
Salicylic acid can be prepared using Reimer - Tiemann’s reaction by treating phenol with:
A. Methyl chloride in the presence of anhydrous aluminium chloride
B. Carbon dioxide under pressure in sodium hydroxide solution
C. Carbon tetrachloride and concentrated sodium hydroxide
D. Sodium nitrite and a few drops of concentrated sulphuric acid
Answer
240.6k+ views
Hint: The Riemer-Tiemann reaction involves the ortho-formylation of phenol. In essence, it is a nucleophilic substitution reaction.
Complete Step by Step Solution:
The Riemer-Tiemann reaction is used for the ortho-formylation of phenols using a strong base in the presence of carbon tetrachloride (\[CC{l_4}\]). The strong base most commonly used is concentrated sodium hydroxide (\[NaOH\]) or potassium hydroxide (\[KOH\]).
While phenol is soluble in carbon tetrachloride, the hydroxide base is not. Therefore, this reaction is generally carried out in a solvent system that has two phases (biphasic). In its simplest case, the biphasic system consists of an aqueous phase containing the hydroxide base and an organic phase containing the carbon tetrachloride and phenol. The two phases are brought together (by rapid mixing or by using phase transfer catalysts) and heated to initiate the reaction. Although heating is required to start the reaction, once it is underway the reaction itself becomes highly exothermic.
The Riemer-Tiemann reaction of phenol with\[CC{l_4}\]and concentrated sodium hydroxide leads to the formation of salicylic acid as the product.
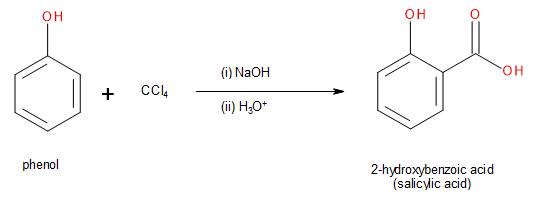
Image: Conversion of phenol into salicylic acid through Riemer-Tiemann reaction
Thus, the correct option is C.
Note: Although the reaction discussed above is termed as a Riemer-Tiemann reaction, it is a variation of it. The actual Reimer-Tiemann reaction consists of the reaction of phenol with chloroform (\[CHC{l_3}\]) and a strong hydroxide base to form salicylaldehyde as shown below.
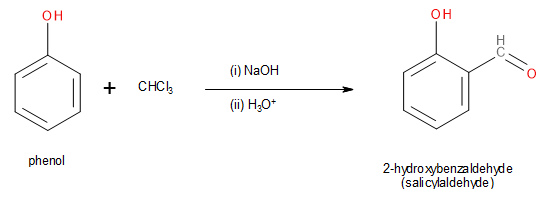
Image: Riemer-Tiemann reaction of phenol.
Complete Step by Step Solution:
The Riemer-Tiemann reaction is used for the ortho-formylation of phenols using a strong base in the presence of carbon tetrachloride (\[CC{l_4}\]). The strong base most commonly used is concentrated sodium hydroxide (\[NaOH\]) or potassium hydroxide (\[KOH\]).
While phenol is soluble in carbon tetrachloride, the hydroxide base is not. Therefore, this reaction is generally carried out in a solvent system that has two phases (biphasic). In its simplest case, the biphasic system consists of an aqueous phase containing the hydroxide base and an organic phase containing the carbon tetrachloride and phenol. The two phases are brought together (by rapid mixing or by using phase transfer catalysts) and heated to initiate the reaction. Although heating is required to start the reaction, once it is underway the reaction itself becomes highly exothermic.
The Riemer-Tiemann reaction of phenol with\[CC{l_4}\]and concentrated sodium hydroxide leads to the formation of salicylic acid as the product.

Image: Conversion of phenol into salicylic acid through Riemer-Tiemann reaction
Thus, the correct option is C.
Note: Although the reaction discussed above is termed as a Riemer-Tiemann reaction, it is a variation of it. The actual Reimer-Tiemann reaction consists of the reaction of phenol with chloroform (\[CHC{l_3}\]) and a strong hydroxide base to form salicylaldehyde as shown below.

Image: Riemer-Tiemann reaction of phenol.
Recently Updated Pages
Types of Solutions in Chemistry: Explained Simply

JEE Main Mock Test 2025-26: Principles Related To Practical

JEE Main 2025-26 Organic Compounds Containing Nitrogen Mock Test

JEE Main 2025-26 Mock Test: Organic Compounds Containing Oxygen

JEE Main 2025-26 Redox Reactions & Electro Mock Test

JEE Main Solutions Mock Test 1-2 (2025-26): Free Practice & Answers

Trending doubts
JEE Main 2026: Session 1 Results Out and Session 2 Registration Open, City Intimation Slip, Exam Dates, Syllabus & Eligibility

Ideal and Non-Ideal Solutions Explained for Class 12 Chemistry

JEE Main Participating Colleges 2026 - A Complete List of Top Colleges

Clemmensen and Wolff Kishner Reductions Explained for JEE & NEET

Degree of Dissociation: Meaning, Formula, Calculation & Uses

Understanding the Angle of Deviation in a Prism

Other Pages
NCERT Solutions For Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 10 Biomolecules - 2025-26

NCERT Solutions For Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 4 The D And F Block Elements - 2025-26

JEE Advanced Marks vs Ranks 2025: Understanding Category-wise Qualifying Marks and Previous Year Cut-offs

NCERT Solutions For Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 2 Electrochemistry - 2025-26

JEE Advanced 2026 - Exam Date (Released), Syllabus, Registration, Eligibility, Preparation, and More

NCERT Solutions For Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 1 Solutions - 2025-26




