
Nitrobenzene gives N-phenylhydroxylamine by
A. Sn/HCl
B. \[{H_2}/Pd - C\]
C. Zn/NaOH
D. Zn/\[N{H_4}Cl\]
Answer
233.1k+ views
Hint: The conversion of nitrobenzene to N-phenylhydroxyamine is done with the help of a reducing agent. Here, the double-bonded oxygen group present in a nitro group is converted to oxime or a hydroxyl group.
Complete Step by Step Solution:
Nitrobenzene is converted to N-phenylhydroxylamine in presence of zinc dust along with ammonium chloride. It acts as a mild reducing agent which reduces the double bond oxygen present in the nitro group into an oxime. The zinc donates the electron pair to convert into a divalent cation.
The reaction between nitrobenzene and zinc dust in the presence of ammonium chloride is shown below.
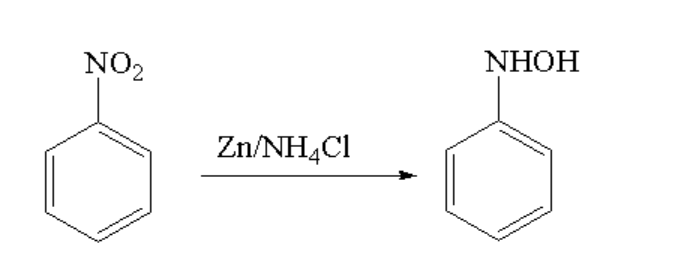
Image: Conversion of nitrobenzene to N-phenylhydroxyl amine
The reaction mechanism is shown below:
\[Ph - N{O_2} \to Ph - N = O \overset{2e^{-}/Zn^{2+}}{\rightarrow} PhNH(OH)\]
Here, Ph is the phenyl group
The nitrogen atom present in the nitro group is partially positive in nature. The zinc atom transfers its one electron to the nitrogen as a result one electron moves to oxygen and another electron to the nitrogen atom in \[N = O\]. The reaction of a proton with both \[ - {O^ - }\] forms N, N-hydroxybenzene which is very unstable due to the presence of two hydroxyl groups. By losing water molecules it forms the intermediate product nitrosobenzene which on reacting with zinc ion forms N-phenyl hydroxylamine.
Thus, Nitrobenzene gives N-phenylhydroxylamine by Zn/\[N{H_4}Cl\].
Therefore, the correct option is D.
Note: Reduction is defined as a reaction where there is a decrease in the oxidation state of the central atom. In the given reaction ammonium chloride is used as a promoter for zinc dust.
Complete Step by Step Solution:
Nitrobenzene is converted to N-phenylhydroxylamine in presence of zinc dust along with ammonium chloride. It acts as a mild reducing agent which reduces the double bond oxygen present in the nitro group into an oxime. The zinc donates the electron pair to convert into a divalent cation.
The reaction between nitrobenzene and zinc dust in the presence of ammonium chloride is shown below.

Image: Conversion of nitrobenzene to N-phenylhydroxyl amine
The reaction mechanism is shown below:
\[Ph - N{O_2} \to Ph - N = O \overset{2e^{-}/Zn^{2+}}{\rightarrow} PhNH(OH)\]
Here, Ph is the phenyl group
The nitrogen atom present in the nitro group is partially positive in nature. The zinc atom transfers its one electron to the nitrogen as a result one electron moves to oxygen and another electron to the nitrogen atom in \[N = O\]. The reaction of a proton with both \[ - {O^ - }\] forms N, N-hydroxybenzene which is very unstable due to the presence of two hydroxyl groups. By losing water molecules it forms the intermediate product nitrosobenzene which on reacting with zinc ion forms N-phenyl hydroxylamine.
Thus, Nitrobenzene gives N-phenylhydroxylamine by Zn/\[N{H_4}Cl\].
Therefore, the correct option is D.
Note: Reduction is defined as a reaction where there is a decrease in the oxidation state of the central atom. In the given reaction ammonium chloride is used as a promoter for zinc dust.
Recently Updated Pages
JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 (January 31 Evening Shift) Question Paper with Solutions [PDF]

JEE Main 2023 January 30 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 25 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 24 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

Trending doubts
JEE Main 2026: Session 2 Registration Open, City Intimation Slip, Exam Dates, Syllabus & Eligibility

JEE Main 2026 Application Login: Direct Link, Registration, Form Fill, and Steps

Understanding the Angle of Deviation in a Prism

Hybridisation in Chemistry – Concept, Types & Applications

How to Convert a Galvanometer into an Ammeter or Voltmeter

Understanding the Electric Field of a Uniformly Charged Ring

Other Pages
JEE Advanced Marks vs Ranks 2025: Understanding Category-wise Qualifying Marks and Previous Year Cut-offs

NCERT Solutions For Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 1 Solutions (2025-26)

Solutions Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 1 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

NCERT Solutions For Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 4 The d and f Block Elements (2025-26)

Biomolecules Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 10 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

NCERT Solutions For Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 10 Biomolecules (2025-26)




