
Oxirane is
A. Ethylene oxide
B. Diethyl ether
C. Ethyl glycolate
D. Glycolic ester
Answer
233.1k+ views
Hint: Oxirane is an organic compound having the chemical formula \[{{\rm{C}}_{\rm{2}}}{{\rm{H}}_{\rm{4}}}{\rm{O}}\]. It is a three-membered cyclic compound containing the ether functional group. It is also the simplest epoxide.
Complete Step by Step Solution:
Oxirane is the IUPAC name of \[{{\rm{C}}_{\rm{2}}}{{\rm{H}}_{\rm{4}}}{\rm{O}}\]. This compound is also known as ethylene oxide. This is a simple epoxide which is a three-membered ring having one oxygen atom and two carbon atoms. The atoms are bonded to each other through sigma bonds.
The structure of the compound is as comes after:
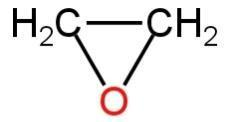
Image: Structure of oxirane.
As it is a strained ring, it readily takes part in several additional reactions which involve ring-opening.
Ethylene oxide has no colour and is an explosive gas with a slightly sweet aroma.
It is industrially yielded by oxidation of ethylene in the presence of a silver catalyst.
The reaction happens as comes next:

Image: Production of oxirane
It is utilised for producing numerous products like detergents, thickeners, solvents, plastics, and different organic chemicals like ethylene glycol, ethanolamines, polyglycol ethers, etc. Ethylene oxide is soluble in water, ethanol, diethyl ether, and many organic solvents. So, oxirane is ethylene oxide.
So, option A is correct.
Note: In epoxides, the ring atoms i.e., two carbon atoms and one oxygen atom are \[{\rm{s}}{{\rm{p}}^{\rm{3}}}\] hybridised. The two \[{\rm{s}}{{\rm{p}}^{\rm{3}}}\] hybrid bonds of oxygen are filled. The C-O-C bond angle of an epoxide must be \[{\rm{60^\circ }}\], a significant divergence from the tetrahedral bond angle. So, epoxides have an angle strain making them much more reactive than ethers as opening the ring relieves the strain.
Complete Step by Step Solution:
Oxirane is the IUPAC name of \[{{\rm{C}}_{\rm{2}}}{{\rm{H}}_{\rm{4}}}{\rm{O}}\]. This compound is also known as ethylene oxide. This is a simple epoxide which is a three-membered ring having one oxygen atom and two carbon atoms. The atoms are bonded to each other through sigma bonds.
The structure of the compound is as comes after:

Image: Structure of oxirane.
As it is a strained ring, it readily takes part in several additional reactions which involve ring-opening.
Ethylene oxide has no colour and is an explosive gas with a slightly sweet aroma.
It is industrially yielded by oxidation of ethylene in the presence of a silver catalyst.
The reaction happens as comes next:

Image: Production of oxirane
It is utilised for producing numerous products like detergents, thickeners, solvents, plastics, and different organic chemicals like ethylene glycol, ethanolamines, polyglycol ethers, etc. Ethylene oxide is soluble in water, ethanol, diethyl ether, and many organic solvents. So, oxirane is ethylene oxide.
So, option A is correct.
Note: In epoxides, the ring atoms i.e., two carbon atoms and one oxygen atom are \[{\rm{s}}{{\rm{p}}^{\rm{3}}}\] hybridised. The two \[{\rm{s}}{{\rm{p}}^{\rm{3}}}\] hybrid bonds of oxygen are filled. The C-O-C bond angle of an epoxide must be \[{\rm{60^\circ }}\], a significant divergence from the tetrahedral bond angle. So, epoxides have an angle strain making them much more reactive than ethers as opening the ring relieves the strain.
Recently Updated Pages
JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 (January 31 Evening Shift) Question Paper with Solutions [PDF]

JEE Main 2023 January 30 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 25 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 24 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

Trending doubts
JEE Main 2026: Session 2 Registration Open, City Intimation Slip, Exam Dates, Syllabus & Eligibility

JEE Main 2026 Application Login: Direct Link, Registration, Form Fill, and Steps

JEE Main Marking Scheme 2026- Paper-Wise Marks Distribution and Negative Marking Details

Understanding the Angle of Deviation in a Prism

Hybridisation in Chemistry – Concept, Types & Applications

How to Convert a Galvanometer into an Ammeter or Voltmeter

Other Pages
JEE Advanced Marks vs Ranks 2025: Understanding Category-wise Qualifying Marks and Previous Year Cut-offs

NCERT Solutions For Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 1 Solutions (2025-26)

Solutions Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 1 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

NCERT Solutions For Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 4 The d and f Block Elements (2025-26)

Biomolecules Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 10 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

NCERT Solutions For Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 10 Biomolecules (2025-26)




