
Isopropyl alcohol is obtained by reacting which of the following alkenes with conc. \[{{\rm{H}}_{\rm{2}}}{\rm{S}}{{\rm{O}}_{\rm{4}}}\] and \[{{\rm{H}}_{\rm{2}}}{\rm{O}}\]
A) Ethylene
B) Propylene
C) 2-methylpropene
D) Isoprene
Answer
233.1k+ views
Hint: The chemical representation of the compound isopropyl alcohol is \[{\rm{C}}{{\rm{H}}_{\rm{3}}} - {\rm{CH(OH)}} - {\rm{C}}{{\rm{H}}_{\rm{3}}}\] . Now, we have to identify the alkene that gives isopropyl alcohol on reaction with conc. Sulphuric acid.
Complete Step by Step Answer:
Let’s discuss the options one by one.
Option A is ethylene (Ethene). The chemical representation of ethene is \[{\rm{C}}{{\rm{H}}_{\rm{2}}} = {\rm{C}}{{\rm{H}}_{\rm{2}}}\] . But, in the isopropyl alcohol, there is the presence of three atoms of carbon. So, A does not give isopropyl alcohol when it reacts with conc. sulphuric acid.
Option C is 2-methyl propene. The chemical representation of 2-methyl propene is \[{{\rm{H}}_{\rm{3}}}{\rm{C}} - {\rm{HC(C}}{{\rm{H}}_{\rm{3}}}{\rm{)}} - {\rm{C}}{{\rm{H}}_{\rm{3}}}\] . So, there is a methyl substituent in C2. But, in isopropyl alcohol, there is no methyl substituent. Therefore, 2-methylpropene also does not give isopropyl alcohol.
Option D is isoprene. Isoprene has the chemical representation of \[{\rm{C}}{{\rm{H}}_{\rm{2}}} = {\rm{C(C}}{{\rm{H}}_{\rm{3}}}{\rm{)}} - {\rm{CH}} = {\rm{C}}{{\rm{H}}_{\rm{2}}}\] . It has five atoms of carbon in the compound. So, it does not give isopropyl alcohol when it undergoes a reaction with concentrated sulphuric acid.
Option B is propylene. The reaction of propylene with conc. Sulphuric acid gives isopropyl alcohol. The reaction happens in the following way:
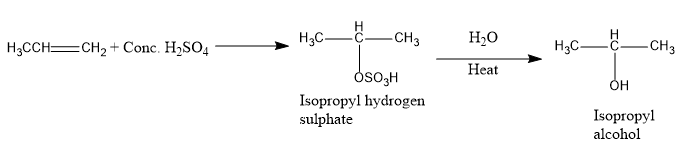
Image: Formation of isopropyl alcohol
Therefore, when propylene undergoes a reaction with sulphuric acid, isopropyl alcohol forms.
Therefore, option B is right.
Note: Isopropyl alcohol is a liquid of no colour and is a useful component in many household items namely disinfectants, cleaners, hand sanitizers, etc. Its use in the pharmaceutical industry is also significant.
Complete Step by Step Answer:
Let’s discuss the options one by one.
Option A is ethylene (Ethene). The chemical representation of ethene is \[{\rm{C}}{{\rm{H}}_{\rm{2}}} = {\rm{C}}{{\rm{H}}_{\rm{2}}}\] . But, in the isopropyl alcohol, there is the presence of three atoms of carbon. So, A does not give isopropyl alcohol when it reacts with conc. sulphuric acid.
Option C is 2-methyl propene. The chemical representation of 2-methyl propene is \[{{\rm{H}}_{\rm{3}}}{\rm{C}} - {\rm{HC(C}}{{\rm{H}}_{\rm{3}}}{\rm{)}} - {\rm{C}}{{\rm{H}}_{\rm{3}}}\] . So, there is a methyl substituent in C2. But, in isopropyl alcohol, there is no methyl substituent. Therefore, 2-methylpropene also does not give isopropyl alcohol.
Option D is isoprene. Isoprene has the chemical representation of \[{\rm{C}}{{\rm{H}}_{\rm{2}}} = {\rm{C(C}}{{\rm{H}}_{\rm{3}}}{\rm{)}} - {\rm{CH}} = {\rm{C}}{{\rm{H}}_{\rm{2}}}\] . It has five atoms of carbon in the compound. So, it does not give isopropyl alcohol when it undergoes a reaction with concentrated sulphuric acid.
Option B is propylene. The reaction of propylene with conc. Sulphuric acid gives isopropyl alcohol. The reaction happens in the following way:

Image: Formation of isopropyl alcohol
Therefore, when propylene undergoes a reaction with sulphuric acid, isopropyl alcohol forms.
Therefore, option B is right.
Note: Isopropyl alcohol is a liquid of no colour and is a useful component in many household items namely disinfectants, cleaners, hand sanitizers, etc. Its use in the pharmaceutical industry is also significant.
Recently Updated Pages
JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 (January 31 Evening Shift) Question Paper with Solutions [PDF]

JEE Main 2023 January 30 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 25 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 24 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

Trending doubts
JEE Main 2026: Session 2 Registration Open, City Intimation Slip, Exam Dates, Syllabus & Eligibility

JEE Main 2026 Application Login: Direct Link, Registration, Form Fill, and Steps

Understanding the Angle of Deviation in a Prism

Hybridisation in Chemistry – Concept, Types & Applications

How to Convert a Galvanometer into an Ammeter or Voltmeter

Understanding the Electric Field of a Uniformly Charged Ring

Other Pages
JEE Advanced Marks vs Ranks 2025: Understanding Category-wise Qualifying Marks and Previous Year Cut-offs

NCERT Solutions For Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 1 Solutions (2025-26)

Solutions Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 1 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

NCERT Solutions For Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 4 The d and f Block Elements (2025-26)

Biomolecules Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 10 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

NCERT Solutions For Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 10 Biomolecules (2025-26)




