
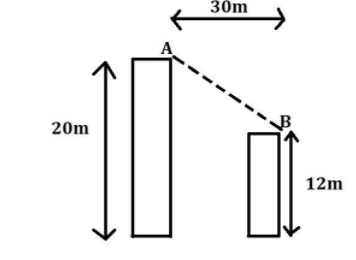
A boy wants to throw a ball from a point \[A\] so as to just clear the cliff at \[B\]. The minimum horizontal velocity with which the body should throw the ball is $(g = 10\;{\text{m}}/{{\text{s}}^2})$
(A) \[2.4m/s\]
(B) \[23.8m/s\]
(C) \[238m/s\]
(D) \[47.4m/s\]
Answer
233.1k+ views
Hint: Let us suppose a ball is thrown downwards from the edge of a cliff at an initial velocity \[u\] \[m/s\]. We know that the ball would be under the effect of gravity and would be having a positive acceleration. To find out the velocity with which the boy should throw the ball, we have to apply the equation of kinematics.
Formula Used: We will be using the following formula,
\[u = \dfrac{S}{{\sqrt {\dfrac{{2({h_1} - {h_2})}}{g}} }}\]
Where
\[u\] is the required velocity
\[S\] is the distance between the cliffs
\[{h_1}\] is the height of the taller cliff
\[{h_2}\] is the height of the shorter cliff
\[g\] is the acceleration due to gravity
Complete Step-by-Step Solution:
According to the question, the following information is provided to us:
The height of the taller cliff, \[{h_1} = 20m\]
The height of the shorter cliff, \[{h_2} = 12m/s\]
The distance between the cliffs, \[S = 30m\]
And the acceleration due to gravity, \[g = 10m/{s^2}\]
Now we will put all these values provided to us in the above formula to find out the required velocity
So, we get
\[u = \dfrac{S}{{\sqrt {\dfrac{{2({h_1} - {h_2})}}{g}} }}\]
\[ \Rightarrow u = \dfrac{{30}}{{\sqrt {\dfrac{{2(20 - 12)}}{{10}}} }}\]
Upon further solving, we get
\[\therefore u = 23.80m/s\]
Hence, the correct option is (B.)
Note: Kinematic equations are a set of four equations that can be used, if other information is known, to predict unknown information about the motion of an object. For any motion that can be described as being either a constant velocity motion or a constant acceleration motion, the equations can be used. Over any time period during which the acceleration changes, they can never be used. Four variables are part of each of the kinematic equations. The value of the fourth variable can be calculated if the values of three of the four variables are known.
Formula Used: We will be using the following formula,
\[u = \dfrac{S}{{\sqrt {\dfrac{{2({h_1} - {h_2})}}{g}} }}\]
Where
\[u\] is the required velocity
\[S\] is the distance between the cliffs
\[{h_1}\] is the height of the taller cliff
\[{h_2}\] is the height of the shorter cliff
\[g\] is the acceleration due to gravity
Complete Step-by-Step Solution:
According to the question, the following information is provided to us:
The height of the taller cliff, \[{h_1} = 20m\]
The height of the shorter cliff, \[{h_2} = 12m/s\]
The distance between the cliffs, \[S = 30m\]
And the acceleration due to gravity, \[g = 10m/{s^2}\]
Now we will put all these values provided to us in the above formula to find out the required velocity
So, we get
\[u = \dfrac{S}{{\sqrt {\dfrac{{2({h_1} - {h_2})}}{g}} }}\]
\[ \Rightarrow u = \dfrac{{30}}{{\sqrt {\dfrac{{2(20 - 12)}}{{10}}} }}\]
Upon further solving, we get
\[\therefore u = 23.80m/s\]
Hence, the correct option is (B.)
Note: Kinematic equations are a set of four equations that can be used, if other information is known, to predict unknown information about the motion of an object. For any motion that can be described as being either a constant velocity motion or a constant acceleration motion, the equations can be used. Over any time period during which the acceleration changes, they can never be used. Four variables are part of each of the kinematic equations. The value of the fourth variable can be calculated if the values of three of the four variables are known.
Recently Updated Pages
JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 (January 31 Evening Shift) Question Paper with Solutions [PDF]

JEE Main 2023 January 30 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 25 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 24 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

Trending doubts
JEE Main 2026: Session 2 Registration Open, City Intimation Slip, Exam Dates, Syllabus & Eligibility

JEE Main 2026 Application Login: Direct Link, Registration, Form Fill, and Steps

Understanding the Angle of Deviation in a Prism

Hybridisation in Chemistry – Concept, Types & Applications

How to Convert a Galvanometer into an Ammeter or Voltmeter

Understanding Uniform Acceleration in Physics

Other Pages
JEE Advanced Marks vs Ranks 2025: Understanding Category-wise Qualifying Marks and Previous Year Cut-offs

Laws of Motion Class 11 Physics Chapter 4 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Waves Class 11 Physics Chapter 14 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Mechanical Properties of Fluids Class 11 Physics Chapter 9 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Thermodynamics Class 11 Physics Chapter 11 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Units And Measurements Class 11 Physics Chapter 1 CBSE Notes - 2025-26




