
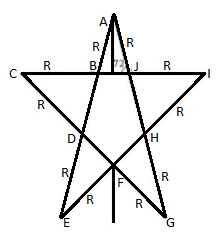
n the given star network the equivalent resistance between $A$ and $F$ is:
(A) $1.944\,R$
(B) $0.973\,R$
(C) $0.486\,R$
(D) $0.243\,R$
Answer
233.4k+ views
Hint: In the given network first the resistance of the branch B to J is determined. By using that resistance value, the resistance of the triangle $BCD$ is determined. That resistance is the same for the remaining triangle of $DEF$, $FGH$ and $HIJ$. By using this, the resistance of the AF is determined.
Complete step by step solution
Assume that the line from the A meets the line BJ at the centre and the meeting point is L, then the equation is given by,
$BJ = 2 \times LJ$
Assume the triangle $AEJ$ is the right angle triangle, and the angle of $J$ is given as ${72^ \circ }$ in the diagram, then above equation is written as,
$BJ = 2 \times R\cos {72^ \circ }$
The value of the $\cos {72^ \circ }$ from the trigonometry is $0.309$, by substituting this value in the above equation, then the above equation is written as,
$BJ = 2 \times 0.309R$
By multiplying the terms, then the above equation is written as,
$BJ = 0.62R$
Now, the resistance of ${R_B}$ in the branch of $BCD$, then the above equation is written as,
${R_B} = \dfrac{{2R \times BJ}}{{2R + BJ}}$
By substituting the value of the $BJ$ in the above equation, then the above equation is written as,
${R_B} = \dfrac{{2R \times 0.62R}}{{2R + 0.62R}}$
By multiplying the terms in the numerator, then the above equation is written as,
${R_B} = \dfrac{{1.24{R^2}}}{{2R + 0.62R}}$
By adding the terms in the denominator, then the above equation is written as,
${R_B} = \dfrac{{1.24{R^2}}}{{2.62R}}$
By cancelling the same terms, then the above equation is written as,
${R_B} = \dfrac{{1.24R}}{{2.62}}$
On dividing the above equation, then the above equation is written as,
${R_B} = 0.473R$
The net resistance of the $AF$ is given by,
${R_{AF}} = \dfrac{{R + 2{R_B}}}{2}$
By substituting the value of the ${R_B}$, then the above equation is written as,
${R_{AF}} = \dfrac{{R + \left( {2 \times 0.473R} \right)}}{2}$
By multiplying the terms in the above equation, then the above equation is written as,
${R_{AF}} = \dfrac{{R + 0.946R}}{2}$
By adding the terms in the above equation, then
${R_{AF}} = \dfrac{{1.946R}}{2}$
By dividing the terms, then the above equation is written as,
${R_{AF}} = 0.973R$
Hence, the option (B) is the correct answer.
Note: Hence the equivalent resistance between the $A$ and $F$ is given by the product of the $0.973$ and the resistance of $R$. The resistance of $R$ is the same in two triangles. So, the equivalent resistance between the $A$ and $F$ depends only on the resistance of $R$.
Complete step by step solution
Assume that the line from the A meets the line BJ at the centre and the meeting point is L, then the equation is given by,
$BJ = 2 \times LJ$
Assume the triangle $AEJ$ is the right angle triangle, and the angle of $J$ is given as ${72^ \circ }$ in the diagram, then above equation is written as,
$BJ = 2 \times R\cos {72^ \circ }$
The value of the $\cos {72^ \circ }$ from the trigonometry is $0.309$, by substituting this value in the above equation, then the above equation is written as,
$BJ = 2 \times 0.309R$
By multiplying the terms, then the above equation is written as,
$BJ = 0.62R$
Now, the resistance of ${R_B}$ in the branch of $BCD$, then the above equation is written as,
${R_B} = \dfrac{{2R \times BJ}}{{2R + BJ}}$
By substituting the value of the $BJ$ in the above equation, then the above equation is written as,
${R_B} = \dfrac{{2R \times 0.62R}}{{2R + 0.62R}}$
By multiplying the terms in the numerator, then the above equation is written as,
${R_B} = \dfrac{{1.24{R^2}}}{{2R + 0.62R}}$
By adding the terms in the denominator, then the above equation is written as,
${R_B} = \dfrac{{1.24{R^2}}}{{2.62R}}$
By cancelling the same terms, then the above equation is written as,
${R_B} = \dfrac{{1.24R}}{{2.62}}$
On dividing the above equation, then the above equation is written as,
${R_B} = 0.473R$
The net resistance of the $AF$ is given by,
${R_{AF}} = \dfrac{{R + 2{R_B}}}{2}$
By substituting the value of the ${R_B}$, then the above equation is written as,
${R_{AF}} = \dfrac{{R + \left( {2 \times 0.473R} \right)}}{2}$
By multiplying the terms in the above equation, then the above equation is written as,
${R_{AF}} = \dfrac{{R + 0.946R}}{2}$
By adding the terms in the above equation, then
${R_{AF}} = \dfrac{{1.946R}}{2}$
By dividing the terms, then the above equation is written as,
${R_{AF}} = 0.973R$
Hence, the option (B) is the correct answer.
Note: Hence the equivalent resistance between the $A$ and $F$ is given by the product of the $0.973$ and the resistance of $R$. The resistance of $R$ is the same in two triangles. So, the equivalent resistance between the $A$ and $F$ depends only on the resistance of $R$.
Recently Updated Pages
JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 (January 31 Evening Shift) Question Paper with Solutions [PDF]

JEE Main 2023 January 30 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 25 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 24 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

Trending doubts
JEE Main 2026: Session 2 Registration Open, City Intimation Slip, Exam Dates, Syllabus & Eligibility

JEE Main 2026 Application Login: Direct Link, Registration, Form Fill, and Steps

Understanding the Angle of Deviation in a Prism

Hybridisation in Chemistry – Concept, Types & Applications

How to Convert a Galvanometer into an Ammeter or Voltmeter

Understanding Uniform Acceleration in Physics

Other Pages
JEE Advanced Marks vs Ranks 2025: Understanding Category-wise Qualifying Marks and Previous Year Cut-offs

Dual Nature of Radiation and Matter Class 12 Physics Chapter 11 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Understanding the Electric Field of a Uniformly Charged Ring

JEE Advanced Weightage 2025 Chapter-Wise for Physics, Maths and Chemistry

Derivation of Equation of Trajectory Explained for Students

Understanding Electromagnetic Waves and Their Importance




