
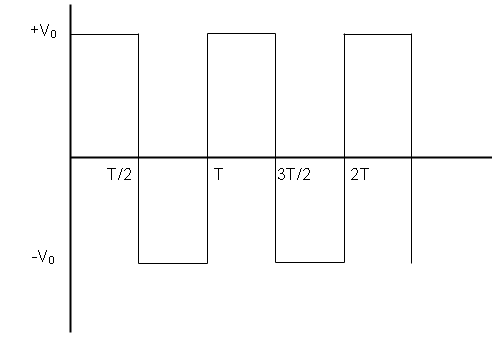
The average and RMS value of voltage for square waves shown in the fig. having a peak value ${V_0}$ are:
(A) $\dfrac{{{V_0}}}{{\sqrt 2 }},\sqrt 2 {V_0}$
(B) $\sqrt 2 {V_0},\dfrac{{{V_0}}}{{\sqrt 2 }}$
(C) ${V_0},{V_0}$
(D) Zero, ${V_0}$
Answer
239.4k+ views
Hint: In this solution, we will use the formula of average and RMS value. We only need to consider one cycle of the voltage to calculate the average and RMS value.
Complete step by step answer:
In the graph given to us, we want to calculate the average and RMS value of voltage.
The average amplitude is the mathematical “mean” of all a waveform’s points over the period of one cycle. It can be mathematically calculated as:
${V_{avg}} = \dfrac{1}{T}\int {{V_0}dt} $
We can see that the waveform of the voltage starts a cycle at $t = 0$ and ends the cycle at $t = T$. To calculate the integral of the wave function given to us, we need to break the integral down into regions where the voltage has constant values. So, we can write
${V_{avg}} = \dfrac{1}{T}\left( {\int\limits_{t = 0}^{t = T/2} {{V_0}dt + } \int\limits_{t = T/2}^{t = T} { - {V_0}dt} } \right)$
The ${V_0}$ term can be taken out of the integral since it is constant. The integral can then be simplified to
${V_{avg}} = \dfrac{{{V_0}}}{T}\left( {\dfrac{T}{2} + \dfrac{T}{2} - T} \right)$
$ \Rightarrow {V_{avg}} = 0$
Hence the average voltage will be zero.
Now, The RMS value stands for Root Mean Square value. It is a way of expressing an AC quantity of voltage or current in terms functionally equivalent to DC. It can be mathematically calculated as
${V_{RMS}} = \sqrt {\dfrac{1}{T}\int\limits_{t = 0}^T {{V^2}dt} } $
The integral can be broken into two parts as
${V_{RMS}} = \sqrt {\dfrac{1}{T}\left( {\int\limits_{t = 0}^{t = T/2} {V_0^2dt} + \int\limits_{t = T/2}^{t = T} {V_0^2dt} } \right)} $
The integral can be simplified as
${V_{RMS}} = \sqrt {\dfrac{{{V_0}^2}}{T}T} $
Or,
${V_{RMS}} = {V_0}$
Hence the correct choice is option (D).
Note: While calculating the average and the RMS value, we must not forget the $1/T$ term outside the integral. We can also find the average value graphically as zero since the area of the graph for one time period is the same in the positive and negative regime and as such, the average value will be zero.
Complete step by step answer:
In the graph given to us, we want to calculate the average and RMS value of voltage.
The average amplitude is the mathematical “mean” of all a waveform’s points over the period of one cycle. It can be mathematically calculated as:
${V_{avg}} = \dfrac{1}{T}\int {{V_0}dt} $
We can see that the waveform of the voltage starts a cycle at $t = 0$ and ends the cycle at $t = T$. To calculate the integral of the wave function given to us, we need to break the integral down into regions where the voltage has constant values. So, we can write
${V_{avg}} = \dfrac{1}{T}\left( {\int\limits_{t = 0}^{t = T/2} {{V_0}dt + } \int\limits_{t = T/2}^{t = T} { - {V_0}dt} } \right)$
The ${V_0}$ term can be taken out of the integral since it is constant. The integral can then be simplified to
${V_{avg}} = \dfrac{{{V_0}}}{T}\left( {\dfrac{T}{2} + \dfrac{T}{2} - T} \right)$
$ \Rightarrow {V_{avg}} = 0$
Hence the average voltage will be zero.
Now, The RMS value stands for Root Mean Square value. It is a way of expressing an AC quantity of voltage or current in terms functionally equivalent to DC. It can be mathematically calculated as
${V_{RMS}} = \sqrt {\dfrac{1}{T}\int\limits_{t = 0}^T {{V^2}dt} } $
The integral can be broken into two parts as
${V_{RMS}} = \sqrt {\dfrac{1}{T}\left( {\int\limits_{t = 0}^{t = T/2} {V_0^2dt} + \int\limits_{t = T/2}^{t = T} {V_0^2dt} } \right)} $
The integral can be simplified as
${V_{RMS}} = \sqrt {\dfrac{{{V_0}^2}}{T}T} $
Or,
${V_{RMS}} = {V_0}$
Hence the correct choice is option (D).
Note: While calculating the average and the RMS value, we must not forget the $1/T$ term outside the integral. We can also find the average value graphically as zero since the area of the graph for one time period is the same in the positive and negative regime and as such, the average value will be zero.
Recently Updated Pages
JEE Main 2025-26 Mock Tests: Free Practice Papers & Solutions

JEE Main 2025-26 Experimental Skills Mock Test – Free Practice

JEE Main 2025-26 Electronic Devices Mock Test: Free Practice Online

JEE Main 2025-26 Atoms and Nuclei Mock Test – Free Practice Online

JEE Main 2025-26: Magnetic Effects of Current & Magnetism Mock Test

JEE Main Mock Test 2025: Properties of Solids and Liquids

Trending doubts
JEE Main 2026: Session 1 Results Out and Session 2 Registration Open, City Intimation Slip, Exam Dates, Syllabus & Eligibility

Ideal and Non-Ideal Solutions Explained for Class 12 Chemistry

JEE Main Participating Colleges 2026 - A Complete List of Top Colleges

Step-by-Step Guide to Young’s Double Slit Experiment Derivation

Understanding the Angle of Deviation in a Prism

Understanding Electromagnetic Waves and Their Importance

Other Pages
CBSE Class 12 Physics Question Paper 2026: Download SET-wise PDF with Answer Key & Analysis

JEE Advanced Marks vs Ranks 2025: Understanding Category-wise Qualifying Marks and Previous Year Cut-offs

Essential Derivations for CBSE Class 12 Physics: Stepwise & PDF Solutions

JEE Advanced 2026 - Exam Date (Released), Syllabus, Registration, Eligibility, Preparation, and More

CBSE Class 12 Physics Question Paper Set 3 (55/2/3) 2025: PDF, Answer Key & Solutions

CBSE Class 12 Physics Question Paper Set 3 (55/1/3) 2025 – PDF, Solutions & Analysis




