
The bond angle in a water molecule is nearly or directed bonds in water forms an angle of
A) \[120^\circ {\rm{C}}\]
B) \[180^\circ {\rm{C}}\]
C) \[109^\circ 28\]
D) \[104^\circ 30\]
Answer
233.1k+ views
Hint: The molecule of water has two bond pairs and two lone pairs. Therefore, the geometry of the molecule is tetrahedral in nature. Here, we will use the VSEPR theory to predict the bond angle.
Complete Step by Step Answer:
Let’s discuss the type of bond formed by the oxygen molecule of water. In the molecule of water, an oxygen atom is bonded to two oxygen atoms. The covalent bond formed between oxygen and hydrogen atoms is polar because of higher difference in electronegativity of these two atoms. So, there are two bond pairs of the oxygen atom. Also, there are two lone pairs of oxygen atoms. So, the two bond pairs and lone pairs are arranged in the tetrahedral geometry around the central atom.
We know, the bond angle in a tetrahedral molecule is \[109.5^\circ C\] . In case of water, due to the repulsion of two lone pairs and repulsion of lone pair and bond pair, the decrease of bond angle from \[109.5^\circ C\]to \[104.5^\circ C\]which is approximate to \[105^\circ {\rm{C}}\] .
Now, we will draw the structure of the water molecule.
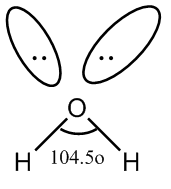
Image: Molecule of water
So, we see that the molecule of water has a bent shape.
Therefore, option D is right.
Note: The VSEPR theory based on the lone pairs and bond pairs around the central atom predicts the shape of molecules. According to this theory, the repulsion is highest in case of two lone pairs and lowest in case of two bond pairs and the repulsion of bond pair and lone pairs is between these two.
Complete Step by Step Answer:
Let’s discuss the type of bond formed by the oxygen molecule of water. In the molecule of water, an oxygen atom is bonded to two oxygen atoms. The covalent bond formed between oxygen and hydrogen atoms is polar because of higher difference in electronegativity of these two atoms. So, there are two bond pairs of the oxygen atom. Also, there are two lone pairs of oxygen atoms. So, the two bond pairs and lone pairs are arranged in the tetrahedral geometry around the central atom.
We know, the bond angle in a tetrahedral molecule is \[109.5^\circ C\] . In case of water, due to the repulsion of two lone pairs and repulsion of lone pair and bond pair, the decrease of bond angle from \[109.5^\circ C\]to \[104.5^\circ C\]which is approximate to \[105^\circ {\rm{C}}\] .
Now, we will draw the structure of the water molecule.

Image: Molecule of water
So, we see that the molecule of water has a bent shape.
Therefore, option D is right.
Note: The VSEPR theory based on the lone pairs and bond pairs around the central atom predicts the shape of molecules. According to this theory, the repulsion is highest in case of two lone pairs and lowest in case of two bond pairs and the repulsion of bond pair and lone pairs is between these two.
Recently Updated Pages
JEE Main 2026 Session 2 Registration Open, Exam Dates, Syllabus & Eligibility

JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 (January 31 Evening Shift) Question Paper with Solutions [PDF]

JEE Main 2023 January 30 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 25 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

Trending doubts
JEE Main Marking Scheme 2026- Paper-Wise Marks Distribution and Negative Marking Details

Understanding Average and RMS Value in Electrical Circuits

Understanding Collisions: Types and Examples for Students

Ideal and Non-Ideal Solutions Explained for Class 12 Chemistry

Understanding Atomic Structure for Beginners

AssertionIn electrolytic refining of metal impure metal class 12 chemistry JEE_Main

Other Pages
JEE Advanced Weightage 2025 Chapter-Wise for Physics, Maths and Chemistry

NCERT Solutions For Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 2 Solutions Hindi Medium (2025-26)

CBSE Class 12 Chemistry Set 1 56/2/1 2025: Question Paper, Answers & Analysis

CBSE Class 12 Chemistry Question Paper Set 3 2025 with Answers

Inductive Effect and Its Role in Acidic Strength

Degree of Dissociation: Meaning, Formula, Calculation & Uses




