JEE Advanced Weightage 2025 Chapter-Wise for Physics, Maths and Chemistry

Derivation of Equation of Trajectory Explained for Students

Understanding Electromagnetic Waves and Their Importance




