
Man A sitting in a car moving with a speed of $54 km/hr$ observes a man B in front of the car crossing perpendicularly a road of width $15 m$ in three seconds. Then the velocity of man B (in m/s) will be:
A) $5\sqrt {10} $ $\text{towards the car at some angle.}$
B) $5\sqrt {10} $ $\text{away from the car at some angle.}$
C) $\text{5 perpendicular to the road.}$
D) $\text{15 along the road.}$
Answer
233.1k+ views
Hint: The relative velocity is the velocity of a body with respect to another body. Generally the velocity is represented with respect to the ground but sometimes the point of reference changes and we need to then solve and get the relative velocity of the body.
Complete step by step solution:
The speed of man A in $m/s$ is equal to,
$ \Rightarrow 54 \times \dfrac{5}{{18}} = 15m/s$
The speed of man B is equal to,
$ \Rightarrow {V_B} = \dfrac{{15}}{3} m/s$
$ \Rightarrow {V_B} = 5m/s$.
Since the man A observes the man B moving in the perpendicular direction then the vector representation can be used to solve this further.
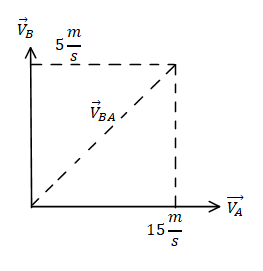
Let resultant velocity of the velocity of man B with respect to man A is given by ${V_{BA}}$.
The magnitude of the speed of the man B observed from man A is given by.
Applying Pythagoras we get,
$ \Rightarrow {V_{BA}} = \sqrt {{5^2} + {{15}^2}} $
$ \Rightarrow {V_{BA}} = \sqrt {25 + 225} $
$ \Rightarrow {V_{BA}} = \sqrt {250} $
$ \Rightarrow {V_{BA}} = 5\sqrt {10} m/s$.
The speed of man B with respect to man A is equal to ${V_{BA}} = 5\sqrt {10} m/s$ and is away from the car at some angle.
The correct answer for this problem is option B.
Note: The vector addition and subtraction is very useful in solving problems like these and therefore it is advised for students to understand and remember the formula of the vector addition and vector substation and also the magnitude calculation of the same.
Complete step by step solution:
The speed of man A in $m/s$ is equal to,
$ \Rightarrow 54 \times \dfrac{5}{{18}} = 15m/s$
The speed of man B is equal to,
$ \Rightarrow {V_B} = \dfrac{{15}}{3} m/s$
$ \Rightarrow {V_B} = 5m/s$.
Since the man A observes the man B moving in the perpendicular direction then the vector representation can be used to solve this further.

Let resultant velocity of the velocity of man B with respect to man A is given by ${V_{BA}}$.
The magnitude of the speed of the man B observed from man A is given by.
Applying Pythagoras we get,
$ \Rightarrow {V_{BA}} = \sqrt {{5^2} + {{15}^2}} $
$ \Rightarrow {V_{BA}} = \sqrt {25 + 225} $
$ \Rightarrow {V_{BA}} = \sqrt {250} $
$ \Rightarrow {V_{BA}} = 5\sqrt {10} m/s$.
The speed of man B with respect to man A is equal to ${V_{BA}} = 5\sqrt {10} m/s$ and is away from the car at some angle.
The correct answer for this problem is option B.
Note: The vector addition and subtraction is very useful in solving problems like these and therefore it is advised for students to understand and remember the formula of the vector addition and vector substation and also the magnitude calculation of the same.
Recently Updated Pages
JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 (January 31 Evening Shift) Question Paper with Solutions [PDF]

JEE Main 2023 January 30 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 25 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 24 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

Trending doubts
JEE Main 2026: Session 2 Registration Open, City Intimation Slip, Exam Dates, Syllabus & Eligibility

JEE Main 2026 Application Login: Direct Link, Registration, Form Fill, and Steps

JEE Main Marking Scheme 2026- Paper-Wise Marks Distribution and Negative Marking Details

Understanding the Angle of Deviation in a Prism

Hybridisation in Chemistry – Concept, Types & Applications

How to Convert a Galvanometer into an Ammeter or Voltmeter

Other Pages
JEE Advanced Marks vs Ranks 2025: Understanding Category-wise Qualifying Marks and Previous Year Cut-offs

Laws of Motion Class 11 Physics Chapter 4 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Waves Class 11 Physics Chapter 14 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Mechanical Properties of Fluids Class 11 Physics Chapter 9 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Thermodynamics Class 11 Physics Chapter 11 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Units And Measurements Class 11 Physics Chapter 1 CBSE Notes - 2025-26




