
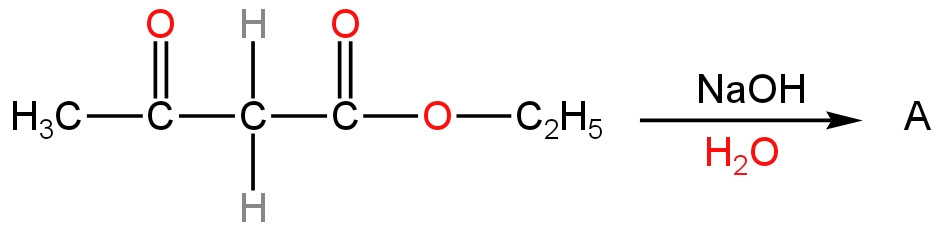
Product A in the reaction is
A. Acetic acid
B. Ethyl alcohol
C. Acetone
D. Propionaldehyde
Answer
233.1k+ views
Hint: Ester are sweet-smelling substances created by the reaction of carboxylic acid and alcohol. Ester on reaction with sodium hydroxide undergoes hydrolysis and forms carboxylate salt and alcohol.
Complete Step by Step Solution:
Esters are organic substances formed by the reaction of carboxylic acids and alcohols in the presence of a dehydrating agent like sulfuric acid. It undergoes hydrolysis to form alcohol and carboxylic acid or carboxylate salt. Hydrolysis is the combination of an organic compound with water by the breakdown of the organic compound.
In the given reaction, the given ester is ethyl acetoacetate or ethyl 3-oxobutanoate.
This compound undergoes hydrolysis in the presence of sodium hydroxide which is a base.
It is called the base hydrolysis of the ester.
Mechanism:
The hydroxide ion from sodium hydroxide attacks the electrophilic carbonyl carbon of the ester leading to the formation of a tetrahedral intermediate. Then the loss of the alkoxide ion takes place. Then acid-base equilibrium is formed. Alkoxide ions abstract a proton from the alcohol and carboxylate ions are formed.
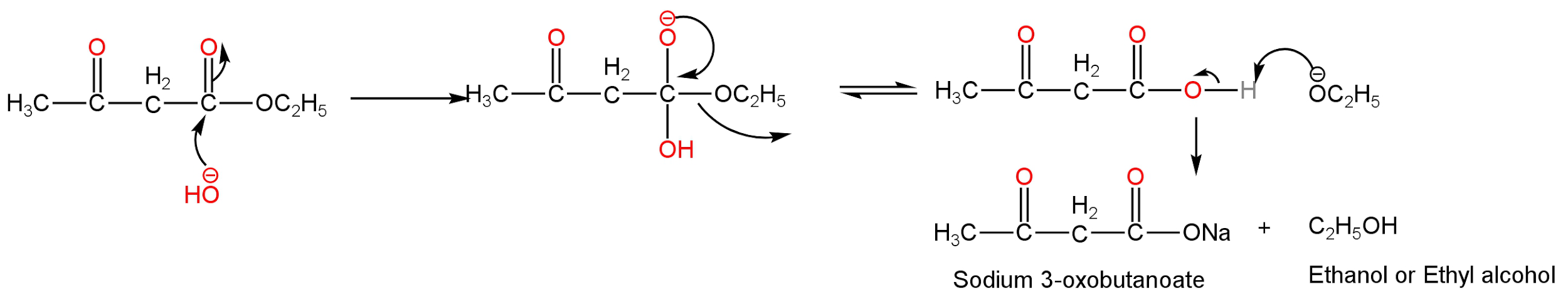
Image: Mechanism of base hydrolysis of ethyl acetoacetate.
Hence, ethyl acetoacetate undergoes hydrolysis in presence of sodium hydroxide to form sodium 3-oxo butanoate and ethyl alcohol.
So, option B is correct.
Note: In the given compound, we see that there are two carbonyl carbon but the hydroxide ion is nucleophilic hence attacking the electrophilic carbonyl carbon. The carbonyl carbon on the left-hand side has a methyl group attached to it which is an electron-releasing group decreasing the electrophilicity of the carbon.
Complete Step by Step Solution:
Esters are organic substances formed by the reaction of carboxylic acids and alcohols in the presence of a dehydrating agent like sulfuric acid. It undergoes hydrolysis to form alcohol and carboxylic acid or carboxylate salt. Hydrolysis is the combination of an organic compound with water by the breakdown of the organic compound.
In the given reaction, the given ester is ethyl acetoacetate or ethyl 3-oxobutanoate.
This compound undergoes hydrolysis in the presence of sodium hydroxide which is a base.
It is called the base hydrolysis of the ester.
Mechanism:
The hydroxide ion from sodium hydroxide attacks the electrophilic carbonyl carbon of the ester leading to the formation of a tetrahedral intermediate. Then the loss of the alkoxide ion takes place. Then acid-base equilibrium is formed. Alkoxide ions abstract a proton from the alcohol and carboxylate ions are formed.

Image: Mechanism of base hydrolysis of ethyl acetoacetate.
Hence, ethyl acetoacetate undergoes hydrolysis in presence of sodium hydroxide to form sodium 3-oxo butanoate and ethyl alcohol.
So, option B is correct.
Note: In the given compound, we see that there are two carbonyl carbon but the hydroxide ion is nucleophilic hence attacking the electrophilic carbonyl carbon. The carbonyl carbon on the left-hand side has a methyl group attached to it which is an electron-releasing group decreasing the electrophilicity of the carbon.
Recently Updated Pages
Types of Solutions in Chemistry: Explained Simply

JEE General Topics in Chemistry Important Concepts and Tips

JEE Extractive Metallurgy Important Concepts and Tips for Exam Preparation

JEE Amino Acids and Peptides Important Concepts and Tips for Exam Preparation

JEE Atomic Structure and Chemical Bonding important Concepts and Tips

Electricity and Magnetism Explained: Key Concepts & Applications

Trending doubts
JEE Main 2026: Session 2 Registration Open, City Intimation Slip, Exam Dates, Syllabus & Eligibility

JEE Main 2026 Application Login: Direct Link, Registration, Form Fill, and Steps

JEE Main Marking Scheme 2026- Paper-Wise Marks Distribution and Negative Marking Details

Understanding the Angle of Deviation in a Prism

Hybridisation in Chemistry – Concept, Types & Applications

How to Convert a Galvanometer into an Ammeter or Voltmeter

Other Pages
JEE Advanced Marks vs Ranks 2025: Understanding Category-wise Qualifying Marks and Previous Year Cut-offs

NCERT Solutions For Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 1 Solutions (2025-26)

Solutions Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 1 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

NCERT Solutions For Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 4 The d and f Block Elements (2025-26)

Biomolecules Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 10 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

NCERT Solutions For Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 10 Biomolecules (2025-26)




