
Propionamide on Hofmann degradation gives-
A. Methyl amine
B. Ethyl amine
C. Propyl amine
D. Ethyl cyanide
Answer
240.6k+ views
Hint: Propionamide is an amide compound with general formula \[RCON{H_2}\] . The compound formed has one less carbon atom than the amide.
Complete Step by Step Solution:
Hoffmann degradation reaction is a type of reaction where primary amide is converted to a primary amine. The reaction takes place in presence of a strong base which attacks the amide. The reaction takes place by heating the primary amide using a halogen mixture of chlorine or bromine, a strong base and water.
In this reaction, halogen mainly reacts with sodium hydroxide which forms sodium hypobromite which changes the primary amide into an isocyanate intermediate. Water attacks the isocyanate intermediate causing the proton transfer and resulting in the formation of ammonium cation. Due to the thermal condition, the carbon dioxide explodes and after quenching ammonium cation, a primary amine product is formed.
When propionamide is heated with bromine in presence of potassium hydroxide or when propionamide undergoes Hofmann degradation, the product formed is ethyl amine.
The Hoffman degradation reaction of propionamide is shown below.
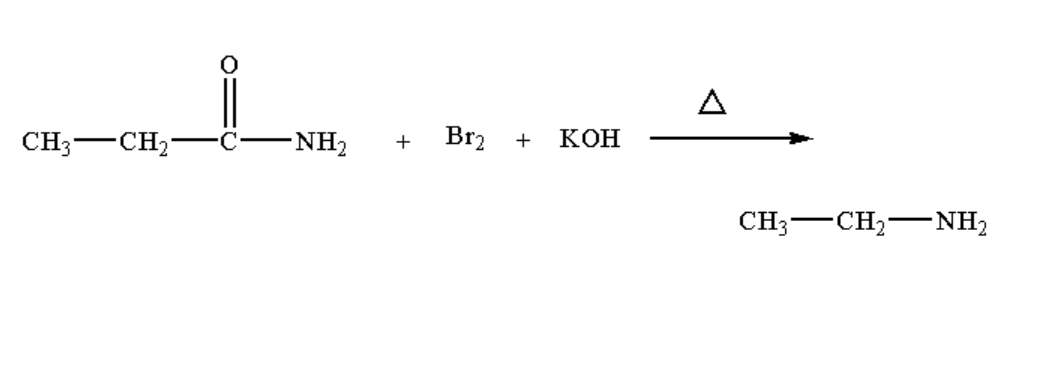
Image: Hofmann degradation reaction of propionamide
Therefore, the correct option is B.
Note: Hofmann degradation reaction is also termed as Hoffmann bromamide reaction. There is another term known as Hofmann elimination reaction in which tertiary amines and alkenes are formed as a product by reacting quaternary ammonium with methyl iodide and heating the compound formed with silver oxide and water.
The general reaction is shown below.
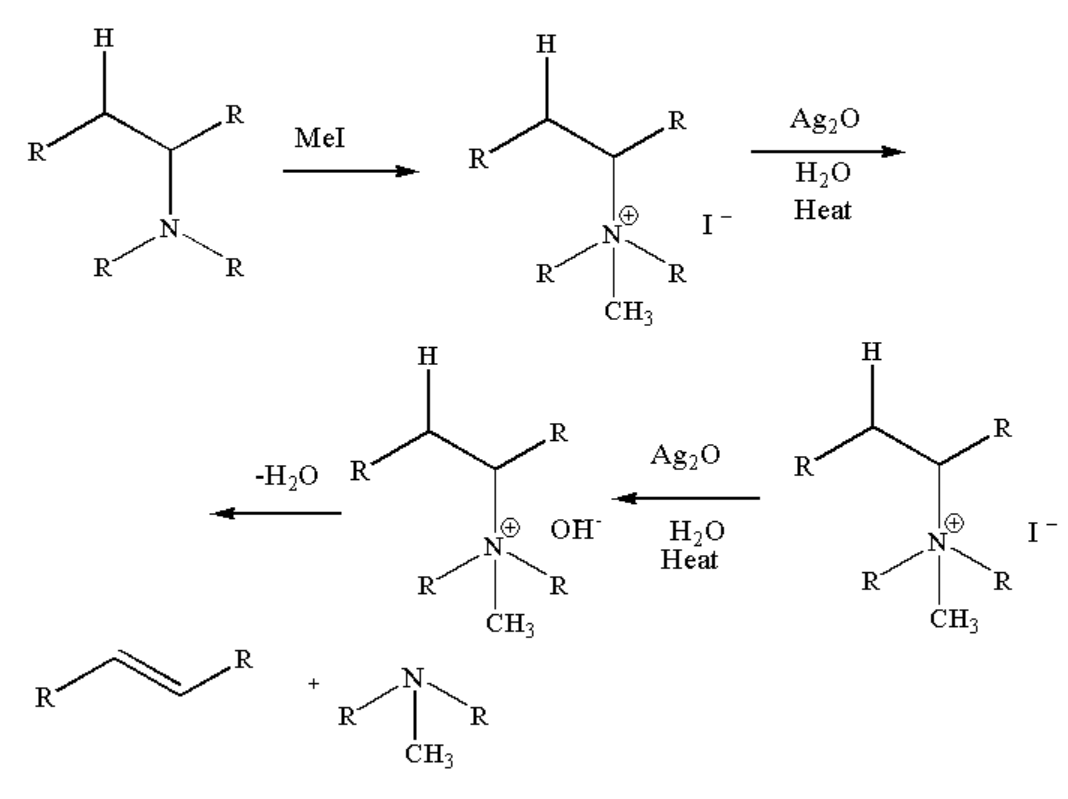
Image: Hofmann elimination reaction
Complete Step by Step Solution:
Hoffmann degradation reaction is a type of reaction where primary amide is converted to a primary amine. The reaction takes place in presence of a strong base which attacks the amide. The reaction takes place by heating the primary amide using a halogen mixture of chlorine or bromine, a strong base and water.
In this reaction, halogen mainly reacts with sodium hydroxide which forms sodium hypobromite which changes the primary amide into an isocyanate intermediate. Water attacks the isocyanate intermediate causing the proton transfer and resulting in the formation of ammonium cation. Due to the thermal condition, the carbon dioxide explodes and after quenching ammonium cation, a primary amine product is formed.
When propionamide is heated with bromine in presence of potassium hydroxide or when propionamide undergoes Hofmann degradation, the product formed is ethyl amine.
The Hoffman degradation reaction of propionamide is shown below.

