
The addition of HBr to an alkene in the presence of peroxide is an example of:
A. Electrophilic addition reaction
B. Nucleophilic addition reaction
C. Free-radical addition reaction
D. Formation of carbocation as an intermediate
Answer
242.1k+ views
Hint: When hydrogen bromide is added to alkenes in presence of peroxide, it reacts with anti-Markovnikov’s addition mechanism. Peroxides form free radicals that initiate the reaction and add bromine radical at terminal carbon.
Complete step-by-step answer:
Peroxides have a weak oxygen-oxygen bond which on heating results in homolytic fragmentation of this bond i.e. the bond breaks in order to leave one unpaired electron on each atom involved in the reaction. Strong sources of light such as floodlight or other source of light radiation which reaches into the near UV might also serve to weaken this bond.
Only a catalytic amount of peroxide is needed to get the reaction started, although one molar equivalent of HBr is essentially required to result in complete addition of HBr to the alkene.
This results in a highly reactive alkoxy radical which then abstracts hydrogen from H-Br, releasing a bromine radical. The bromine radical is the one that is added to the alkene from the molecule hydrogen bromide.
Preferably addition to an alkene tends to occur in such a way that the most stable free radical is formed, tertiary radical here in HBr. That’s the reason that bromine ends up on the least substituted carbon of the alkene. This tertiary radical then eliminates hydrogen from H-Br, liberating a bromine radical, and this way the cycle continues.
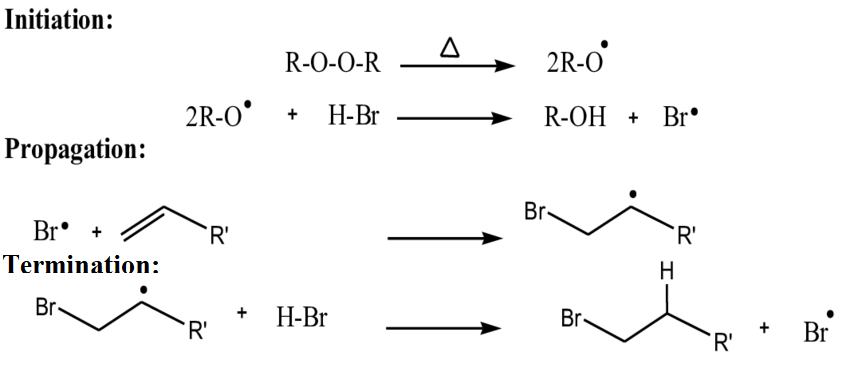
Hence, the correct option is (C).
Note: In absence of peroxide, if alkene reacts with hydrogen bromide, the attack of bromine is due to electrophilic addition reaction in which carbocation is formed as an intermediate. It is also called Markovnikov’s addition in which attack takes place on more substituted carbon.
Complete step-by-step answer:
Peroxides have a weak oxygen-oxygen bond which on heating results in homolytic fragmentation of this bond i.e. the bond breaks in order to leave one unpaired electron on each atom involved in the reaction. Strong sources of light such as floodlight or other source of light radiation which reaches into the near UV might also serve to weaken this bond.
Only a catalytic amount of peroxide is needed to get the reaction started, although one molar equivalent of HBr is essentially required to result in complete addition of HBr to the alkene.
This results in a highly reactive alkoxy radical which then abstracts hydrogen from H-Br, releasing a bromine radical. The bromine radical is the one that is added to the alkene from the molecule hydrogen bromide.
Preferably addition to an alkene tends to occur in such a way that the most stable free radical is formed, tertiary radical here in HBr. That’s the reason that bromine ends up on the least substituted carbon of the alkene. This tertiary radical then eliminates hydrogen from H-Br, liberating a bromine radical, and this way the cycle continues.

Hence, the correct option is (C).
Note: In absence of peroxide, if alkene reacts with hydrogen bromide, the attack of bromine is due to electrophilic addition reaction in which carbocation is formed as an intermediate. It is also called Markovnikov’s addition in which attack takes place on more substituted carbon.
Recently Updated Pages
Know The Difference Between Fluid And Liquid

Difference Between Crystalline and Amorphous Solid: Table & Examples

Types of Solutions in Chemistry: Explained Simply

Hess Law of Constant Heat Summation: Definition, Formula & Applications

Disproportionation Reaction: Definition, Example & JEE Guide

JEE Extractive Metallurgy Important Concepts and Tips for Exam Preparation

Trending doubts
JEE Main 2026: Session 1 Results Out and Session 2 Registration Open, City Intimation Slip, Exam Dates, Syllabus & Eligibility

Ideal and Non-Ideal Solutions Explained for Class 12 Chemistry

JEE Main Participating Colleges 2026 - A Complete List of Top Colleges

Clemmensen and Wolff Kishner Reductions Explained for JEE & NEET

Degree of Dissociation: Meaning, Formula, Calculation & Uses

Understanding the Angle of Deviation in a Prism

Other Pages
JEE Advanced Marks vs Ranks 2025: Understanding Category-wise Qualifying Marks and Previous Year Cut-offs

JEE Advanced 2026 - Exam Date (Released), Syllabus, Registration, Eligibility, Preparation, and More

CBSE Notes Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 9 - Hydrocarbons - 2025-26

CBSE Notes Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 5 - Thermodynamics - 2025-26

CBSE Notes Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 6 - Equilibrium - 2025-26

Inductive Effect and Its Role in Acidic Strength




