
Mutual inductance depends on
A. the medium between the coils
B. the separation between the coils
C. both(A) and (B)
D. it is independent of medium
Answer
232.8k+ views
Hint: We know that a changing current in a coil induced magnetic flux through a neighboring coil. As a result, an emf is convinced in bordering coils. This commerce of one coil’s glamorous field on another coil is known as mutual inductance.
Complete step by step solution:
We know that when two coils are brought into the neighborhood with each other, the magnetic field in one of the coils gets linked with the other coil. This results in the induction of voltage in the alternate coil.
The expression for mutual inductance of the second coil concerning the first is given by the expression
\[{M_{sp}} = \dfrac{{{N_s}{\phi _s}}}{{{I_p}}}\]
Where \[{N_s}\] is the number of windings in the second coil, \[{\phi _s}\] is the flux in one turn of the second coil due to a change in current\[{I_p}\].
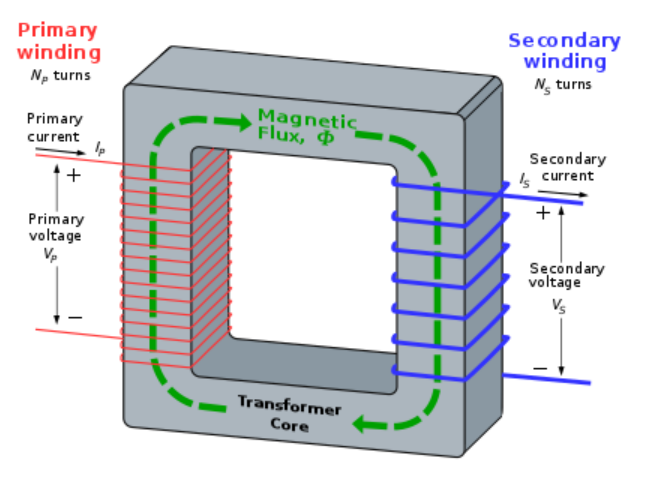
Image: Mutual Induction between two coils
Also, Magnetic flux\[\phi \] is the measurement of a magnetic field passing typically through an area. Magnetic flux through an area is given by the dot product of the magnetic field and area vector.
\[\phi = B.A\]
Therefore, we observe that mutual inductance between two coils depends on the number of turns and magnetic flux which further depends on sampling area and permeability. Therefore, options (A) and (B) are correct.
Hence, option(C) is correct
Note: Most of the students get confused between mutual induction and self induction. Remember that mutual inductance is essentially the creation of an induced EMF in one coil by current flowing in another. Changes in the flow of current in a coil are countered by the coil itself by inducing an EMF in the same coil, i.e. no other coil is involved in self-inductance.
Complete step by step solution:
We know that when two coils are brought into the neighborhood with each other, the magnetic field in one of the coils gets linked with the other coil. This results in the induction of voltage in the alternate coil.
The expression for mutual inductance of the second coil concerning the first is given by the expression
\[{M_{sp}} = \dfrac{{{N_s}{\phi _s}}}{{{I_p}}}\]
Where \[{N_s}\] is the number of windings in the second coil, \[{\phi _s}\] is the flux in one turn of the second coil due to a change in current\[{I_p}\].

Image: Mutual Induction between two coils
Also, Magnetic flux\[\phi \] is the measurement of a magnetic field passing typically through an area. Magnetic flux through an area is given by the dot product of the magnetic field and area vector.
\[\phi = B.A\]
Therefore, we observe that mutual inductance between two coils depends on the number of turns and magnetic flux which further depends on sampling area and permeability. Therefore, options (A) and (B) are correct.
Hence, option(C) is correct
Note: Most of the students get confused between mutual induction and self induction. Remember that mutual inductance is essentially the creation of an induced EMF in one coil by current flowing in another. Changes in the flow of current in a coil are countered by the coil itself by inducing an EMF in the same coil, i.e. no other coil is involved in self-inductance.
Recently Updated Pages
JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 (January 31 Evening Shift) Question Paper with Solutions [PDF]

JEE Main 2023 January 30 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 25 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 24 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

Trending doubts
JEE Main 2026: Session 2 Registration Open, City Intimation Slip, Exam Dates, Syllabus & Eligibility

JEE Main 2026 Application Login: Direct Link, Registration, Form Fill, and Steps

Understanding the Angle of Deviation in a Prism

Hybridisation in Chemistry – Concept, Types & Applications

How to Convert a Galvanometer into an Ammeter or Voltmeter

Understanding Uniform Acceleration in Physics

Other Pages
JEE Advanced Marks vs Ranks 2025: Understanding Category-wise Qualifying Marks and Previous Year Cut-offs

Dual Nature of Radiation and Matter Class 12 Physics Chapter 11 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Understanding the Electric Field of a Uniformly Charged Ring

JEE Advanced Weightage 2025 Chapter-Wise for Physics, Maths and Chemistry

Derivation of Equation of Trajectory Explained for Students

Understanding Electromagnetic Waves and Their Importance




