
\[R - NH - COH\, \overset{POCl_{3},Pyridine}{\rightarrow} \, Product\]
In the given reaction what will be the product?
A. \[R - N = C = O\]
B. \[R - \mathop N\limits^ + \equiv \mathop C\limits^ - \]
C. \[R - C \equiv N\]
D. None of the above
Answer
233.1k+ views
Hint: Reaction of amides with \[POC{l_3}\] i.e., phosphorus oxychloride gives nitriles. This is a dehydration reaction as net elimination is of water. Pyridine is a basic solvent used as a solvent in this reaction.
Complete Step by Step Solution:
In this reaction, \[POC{l_3}\] is a dehydrating agent and pyridine is used as a solvent.
The mechanism of the dehydration with phosphorus oxychloride is as follows:
There is lone pair present in the Nitrogen of amide bond of reactant which is delocalized in the amide group and the negative generates on the oxygen of amide group which attacks the phosphorus of \[POC{l_3}\]as phosphorus has empty d-orbitals, then the compound forms which has a positive charge on nitrogen. To neutralise the charge, hydrogen from the nitrogen of the compound gets removed. Then a lone pair of nitrogen is again delocalized to form a triple bond between nitrogen and carbon which results in cleavage of carbon and oxygen bond as carbon valency is four. Now the resultant \[R - \mathop N\limits^ + \equiv C - H\] has acidic proton which will get removed to give the final product \[R - \mathop N\limits^ + \equiv \mathop C\limits^ - \].
The reaction of a compound having an amide functional group with \[POC{l_3}\] and pyridine gives \[R - \mathop N\limits^ + \equiv \mathop C\limits^ - \] product which is option B by the process called dehydration.
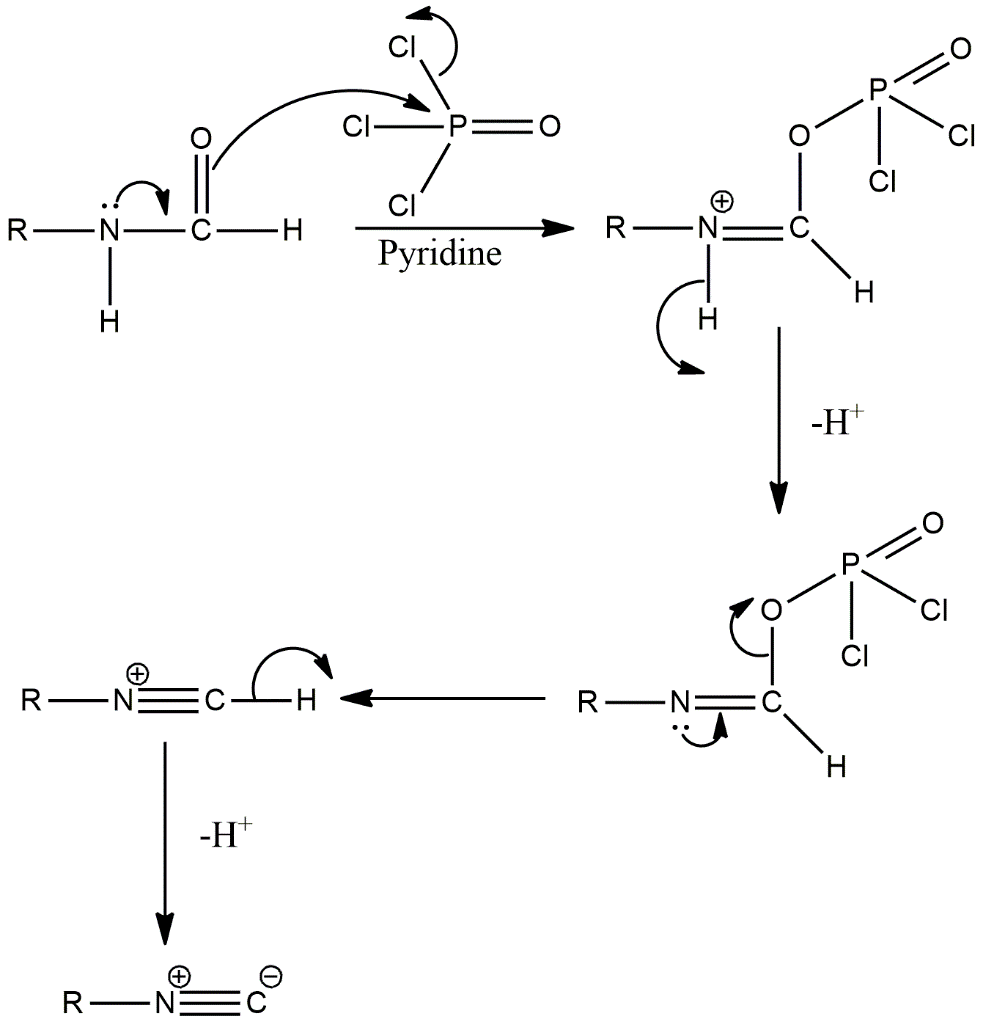
Image: Reaction of a compound containing amide bond with phosphorus oxychloride
So, option B is correct.
Note: Phosphorus is from the third period of the p-block element, that’s why it has empty d -orbitals to accept electrons from the surrounding element. Carbon has four valencies, so to maintain its stability, it cleaves the bond with oxygen as \[C - O\]bond is more polar than\[C - H\].
Complete Step by Step Solution:
In this reaction, \[POC{l_3}\] is a dehydrating agent and pyridine is used as a solvent.
The mechanism of the dehydration with phosphorus oxychloride is as follows:
There is lone pair present in the Nitrogen of amide bond of reactant which is delocalized in the amide group and the negative generates on the oxygen of amide group which attacks the phosphorus of \[POC{l_3}\]as phosphorus has empty d-orbitals, then the compound forms which has a positive charge on nitrogen. To neutralise the charge, hydrogen from the nitrogen of the compound gets removed. Then a lone pair of nitrogen is again delocalized to form a triple bond between nitrogen and carbon which results in cleavage of carbon and oxygen bond as carbon valency is four. Now the resultant \[R - \mathop N\limits^ + \equiv C - H\] has acidic proton which will get removed to give the final product \[R - \mathop N\limits^ + \equiv \mathop C\limits^ - \].
The reaction of a compound having an amide functional group with \[POC{l_3}\] and pyridine gives \[R - \mathop N\limits^ + \equiv \mathop C\limits^ - \] product which is option B by the process called dehydration.

