
Sodium or potassium salts of higher fatty acids are called [MP PET $2003$]
A.Soaps
B.Terpenes
C.Sugars
D.Alkaloids
Answer
233.1k+ views
Hint: Fatty acids are the building blocks of fats in our body system, consisting of long chains of lipid-carboxylic acid found in oils and fats and also in cell membranes as the major component of glycolipids and phospholipids. Salts of fatty acids such as sodium or potassium salts of fatty acids can be used as surface active reagents.
Complete answer:Fats are triglycerides of higher-order fatty acids such as oleic acid, stearic acid, palmitic acid, etc. We can use the sodium or potassium salts of fatty acids as surface active agents or surfactants.
Surface active agents or surfactants are chemical substances that concentrate at the surface of the solution and form surface films hence they reduce the surface tension of the solution. Thereby it helps in removing dirt and dust.
Normal water does not remove dirt from skin and clothes as dirt is oily or greasy in nature. Hence sodium or potassium salts of higher fatty acids or soaps that are water-soluble are able to remove this dirt from water. When a dirty cloth is kept in a soap solution, the long non-polar hydrocarbon tail of soap molecules directs towards the oily dirt particles whereas polar heads are directed towards the water. Therefore forms spherical micelles which are attracted to water and carry dirt particles along with them. In this way, surfactants remove dirt from clothes.
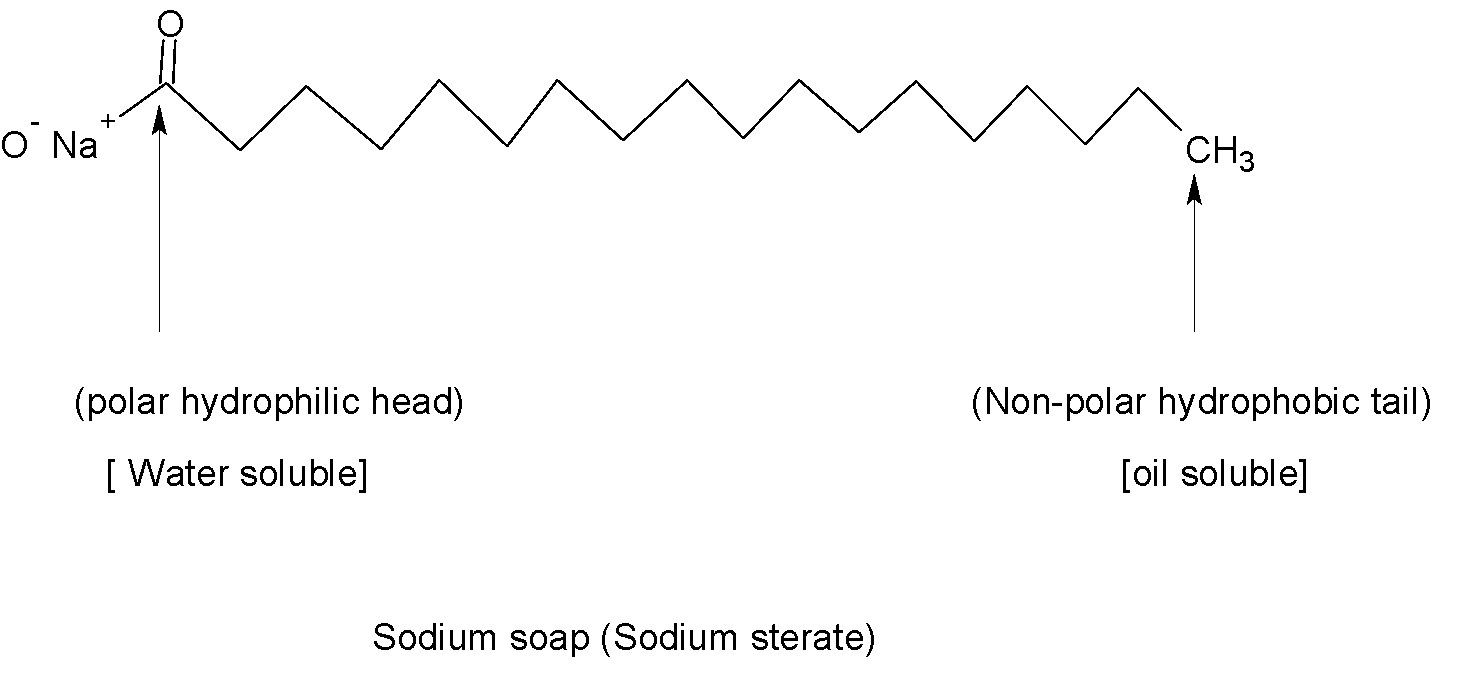
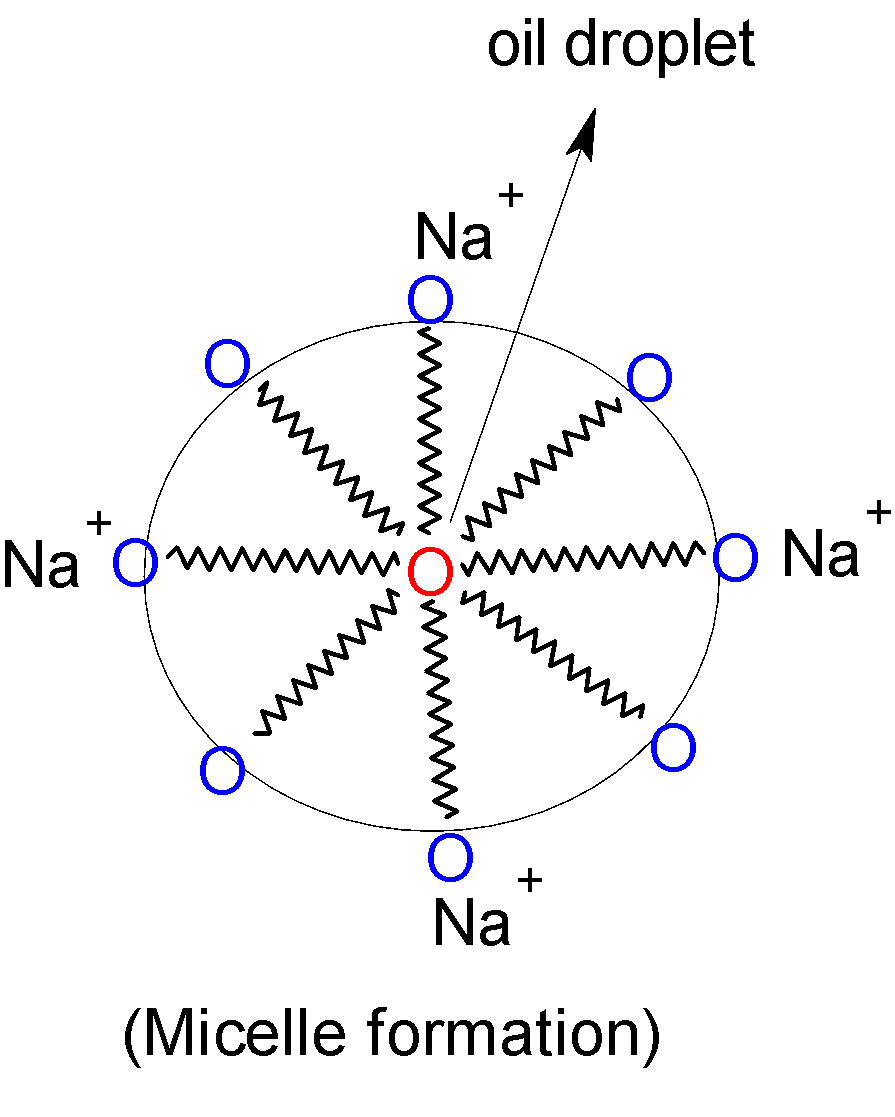
Therefore sodium or potassium salts of higher fatty acids are called soaps.
Thus, option (A) is correct.
Note: Potassium soaps are more soluble as compared to sodium salts. That’s why sodium soaps are used to make bar soap while potassium soaps are used to make liquid soap, shaving cream, etc. Because potassium soaps are softer and more water soluble than sodium soaps.
Complete answer:Fats are triglycerides of higher-order fatty acids such as oleic acid, stearic acid, palmitic acid, etc. We can use the sodium or potassium salts of fatty acids as surface active agents or surfactants.
Surface active agents or surfactants are chemical substances that concentrate at the surface of the solution and form surface films hence they reduce the surface tension of the solution. Thereby it helps in removing dirt and dust.
Normal water does not remove dirt from skin and clothes as dirt is oily or greasy in nature. Hence sodium or potassium salts of higher fatty acids or soaps that are water-soluble are able to remove this dirt from water. When a dirty cloth is kept in a soap solution, the long non-polar hydrocarbon tail of soap molecules directs towards the oily dirt particles whereas polar heads are directed towards the water. Therefore forms spherical micelles which are attracted to water and carry dirt particles along with them. In this way, surfactants remove dirt from clothes.


