
Reagent ${{R}_{1}}$ and ${{R}_{2}}$ are:
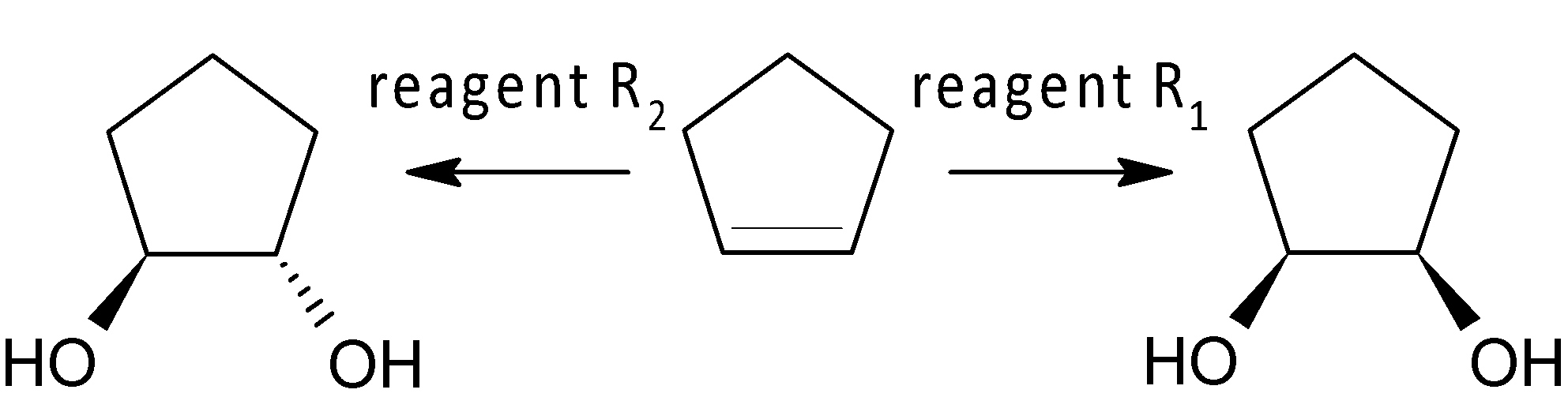
A. cold alkaline $\text{KMn}{{\text{O}}_{\text{4}}}$,$\text{Os}{{\text{O}}_{\text{4}}}\text{/}{{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}{{\text{O}}_{\text{2}}}$
B. cold alkaline $\text{KMn}{{\text{O}}_{\text{4}}}$,$HC{{O}_{3}}H$
C. cold alkaline $\text{KMn}{{\text{O}}_{\text{4}}}$,$\text{C}{{\text{H}}_{\text{3}}}\text{-O-O-C}{{\text{H}}_{\text{3}}}$
D. ${{\text{C}}_{\text{6}}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{5}}}\text{C}{{\text{O}}_{\text{3}}}\text{H}$ ,$HC{{O}_{3}}H$
Answer
233.1k+ views
Hint: This hydroxylation process of alkene occurs through two ways: syn-dihydroxylation (cis-diol) and trans-dihydroxylation (trans-diol). Potassium permanganate $(KMn{{O}_{4}})$ and osmium tetraoxide ($OS{{O}_{4}}$) are reagents to produce cis-diol whereas peroxy acid is used to synthesize trans-diol.
Complete step by step solution:
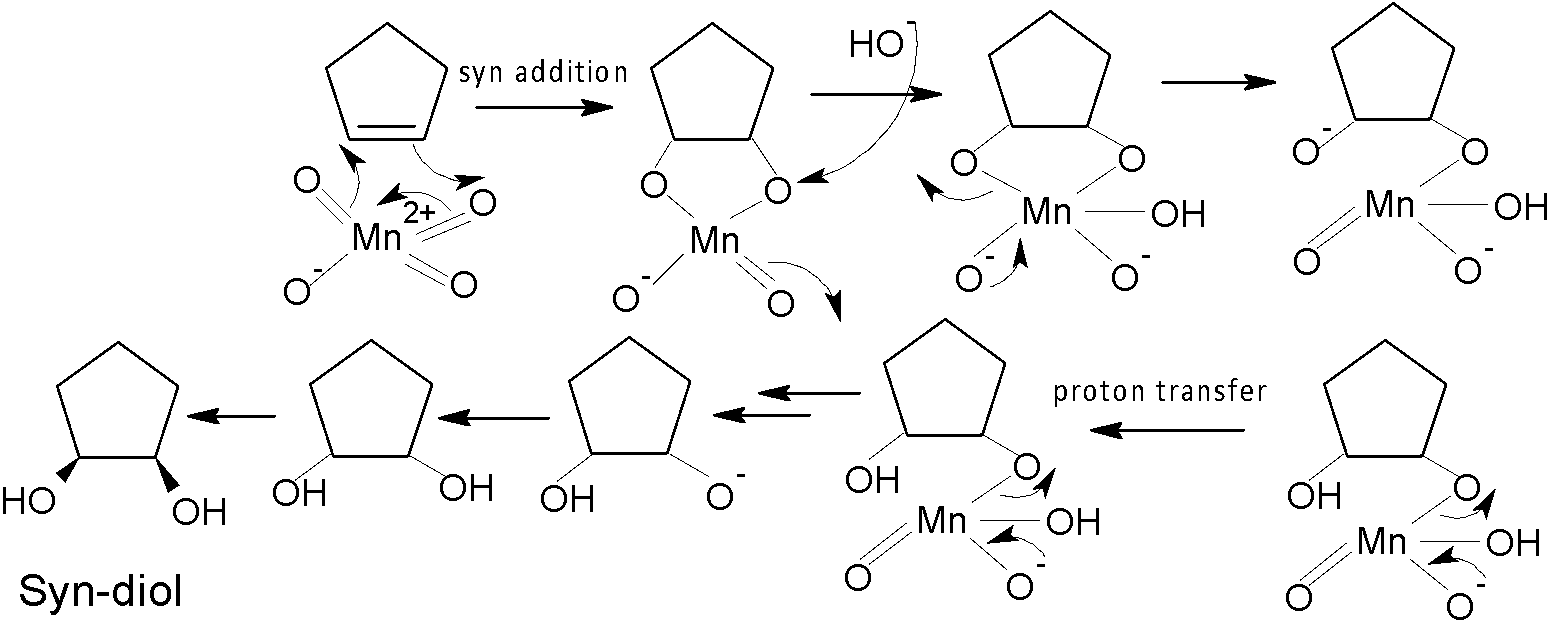
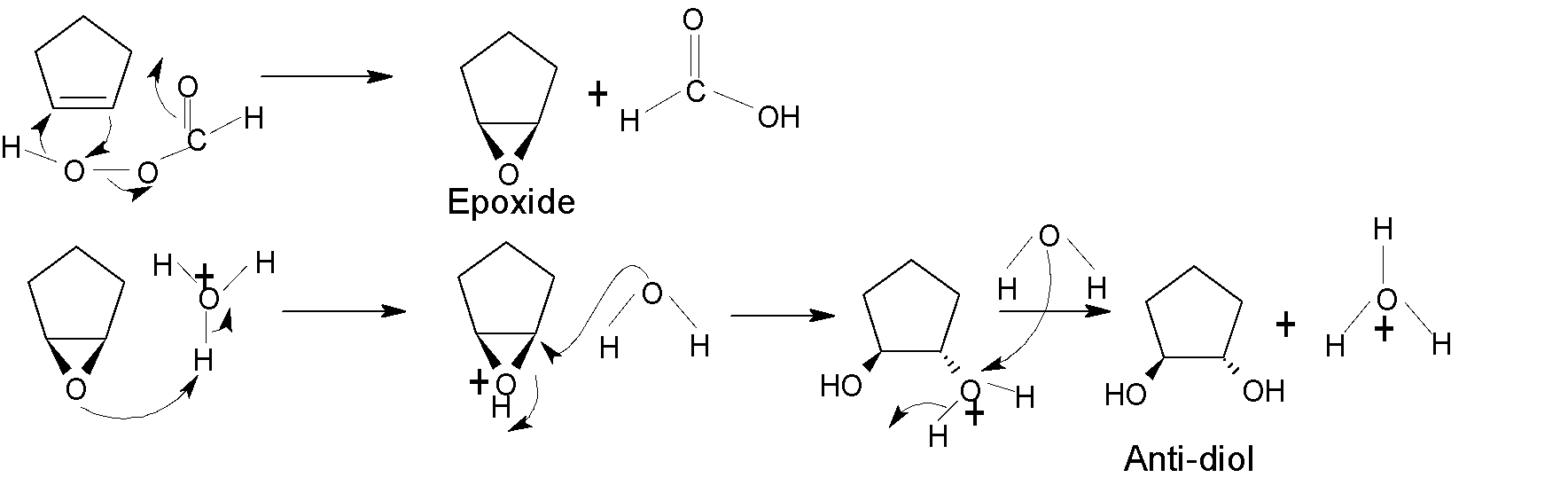
The hydroxylation of alkene happens by adding one $-OH$ group to each of the two carbon atoms of the alkene compound. For the syn-hydroxylation of alkene, cold alkaline $KMn{{O}_{4}}$ and $OS{{O}_{4}}$ oxidising reagent are used in the presence of a basic solution. $OS{{O}_{4}}$is used in a catalytic amount, as ${{H}_{2}}{{O}_{2}}$ reoxidizes the $OS{{O}_{2}}$ return to its original state. Whereas anti-diol is produced by peroxy acid via epoxide formation.
Here ${{R}_{1}}$is used to synthesise syn-diol, whereas the reagent ${{R}_{2}}$is used to produce trans-diol. As we know, cold alkaline $KMn{{O}_{4}}$ is an oxidising reagent that converts alkene to syn-diol. So, ${{R}_{1}}$ would be cold alkaline $KMn{{O}_{4}}$ according to the given option. The mechanism is shown below:
