
The bond order of \[Cl-O\] bond in \[ClO_{4}^{-}\] ion and the effective charge on each oxygen atom respectively are:
A. 1.75,-1
B. 1.75, -0.25
C. 1.5, -0.5
D. 2.0, -0.5
Answer
529.5k+ views
Hint: To solve these types of questions we should first draw the Lewis structure. And then after it, we then count the number of total bonds and then divide it by the number of elements in which these bonds are made with the central atom.
Step by step answer:
We can solve this question, by first drawing the Lewis dot structure of \[ClO_{4}^{-}\] ion.
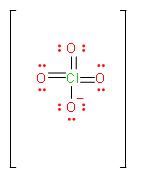
In the above figure, the total number of bonds is 7. And if we try to draw different structures, these bonds will rearrange themselves between four elements. Or we can calculate it by counting the number of resonance structures this molecule can make.
$Bond\,order=\dfrac{total\,number\,of\,bonds}{total\,number\,of\,resonance\,structures}$\[\begin{align}
& Formal\text{ }charge\,of\,first\,oxygen=6-6-\dfrac{2}{2}=-1 \\
& Formal\text{ }charge\,of\,\sec ond,\,third\,and\,fourth\,oxygen=6-4-\dfrac{4}{2}=0 \\
\end{align}\]
\[Bond\,order=\dfrac{7}{4}=1.75\]
So, from the above calculation we found that the bond order of perchlorate ion is 1.75.
Now, we will calculate formal charge on each oxygen atom. First we assign numbers to oxygen atoms.
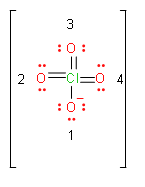
\[Formal\text{ }charge=\text{ }valence\text{ }electrons-unbonded\,electrons-\dfrac{1}{2}bonded\,electrons\]
\[\begin{align}
& Formal\text{ }charge\,of\,first\,oxygen=6-6-\dfrac{2}{2}=-1 \\
& Formal\text{ }charge\,of\,\sec ond,\,third\,and\,fourth\,oxygen=6-4-\dfrac{4}{2}=0 \\
\end{align}\]
So, effective charge on oxygen will become -0.25.
From the above discussion and calculation, we can now say that the answer of this question is option B.
Additional information:
We should know that perchlorate is a chemical compound containing the perchlorate ion \[ClO_{4}^{-}\]. The majority of perchlorates are commercially produced salts. They are mainly used for propellants, exploiting properties as powerful oxidizing agents and to control static electricity in food packaging. Most perchlorates are colourless solids that are soluble in water.
Note: We should also know about bond length. It is defined as the distance between the centres of two covalently bonded atoms. The length of the bond is determined by the number of bonded electrons (the bond order). If bond order is high, there will be stronger pull between two atoms and there will be shorter bond length. Therefore, bond length increases in the following order: triple bond < double bond < single bond.
Step by step answer:
We can solve this question, by first drawing the Lewis dot structure of \[ClO_{4}^{-}\] ion.

In the above figure, the total number of bonds is 7. And if we try to draw different structures, these bonds will rearrange themselves between four elements. Or we can calculate it by counting the number of resonance structures this molecule can make.
$Bond\,order=\dfrac{total\,number\,of\,bonds}{total\,number\,of\,resonance\,structures}$\[\begin{align}
& Formal\text{ }charge\,of\,first\,oxygen=6-6-\dfrac{2}{2}=-1 \\
& Formal\text{ }charge\,of\,\sec ond,\,third\,and\,fourth\,oxygen=6-4-\dfrac{4}{2}=0 \\
\end{align}\]
\[Bond\,order=\dfrac{7}{4}=1.75\]
So, from the above calculation we found that the bond order of perchlorate ion is 1.75.
Now, we will calculate formal charge on each oxygen atom. First we assign numbers to oxygen atoms.

\[Formal\text{ }charge=\text{ }valence\text{ }electrons-unbonded\,electrons-\dfrac{1}{2}bonded\,electrons\]
\[\begin{align}
& Formal\text{ }charge\,of\,first\,oxygen=6-6-\dfrac{2}{2}=-1 \\
& Formal\text{ }charge\,of\,\sec ond,\,third\,and\,fourth\,oxygen=6-4-\dfrac{4}{2}=0 \\
\end{align}\]
So, effective charge on oxygen will become -0.25.
From the above discussion and calculation, we can now say that the answer of this question is option B.
Additional information:
We should know that perchlorate is a chemical compound containing the perchlorate ion \[ClO_{4}^{-}\]. The majority of perchlorates are commercially produced salts. They are mainly used for propellants, exploiting properties as powerful oxidizing agents and to control static electricity in food packaging. Most perchlorates are colourless solids that are soluble in water.
Note: We should also know about bond length. It is defined as the distance between the centres of two covalently bonded atoms. The length of the bond is determined by the number of bonded electrons (the bond order). If bond order is high, there will be stronger pull between two atoms and there will be shorter bond length. Therefore, bond length increases in the following order: triple bond < double bond < single bond.
Recently Updated Pages
Know The Difference Between Fluid And Liquid

Difference Between Crystalline and Amorphous Solid: Table & Examples

Types of Solutions in Chemistry: Explained Simply

Hess Law of Constant Heat Summation: Definition, Formula & Applications

Disproportionation Reaction: Definition, Example & JEE Guide

JEE Extractive Metallurgy Important Concepts and Tips for Exam Preparation

Trending doubts
JEE Main 2026: Session 1 Results Out and Session 2 Registration Open, City Intimation Slip, Exam Dates, Syllabus & Eligibility

Ideal and Non-Ideal Solutions Explained for Class 12 Chemistry

JEE Main Participating Colleges 2026 - A Complete List of Top Colleges

Clemmensen and Wolff Kishner Reductions Explained for JEE & NEET

Degree of Dissociation: Meaning, Formula, Calculation & Uses

Understanding the Angle of Deviation in a Prism

Other Pages
JEE Advanced Marks vs Ranks 2025: Understanding Category-wise Qualifying Marks and Previous Year Cut-offs

JEE Advanced 2026 - Exam Date (Released), Syllabus, Registration, Eligibility, Preparation, and More

CBSE Notes Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 9 - Hydrocarbons - 2025-26

CBSE Notes Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 5 - Thermodynamics - 2025-26

CBSE Notes Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 6 - Equilibrium - 2025-26

Inductive Effect and Its Role in Acidic Strength