Therefore sodium or potassium salts of higher fatty acids are called soaps.
Thus, option (A) is correct.
Note: Potassium soaps are more soluble as compared to sodium salts. That’s why sodium soaps are used to make bar soap while potassium soaps are used to make liquid soap, shaving cream, etc. Because potassium soaps are softer and more water soluble than sodium soaps.
Recently Updated Pages
JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 (January 31 Evening Shift) Question Paper with Solutions [PDF]

JEE Main 2023 January 30 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 25 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 24 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

Trending doubts
JEE Main 2026: Session 2 Registration Open, City Intimation Slip, Exam Dates, Syllabus & Eligibility

JEE Main 2026 Application Login: Direct Link, Registration, Form Fill, and Steps

Understanding the Angle of Deviation in a Prism

Hybridisation in Chemistry – Concept, Types & Applications

How to Convert a Galvanometer into an Ammeter or Voltmeter

Understanding the Electric Field of a Uniformly Charged Ring

Other Pages
JEE Advanced Marks vs Ranks 2025: Understanding Category-wise Qualifying Marks and Previous Year Cut-offs

NCERT Solutions For Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 1 Solutions (2025-26)

Solutions Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 1 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

NCERT Solutions For Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 4 The d and f Block Elements (2025-26)

Biomolecules Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 10 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

NCERT Solutions For Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 10 Biomolecules (2025-26)




