
PVC is obtained from vinyl chloride by a reaction called
A. Addition
B. Isomerization
C. Polymerization
D. Substitution
Answer
241.5k+ views
Hint: Polyvinyl chloride abbreviated as PVC is a widely manufactured synthetic polymer of plastic. It is a white, delicate solid. Polyvinyl chloride is produced by a combination of vinyl chloride.
Complete Step by Step Solution:
PVC is a thermoplastic.
Those plastics that deform on heating and can be bent easily are called thermoplastics.
Due to this, the heat strength of PVC is very low, and the addition of a heat stabilizer during the process is essential to secure the article's properties.
As a thermoplastic, PVC has good insulation properties.
PVC is utilized for generating pipes for public and industrial applications.
PVC fabric is water immune and utilized for its weather-protected qualities in suits, skiing equipment, shoes, jackets, aprons, and patches.
Polyvinyl chloride is produced by the polymerization of vinyl chloride.
Polymerization is defined as the procedure of reacting monomer molecules jointly in a chemical reaction to create polymer chains.
Vinyl chloride monomers and water are installed into the reactor along with a polymerization initiator and other additives.
The initiator is used to commence the reaction. The reaction is exothermic and therefore expects to cool.
The reaction happens as follows:
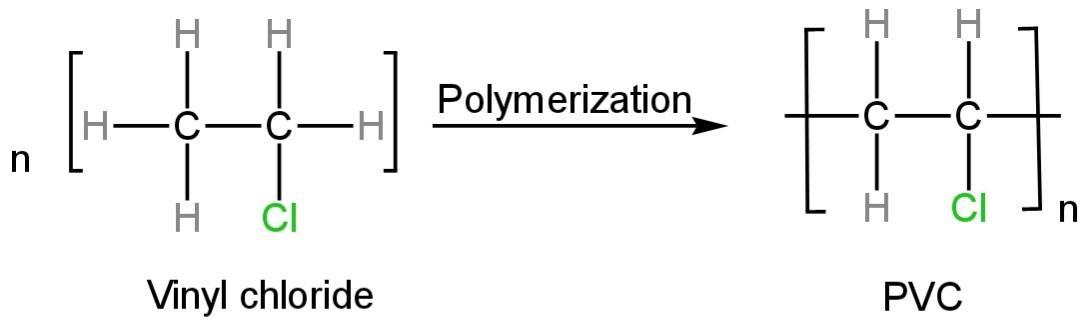
Image: Polymerization of vinyl chloride
So, PVC is obtained from vinyl chloride by a reaction called polymerization.
So, option C is correct.
Note: PVC has two main forms: rigid and flexible. The rigid structure of PVC is utilised in building for pipe and profile applications such as doors and windows. It is also utilised in generating plastic bottles, non-food packaging, food-covering sheets, and plastic cards.It can be rendered softer and more flexible by the addition of plasticizers like phthalate. In this form, it is also used in plumbing, electrical cable insulation, replica leather, flooring, signage, phonograph records, inflatable products, and many applications where it is used instead of rubber.
Complete Step by Step Solution:
PVC is a thermoplastic.
Those plastics that deform on heating and can be bent easily are called thermoplastics.
Due to this, the heat strength of PVC is very low, and the addition of a heat stabilizer during the process is essential to secure the article's properties.
As a thermoplastic, PVC has good insulation properties.
PVC is utilized for generating pipes for public and industrial applications.
PVC fabric is water immune and utilized for its weather-protected qualities in suits, skiing equipment, shoes, jackets, aprons, and patches.
Polyvinyl chloride is produced by the polymerization of vinyl chloride.
Polymerization is defined as the procedure of reacting monomer molecules jointly in a chemical reaction to create polymer chains.
Vinyl chloride monomers and water are installed into the reactor along with a polymerization initiator and other additives.
The initiator is used to commence the reaction. The reaction is exothermic and therefore expects to cool.
The reaction happens as follows:

Image: Polymerization of vinyl chloride
So, PVC is obtained from vinyl chloride by a reaction called polymerization.
So, option C is correct.
Note: PVC has two main forms: rigid and flexible. The rigid structure of PVC is utilised in building for pipe and profile applications such as doors and windows. It is also utilised in generating plastic bottles, non-food packaging, food-covering sheets, and plastic cards.It can be rendered softer and more flexible by the addition of plasticizers like phthalate. In this form, it is also used in plumbing, electrical cable insulation, replica leather, flooring, signage, phonograph records, inflatable products, and many applications where it is used instead of rubber.
Recently Updated Pages
Types of Solutions in Chemistry: Explained Simply

JEE Main Mock Test 2025-26: Principles Related To Practical

JEE Main 2025-26 Organic Compounds Containing Nitrogen Mock Test

JEE Main 2025-26 Mock Test: Organic Compounds Containing Oxygen

JEE Main 2025-26 Redox Reactions & Electro Mock Test

JEE Main Solutions Mock Test 1-2 (2025-26): Free Practice & Answers

Trending doubts
JEE Main 2026: Session 1 Results Out and Session 2 Registration Open, City Intimation Slip, Exam Dates, Syllabus & Eligibility

Ideal and Non-Ideal Solutions Explained for Class 12 Chemistry

JEE Main Participating Colleges 2026 - A Complete List of Top Colleges

Clemmensen and Wolff Kishner Reductions Explained for JEE & NEET

Degree of Dissociation: Meaning, Formula, Calculation & Uses

Understanding the Angle of Deviation in a Prism

Other Pages
CBSE Class 12 Chemistry Question Paper 2026 PDF Download (All Sets) with Answer Key

NCERT Solutions For Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 10 Biomolecules - 2025-26

NCERT Solutions For Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 4 The D And F Block Elements - 2025-26

JEE Advanced Marks vs Ranks 2025: Understanding Category-wise Qualifying Marks and Previous Year Cut-offs

NCERT Solutions For Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 2 Electrochemistry - 2025-26

JEE Advanced 2026 - Exam Date (Released), Syllabus, Registration, Eligibility, Preparation, and More




