
Lenz’s law is in accordance with the law:
A) Conservation of charge
B) Conservation of flux
C) Conservation of momentum
D) Conservation of energy
Answer
529.4k+ views
Hint: Following points are important for the given problem:
(1) Explanation of Faraday’s law of EMI
(2) Direction of induced EMF in the circuit
Complete step by step solution:
According to Lenz's law if the magnetic flux associated with the loop changes, then the induced current is produced in the loop, such that the magnetic field due to the induced current opposes the change in the magnetic flux.
The direction of the magnetic field depends on the condition of the magnetic flux increasing or decreasing.
Remember:
(1) For counter clockwise current, EMF is positive.
(2) For clockwise current, EMF is negative.
Consider when the north pole of the magnet is brought near the force of the coil becomes the North pole according to Lenz’s law due to which the repulsive force acts between the magnet and the coil. Same work has to be done against the repulsive force in bringing the North pole of magnet towards the coil. This mechanical work is obtained in the form of electrical energy i.e. induced current (i) in the coil.
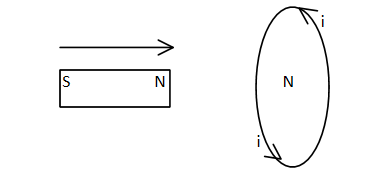
Similarly if the north pole is taken away from the coil, the face becomes the South pole and the attractive forces act between them. In this case the work done is against this attractive force, resulting electrical energy (current)
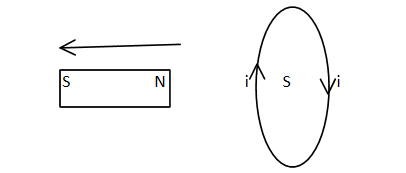
Thus it is clear that Lenz's law is based on the law of conservation of energy.
Note: For such type of problems, the detailed explanation of the following terms is necessary:
(1) Faraday’s law of EMI (experimentally)
(2) Law of conservation of energy
(3) Lenz’s law statement
(1) Explanation of Faraday’s law of EMI
(2) Direction of induced EMF in the circuit
Complete step by step solution:
According to Lenz's law if the magnetic flux associated with the loop changes, then the induced current is produced in the loop, such that the magnetic field due to the induced current opposes the change in the magnetic flux.
The direction of the magnetic field depends on the condition of the magnetic flux increasing or decreasing.
Remember:
(1) For counter clockwise current, EMF is positive.
(2) For clockwise current, EMF is negative.
Consider when the north pole of the magnet is brought near the force of the coil becomes the North pole according to Lenz’s law due to which the repulsive force acts between the magnet and the coil. Same work has to be done against the repulsive force in bringing the North pole of magnet towards the coil. This mechanical work is obtained in the form of electrical energy i.e. induced current (i) in the coil.

Similarly if the north pole is taken away from the coil, the face becomes the South pole and the attractive forces act between them. In this case the work done is against this attractive force, resulting electrical energy (current)

Thus it is clear that Lenz's law is based on the law of conservation of energy.
Note: For such type of problems, the detailed explanation of the following terms is necessary:
(1) Faraday’s law of EMI (experimentally)
(2) Law of conservation of energy
(3) Lenz’s law statement
Recently Updated Pages
JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 (January 31 Evening Shift) Question Paper with Solutions [PDF]

JEE Main 2023 January 30 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 25 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 24 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

Trending doubts
JEE Main 2026: Session 2 Registration Open, City Intimation Slip, Exam Dates, Syllabus & Eligibility

JEE Main 2026 Application Login: Direct Link, Registration, Form Fill, and Steps

JEE Main Marking Scheme 2026- Paper-Wise Marks Distribution and Negative Marking Details

Understanding the Angle of Deviation in a Prism

Hybridisation in Chemistry – Concept, Types & Applications

How to Convert a Galvanometer into an Ammeter or Voltmeter

Other Pages
JEE Advanced Marks vs Ranks 2025: Understanding Category-wise Qualifying Marks and Previous Year Cut-offs

Understanding Uniform Acceleration in Physics

Dual Nature of Radiation and Matter Class 12 Physics Chapter 11 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Understanding Electromagnetic Waves and Their Importance

Understanding the Electric Field of a Uniformly Charged Ring

JEE Advanced Weightage 2025 Chapter-Wise for Physics, Maths and Chemistry




