
The banana bond in diborane is constituted by?
(A) 2 Atoms and 2 electrons
(B) 2 Atoms and 3 electrons
(C) 3 Atoms and 2 electrons
(D) 3 Atoms and 3 electrons
Answer
242.4k+ views
Hint: Diborane forms 4 normal covalent bonds with 4 H atoms. The banana bonds are formed in between the B atoms. There are a total of 2 banana bonds in diborane.
Complete-step- by- step answer:
Diborane is a chemical compound with the formula-${{B}_{2}}{{H}_{6}}$ .
It is a colourless, highly flammable gas with a repulsive sweet odour. It is extremely toxic.
Combustion of diborane is extremely exothermic.
To understand what is meant by a banana bond, let us look into the structure of diborane.
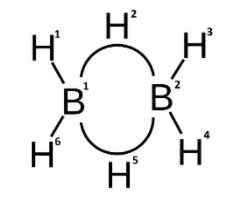
In diborane, first we need to know that the B with atomic number 5, has the electronic configuration- $1{{s}^{2}}2{{s}^{2}}2{{p}^{1}}$. While hybridising, one of the 2s valence electrons is excited to a 2p orbital and we get 4 $s{{p}^{3}}$ hybridised orbitals. Among these 4 hybrid orbitals, 3 of them have one electron each. And, one of them is an empty orbital.
Each B atom in ${{B}_{2}}{{H}_{6}}$ forms 2 normal covalent bonds with the 1s orbitals of the H atoms. Hence, in total the 2 B atoms form 4 normal covalent bonds. These bonds are 2 centre – 2 electron bonds named according to the atoms and number of electrons.
The 2 B atoms are now left with one orbital with an unpaired electron and one empty orbital each. These are the orbitals that form the two bridging B-H-B bonds with the two 1s orbitals of the H atoms. These bonds are commonly known as the banana bonds.
Now, let us look at the number of atoms and electrons in the banana bonds.
Each banana bond has contributions of 2 B atoms and 1 H atom. Hence, there are 3 atoms.
The number of electrons in each bond will be, one electron from H atom, and a total of one electron from both the B atoms. Hence, the number of electrons is 2.
Therefore we can conclude that the banana bond in diborane consists of 3 atoms and 2 electrons.
So, the correct answer is (C).
Additional Information:
Diborane is a chemical compound with many applications in various fields.
i) Diborane and some of its variants are used as reagents for hydroboration.
ii) It is also used as a reducing agent and can readily reduce carboxylic acids to corresponding alcohols.
iii) Diborane has been tested as a rocket propellant as its combustion is extremely exothermic.
iv) It is used as a rubber vulcaniser and as a catalyst for polymerisation reactions.
v) It is used as a doping agent for semiconductor production.
Note: Banana bonds are also called as 3-centre 2-electron bonds. It signifies that the bond is constituted by 3 atoms and 2 electrons. While drawing the structure of diborane, it is advised to use curved lines to show the banana bonds.
Complete-step- by- step answer:
Diborane is a chemical compound with the formula-${{B}_{2}}{{H}_{6}}$ .
It is a colourless, highly flammable gas with a repulsive sweet odour. It is extremely toxic.
Combustion of diborane is extremely exothermic.
To understand what is meant by a banana bond, let us look into the structure of diborane.

In diborane, first we need to know that the B with atomic number 5, has the electronic configuration- $1{{s}^{2}}2{{s}^{2}}2{{p}^{1}}$. While hybridising, one of the 2s valence electrons is excited to a 2p orbital and we get 4 $s{{p}^{3}}$ hybridised orbitals. Among these 4 hybrid orbitals, 3 of them have one electron each. And, one of them is an empty orbital.
Each B atom in ${{B}_{2}}{{H}_{6}}$ forms 2 normal covalent bonds with the 1s orbitals of the H atoms. Hence, in total the 2 B atoms form 4 normal covalent bonds. These bonds are 2 centre – 2 electron bonds named according to the atoms and number of electrons.
The 2 B atoms are now left with one orbital with an unpaired electron and one empty orbital each. These are the orbitals that form the two bridging B-H-B bonds with the two 1s orbitals of the H atoms. These bonds are commonly known as the banana bonds.
Now, let us look at the number of atoms and electrons in the banana bonds.
Each banana bond has contributions of 2 B atoms and 1 H atom. Hence, there are 3 atoms.
The number of electrons in each bond will be, one electron from H atom, and a total of one electron from both the B atoms. Hence, the number of electrons is 2.
Therefore we can conclude that the banana bond in diborane consists of 3 atoms and 2 electrons.
So, the correct answer is (C).
Additional Information:
Diborane is a chemical compound with many applications in various fields.
i) Diborane and some of its variants are used as reagents for hydroboration.
ii) It is also used as a reducing agent and can readily reduce carboxylic acids to corresponding alcohols.
iii) Diborane has been tested as a rocket propellant as its combustion is extremely exothermic.
iv) It is used as a rubber vulcaniser and as a catalyst for polymerisation reactions.
v) It is used as a doping agent for semiconductor production.
Note: Banana bonds are also called as 3-centre 2-electron bonds. It signifies that the bond is constituted by 3 atoms and 2 electrons. While drawing the structure of diborane, it is advised to use curved lines to show the banana bonds.
Recently Updated Pages
Know The Difference Between Fluid And Liquid

Difference Between Crystalline and Amorphous Solid: Table & Examples

Types of Solutions in Chemistry: Explained Simply

Hess Law of Constant Heat Summation: Definition, Formula & Applications

Disproportionation Reaction: Definition, Example & JEE Guide

JEE Extractive Metallurgy Important Concepts and Tips for Exam Preparation

Trending doubts
JEE Main 2026: Session 1 Results Out and Session 2 Registration Open, City Intimation Slip, Exam Dates, Syllabus & Eligibility

Ideal and Non-Ideal Solutions Explained for Class 12 Chemistry

JEE Main Participating Colleges 2026 - A Complete List of Top Colleges

Degree of Dissociation: Meaning, Formula, Calculation & Uses

Understanding the Angle of Deviation in a Prism

Hybridisation in Chemistry – Concept, Types & Applications

Other Pages
JEE Advanced Marks vs Ranks 2025: Understanding Category-wise Qualifying Marks and Previous Year Cut-offs

CBSE Notes Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 9 - Hydrocarbons - 2025-26

CBSE Notes Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 5 - Thermodynamics - 2025-26

CBSE Notes Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 6 - Equilibrium - 2025-26

CBSE Notes Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 8 - Organic Chemistry Some Basic Principles And Techniques - 2025-26

JEE Advanced Weightage 2025 Chapter-Wise for Physics, Maths and Chemistry