For anti-diol, peroxy acid is the required oxidising reagent.
Mechanism:
In option (A), both the reagents are used to convert alkene to syn-diol.
In option (C), dimethyl peroxide $(C{{H}_{3}}-O-O-C{{H}_{3}})$ can not be used to form anti-diol.
In option (D) both the reagents are used for the synthesis of anti-diol.
So, option (B) is the correct one, whereas reagents ${{\text{R}}_{\text{1}}}\text{and}{{\text{R}}_{\text{2}}}$are cold alkaline $KMn{{O}_{4}}$and $HC{{O}_{3}}H$ respectively.
Thus, the Option (B) is correct.
Note: Osmium hydroxide is very toxic that’s why a catalytic amount $OS{{O}_{4}}$is used with oxidising ${{H}_{2}}{{O}_{2}}$ . It removes some hazards from the system, back to the initial oxidising state $OS{{O}_{4}}$. Because of over oxidation and low yield now $KMn{{O}_{4}}$is not used popularly. $OS{{O}_{4}}$is used instead of $KMn{{O}_{4}}$.
Complete step by step solution:
The hydroxylation of alkene happens by adding one $-OH$ group to each of the two carbon atoms of the alkene compound. For the syn-hydroxylation of alkene, cold alkaline $KMn{{O}_{4}}$ and $OS{{O}_{4}}$ oxidising reagent are used in the presence of a basic solution. $OS{{O}_{4}}$is used in a catalytic amount, as ${{H}_{2}}{{O}_{2}}$ reoxidizes the $OS{{O}_{2}}$ return to its original state. Whereas anti-diol is produced by peroxy acid via epoxide formation.
Here ${{R}_{1}}$is used to synthesise syn-diol, whereas the reagent ${{R}_{2}}$is used to produce trans-diol. As we know, cold alkaline $KMn{{O}_{4}}$ is an oxidising reagent that converts alkene to syn-diol. So, ${{R}_{1}}$ would be cold alkaline $KMn{{O}_{4}}$ according to the given option. The mechanism is shown below:

