
Oxidation of which of the following by air in presence of vanadium pentoxide gives phenol
A. Toluene
B. Benzene
C. Benzaldehyde
D. Phenylacetic acid
Answer
233.1k+ views
Hint: Oxidation of an organic compound is the process of reaction of a compound without oxygen that happens in the presence of an oxidising agent. Phenol is an aromatic organic compound having the molecular formula C6H5OH.
Complete Step by Step Answer:
Phenol has a phenyl group (\[{C_6}{H_5}\]) connected to a hydroxyl group (−OH).
It is mildly acidic and needs cautious handling as it can induce chemical burns.
Oxidation of a compound gives phenol. We have to find out the compound.
A. Toluene
Toluene is a substituted aromatic hydrocarbon.
It has no colour, a water-insoluble liquid with a smell like that of paint thinners.
It is a mono-substituted benzene derivative, having a methyl group (\[C{H_3}\] ) attached to a phenyl group.
Its IUPAC name is methylbenzene.
Oxidation of toluene gives benzoic acid and benzaldehyde in presence of strong oxidising agents like potassium permanganate.
It doesn't give phenol on oxidation with vanadium pentoxide.
So, A is incorrect.
B. Benzene
It is an organic chemical compound having the chemical formula \[{C_6}{H_6}\].
It is composed of six carbon atoms bound in a planar ring with one hydrogen atom connected to each carbon atom.
Benzene on treatment with air in the presence of vanadium pentoxide forms at \[300^\circ C\] temperature and forms phenol.
The reaction happens as follows:
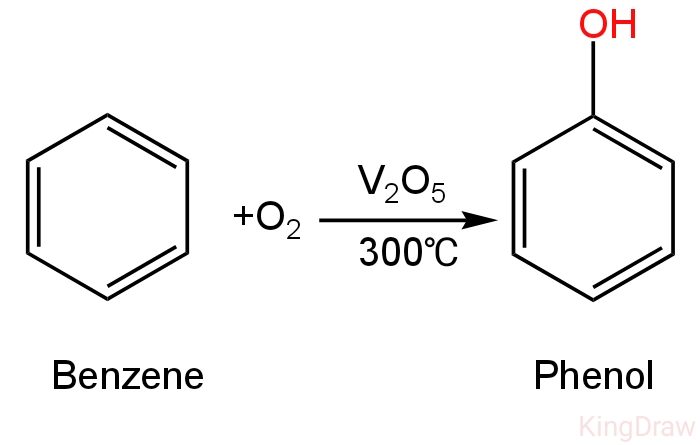
Image: Formation of phenol from benzene.
So, B is correct.
C. Benzaldehyde
Benzaldehyde when exposed to air readily undergoes oxidation by itself to form benzoic acid.
So, C is incorrect.
D. Phenylacetic acid
It is an organic compound comprising a phenyl group and a carboxylic acid group.
It undergoes oxidation to form benzaldehyde.
So, D is incorrect.
Therefore, benzene in reaction with air in presence of vanadium pentoxide forms phenol.
So, option B is correct.
Note: Benzene reacts with air in presence of vanadium pentoxide at \[300^\circ C\] to form phenol. This is known as partial oxidation. But when one molecule of benzene reacts with two molecules of vanadium pentoxide and oxygen at \[500^\circ C\]we get maleic anhydride as the main product.
Complete Step by Step Answer:
Phenol has a phenyl group (\[{C_6}{H_5}\]) connected to a hydroxyl group (−OH).
It is mildly acidic and needs cautious handling as it can induce chemical burns.
Oxidation of a compound gives phenol. We have to find out the compound.
A. Toluene
Toluene is a substituted aromatic hydrocarbon.
It has no colour, a water-insoluble liquid with a smell like that of paint thinners.
It is a mono-substituted benzene derivative, having a methyl group (\[C{H_3}\] ) attached to a phenyl group.
Its IUPAC name is methylbenzene.
Oxidation of toluene gives benzoic acid and benzaldehyde in presence of strong oxidising agents like potassium permanganate.
It doesn't give phenol on oxidation with vanadium pentoxide.
So, A is incorrect.
B. Benzene
It is an organic chemical compound having the chemical formula \[{C_6}{H_6}\].
It is composed of six carbon atoms bound in a planar ring with one hydrogen atom connected to each carbon atom.
Benzene on treatment with air in the presence of vanadium pentoxide forms at \[300^\circ C\] temperature and forms phenol.
The reaction happens as follows:

Image: Formation of phenol from benzene.
So, B is correct.
C. Benzaldehyde
Benzaldehyde when exposed to air readily undergoes oxidation by itself to form benzoic acid.
So, C is incorrect.
D. Phenylacetic acid
It is an organic compound comprising a phenyl group and a carboxylic acid group.
It undergoes oxidation to form benzaldehyde.
So, D is incorrect.
Therefore, benzene in reaction with air in presence of vanadium pentoxide forms phenol.
So, option B is correct.
Note: Benzene reacts with air in presence of vanadium pentoxide at \[300^\circ C\] to form phenol. This is known as partial oxidation. But when one molecule of benzene reacts with two molecules of vanadium pentoxide and oxygen at \[500^\circ C\]we get maleic anhydride as the main product.
Recently Updated Pages
JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 (January 31 Evening Shift) Question Paper with Solutions [PDF]

JEE Main 2023 January 30 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 25 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 24 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

Trending doubts
JEE Main 2026: Session 2 Registration Open, City Intimation Slip, Exam Dates, Syllabus & Eligibility

JEE Main 2026 Application Login: Direct Link, Registration, Form Fill, and Steps

JEE Main Marking Scheme 2026- Paper-Wise Marks Distribution and Negative Marking Details

Understanding the Angle of Deviation in a Prism

Hybridisation in Chemistry – Concept, Types & Applications

How to Convert a Galvanometer into an Ammeter or Voltmeter

Other Pages
JEE Advanced Marks vs Ranks 2025: Understanding Category-wise Qualifying Marks and Previous Year Cut-offs

Hydrocarbons Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 9 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Thermodynamics Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 5 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Equilibrium Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 6 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Organic Chemistry Some Basic Principles And Techniques Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 8 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

NCERT Solutions For Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 7 Redox Reactions (2025-26)




