
Nylon-6,6 is a:
A. Natural polymer
B. Condensation polymer
C. Addition polymer
D. Substitution polymer
Answer
233.1k+ views
Hint: Nylon – 66 is formed with the help of two monomers, each of which contains six carbon atoms. The monomers are hexamethylenediamine and adipic acid. It is formed by the polycondensation of the two monomers.
Complete Step by Step Solution:
First we know about Nylon - 6,6
Nylon 6, 6 belongs to the family of synthetic polymers which have linear amide linkages which are known as linear polyamides or nylon. It is synthesised or prepared by the condensation of two similar monomers having 6 carbon atoms, hexamethylenediamine, and adipic acid.
Synthesis Of Nylon 6 6
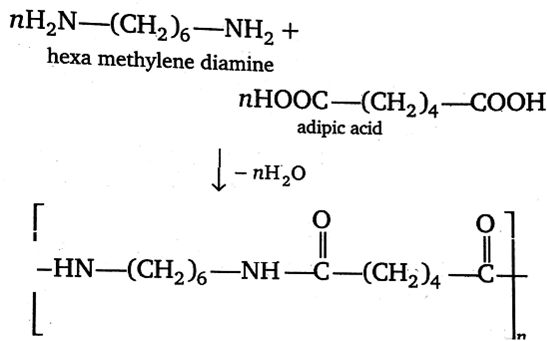
Synthesising or manufacturing the polymer Nylon 6,6 is a step-growth polymerization process that arise through the polycondensation technique, where two monomers hexamethylenediamine $({{H}_{2}}N-{{(C{{H}_{2}})}_{6}}-N{{H}_{2}})$ & adipic acid $(HOOC-{{(C{{H}_{2}})}_{4}}-COOH)$ are condensed to form a polymer called Nylon 6,6. This reaction doesn’t need the catalyst to enhance the rate of the reaction as one of the monomer ie. adipic acid itself acts as a catalyst. Nylon 6,6 is a fibre used in the textile and plastic industries and in daily activities of life.
Note: It is important to note that, cellulose cannot be synthesised by humans because humans take energy from carbohydrates present in food by breaking it into glucose with the help of suitable enzymes but it is very difficult to break cellulose bonding because of the lack of enzyme need to break it.
Complete Step by Step Solution:
First we know about Nylon - 6,6
Nylon 6, 6 belongs to the family of synthetic polymers which have linear amide linkages which are known as linear polyamides or nylon. It is synthesised or prepared by the condensation of two similar monomers having 6 carbon atoms, hexamethylenediamine, and adipic acid.
Synthesis Of Nylon 6 6

Synthesising or manufacturing the polymer Nylon 6,6 is a step-growth polymerization process that arise through the polycondensation technique, where two monomers hexamethylenediamine $({{H}_{2}}N-{{(C{{H}_{2}})}_{6}}-N{{H}_{2}})$ & adipic acid $(HOOC-{{(C{{H}_{2}})}_{4}}-COOH)$ are condensed to form a polymer called Nylon 6,6. This reaction doesn’t need the catalyst to enhance the rate of the reaction as one of the monomer ie. adipic acid itself acts as a catalyst. Nylon 6,6 is a fibre used in the textile and plastic industries and in daily activities of life.
Note: It is important to note that, cellulose cannot be synthesised by humans because humans take energy from carbohydrates present in food by breaking it into glucose with the help of suitable enzymes but it is very difficult to break cellulose bonding because of the lack of enzyme need to break it.
Recently Updated Pages
JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 (January 31 Evening Shift) Question Paper with Solutions [PDF]

JEE Main 2023 January 30 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 25 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 24 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

Trending doubts
JEE Main 2026: Session 2 Registration Open, City Intimation Slip, Exam Dates, Syllabus & Eligibility

JEE Main 2026 Application Login: Direct Link, Registration, Form Fill, and Steps

Understanding the Angle of Deviation in a Prism

Hybridisation in Chemistry – Concept, Types & Applications

How to Convert a Galvanometer into an Ammeter or Voltmeter

Understanding the Electric Field of a Uniformly Charged Ring

Other Pages
JEE Advanced Marks vs Ranks 2025: Understanding Category-wise Qualifying Marks and Previous Year Cut-offs

NCERT Solutions For Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 1 Solutions (2025-26)

Solutions Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 1 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

NCERT Solutions For Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 4 The d and f Block Elements (2025-26)

Biomolecules Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 10 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

NCERT Solutions For Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 10 Biomolecules (2025-26)