Image: Reaction of a compound containing amide bond with phosphorus oxychloride
So, option B is correct.
Note: Phosphorus is from the third period of the p-block element, that’s why it has empty d -orbitals to accept electrons from the surrounding element. Carbon has four valencies, so to maintain its stability, it cleaves the bond with oxygen as \[C - O\]bond is more polar than\[C - H\].
Recently Updated Pages
JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 (January 31 Evening Shift) Question Paper with Solutions [PDF]

JEE Main 2023 January 30 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 25 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 24 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

Trending doubts
JEE Main 2026: Session 2 Registration Open, City Intimation Slip, Exam Dates, Syllabus & Eligibility

JEE Main 2026 Application Login: Direct Link, Registration, Form Fill, and Steps

JEE Main Marking Scheme 2026- Paper-Wise Marks Distribution and Negative Marking Details

Understanding the Angle of Deviation in a Prism

Hybridisation in Chemistry – Concept, Types & Applications

How to Convert a Galvanometer into an Ammeter or Voltmeter

Other Pages
JEE Advanced Marks vs Ranks 2025: Understanding Category-wise Qualifying Marks and Previous Year Cut-offs

NCERT Solutions For Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 1 Solutions (2025-26)

Solutions Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 1 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

NCERT Solutions For Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 4 The d and f Block Elements (2025-26)

Biomolecules Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 10 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

NCERT Solutions For Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 10 Biomolecules (2025-26)