Image: Hofmann degradation reaction of propionamide
Therefore, the correct option is B.
Note: Hofmann degradation reaction is also termed as Hoffmann bromamide reaction. There is another term known as Hofmann elimination reaction in which tertiary amines and alkenes are formed as a product by reacting quaternary ammonium with methyl iodide and heating the compound formed with silver oxide and water.
The general reaction is shown below.

Image: Hofmann elimination reaction
Recently Updated Pages
Types of Solutions in Chemistry: Explained Simply

JEE Main Mock Test 2025-26: Principles Related To Practical

JEE Main 2025-26 Organic Compounds Containing Nitrogen Mock Test

JEE Main 2025-26 Mock Test: Organic Compounds Containing Oxygen

JEE Main 2025-26 Redox Reactions & Electro Mock Test

JEE Main Solutions Mock Test 1-2 (2025-26): Free Practice & Answers

Trending doubts
JEE Main 2026: Session 1 Results Out and Session 2 Registration Open, City Intimation Slip, Exam Dates, Syllabus & Eligibility

Ideal and Non-Ideal Solutions Explained for Class 12 Chemistry

JEE Main Participating Colleges 2026 - A Complete List of Top Colleges

Clemmensen and Wolff Kishner Reductions Explained for JEE & NEET

Degree of Dissociation: Meaning, Formula, Calculation & Uses

Understanding the Angle of Deviation in a Prism

Other Pages
CBSE Class 12 Chemistry Question Paper 2026 PDF Download (All Sets) with Answer Key

NCERT Solutions For Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 10 Biomolecules - 2025-26

NCERT Solutions For Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 4 The D And F Block Elements - 2025-26

JEE Advanced Marks vs Ranks 2025: Understanding Category-wise Qualifying Marks and Previous Year Cut-offs

NCERT Solutions For Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 2 Electrochemistry - 2025-26

JEE Advanced 2026 - Exam Date (Released), Syllabus, Registration, Eligibility, Preparation, and More




