
Rainbow appears due to dispersion of sunlight by __________.
(A) Water droplets
(B) Prism
(C) Glass Block
(D) All
Answer
240k+ views
Hint To find the correct answer, you firstly need to know that rainbow is a naturally occurring phenomenon and why and how it is produced. Also, as the name suggests, rainbow has a close correlation with the rain as rainbow is produced after the rain has stopped and there is still moisture in the air.
Complete step by step answer
As mentioned in the hint section of the solution, to solve the question, you first need to have a basic understanding about the rainbow. Let us share some information about rainbow first:
Rainbows are formed by a combination of refraction and reflection. You may have noticed that you see a rainbow only when you look away from the sun. It is so as the light from the sun enters a drop of water and is reflected from the back of the drop, as shown in the image. This is the only time when reflection happens in the whole process. As for refraction of the sunlight, the light rays from the sun are refracted both as they enter and as they leave the drop. Since the index of refraction of water varies with wavelength, the light is dispersed, and a rainbow is observed. Keep in mind that there is no dispersion caused by reflection at the back surface, since the law of reflection does not depend on wavelength. The actual rainbow of colors seen by an observer depends on the myriad of rays being refracted and reflected toward the observer’s eyes from numerous drops of water.
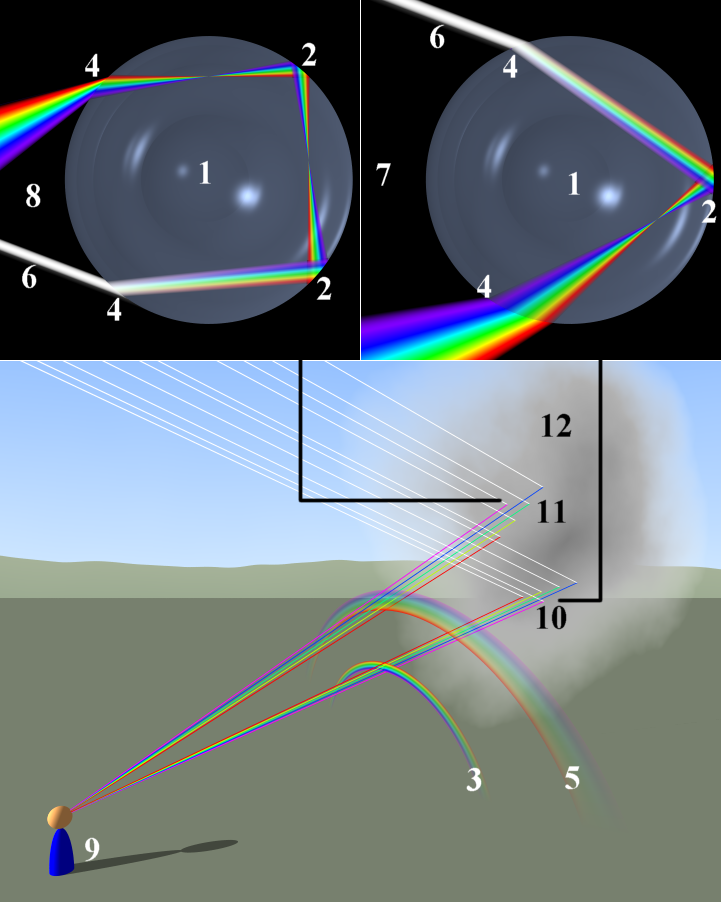
As we have described about the rainbow, it must be clear that the rainbow appears due to the dispersion of sunlight by water droplets that are present in the air due to the rain.
Hence, the correct option is option (A).
Note It should be noted that even though the VIBGYOR effect of white light or sun rays can be observed in a lab through the help of a prism, it would not be considered a rainbow since rainbow is a naturally occurring phenomenon and only the one due to the dispersion of light rays from water droplets is referred to as the rainbow.
Complete step by step answer
As mentioned in the hint section of the solution, to solve the question, you first need to have a basic understanding about the rainbow. Let us share some information about rainbow first:
Rainbows are formed by a combination of refraction and reflection. You may have noticed that you see a rainbow only when you look away from the sun. It is so as the light from the sun enters a drop of water and is reflected from the back of the drop, as shown in the image. This is the only time when reflection happens in the whole process. As for refraction of the sunlight, the light rays from the sun are refracted both as they enter and as they leave the drop. Since the index of refraction of water varies with wavelength, the light is dispersed, and a rainbow is observed. Keep in mind that there is no dispersion caused by reflection at the back surface, since the law of reflection does not depend on wavelength. The actual rainbow of colors seen by an observer depends on the myriad of rays being refracted and reflected toward the observer’s eyes from numerous drops of water.

As we have described about the rainbow, it must be clear that the rainbow appears due to the dispersion of sunlight by water droplets that are present in the air due to the rain.
Hence, the correct option is option (A).
Note It should be noted that even though the VIBGYOR effect of white light or sun rays can be observed in a lab through the help of a prism, it would not be considered a rainbow since rainbow is a naturally occurring phenomenon and only the one due to the dispersion of light rays from water droplets is referred to as the rainbow.
Recently Updated Pages
Dimensions of Charge: Dimensional Formula, Derivation, SI Units & Examples

How to Calculate Moment of Inertia: Step-by-Step Guide & Formulas

Circuit Switching vs Packet Switching: Key Differences Explained

Dimensions of Pressure in Physics: Formula, Derivation & SI Unit

JEE Extractive Metallurgy Important Concepts and Tips for Exam Preparation

JEE General Topics in Chemistry Important Concepts and Tips

Trending doubts
JEE Main 2026: Session 1 Results Out and Session 2 Registration Open, City Intimation Slip, Exam Dates, Syllabus & Eligibility

Ideal and Non-Ideal Solutions Explained for Class 12 Chemistry

JEE Main Participating Colleges 2026 - A Complete List of Top Colleges

Understanding the Angle of Deviation in a Prism

Hybridisation in Chemistry – Concept, Types & Applications

Understanding the Electric Field of a Uniformly Charged Ring

Other Pages
JEE Advanced Marks vs Ranks 2025: Understanding Category-wise Qualifying Marks and Previous Year Cut-offs

JEE Advanced 2026 - Exam Date (Released), Syllabus, Registration, Eligibility, Preparation, and More

CBSE Notes Class 11 Physics Chapter 4 - Laws of Motion - 2025-26

CBSE Notes Class 11 Physics Chapter 14 - Waves - 2025-26

CBSE Notes Class 11 Physics Chapter 9 - Mechanical Properties of Fluids - 2025-26

CBSE Notes Class 11 Physics Chapter 11 - Thermodynamics - 2025-26