For anti-diol, peroxy acid is the required oxidising reagent.
Mechanism:

In option (A), both the reagents are used to convert alkene to syn-diol.
In option (C), dimethyl peroxide $(C{{H}_{3}}-O-O-C{{H}_{3}})$ can not be used to form anti-diol.
In option (D) both the reagents are used for the synthesis of anti-diol.
So, option (B) is the correct one, whereas reagents ${{\text{R}}_{\text{1}}}\text{and}{{\text{R}}_{\text{2}}}$are cold alkaline $KMn{{O}_{4}}$and $HC{{O}_{3}}H$ respectively.
Thus, the Option (B) is correct.
Note: Osmium hydroxide is very toxic that’s why a catalytic amount $OS{{O}_{4}}$is used with oxidising ${{H}_{2}}{{O}_{2}}$ . It removes some hazards from the system, back to the initial oxidising state $OS{{O}_{4}}$. Because of over oxidation and low yield now $KMn{{O}_{4}}$is not used popularly. $OS{{O}_{4}}$is used instead of $KMn{{O}_{4}}$.
Recently Updated Pages
JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 (January 31 Evening Shift) Question Paper with Solutions [PDF]

JEE Main 2023 January 30 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 25 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 24 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

Trending doubts
JEE Main 2026: Session 2 Registration Open, City Intimation Slip, Exam Dates, Syllabus & Eligibility

JEE Main 2026 Application Login: Direct Link, Registration, Form Fill, and Steps

JEE Main Marking Scheme 2026- Paper-Wise Marks Distribution and Negative Marking Details

Understanding the Angle of Deviation in a Prism

Hybridisation in Chemistry – Concept, Types & Applications

How to Convert a Galvanometer into an Ammeter or Voltmeter

Other Pages
JEE Advanced Marks vs Ranks 2025: Understanding Category-wise Qualifying Marks and Previous Year Cut-offs

NCERT Solutions For Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 1 Solutions (2025-26)

Solutions Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 1 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

NCERT Solutions For Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 4 The d and f Block Elements (2025-26)

Biomolecules Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 10 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

NCERT Solutions For Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 10 Biomolecules (2025-26)




