
In the reaction

The compound ‘B’ is
(A) Acetic acid
(B) Acetone
(C) Acetaldehyde
(D) Ethyl alcohol
Answer
233.1k+ views
Hint: The reaction of nitrile with Grignard reagent will result in the formation of compound ‘A’. This compound ‘A’ will then get hydrolysed to form the compound ‘B’. We have to identify the final compound ‘B’ formed after hydrolysis.
Complete Step by Step Solution:
The reaction involves the reaction between the nitrile group and the Grignard reagent.
Firstly, we should understand the nature of the nitrile group. The nitrile group (or cyano group) is electron-withdrawing in nature. The nitrile ($-CN$) group is less basic than other nitrogen-containing compounds such as amines. It is polar in nature. The Grignard reagent ($RMgX$) is prepared by the reaction of an alkyl halide ($RX$) with magnesium ($Mg$). The Grignard reagent helps in the formation of carbon-carbon bonds.
The first step of the reaction is the nucleophilic attack of the Grignard reagent. The reaction between nitrile and Grignard reagent proceeds through the formation of imines. This will get hydrolysed to yield a ketone. So, as in the given reaction, methyl cyanide ($C{{H}_{3}}CN$) is treated with methyl magnesium iodide ($RMgI$), and an imines is formed. This will get hydrolysed and yield acetone ($C{{H}_{3}}COC{{H}_{3}}$ )
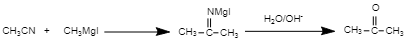
Hence, in the above reaction, the compound ‘B’ is acetone ($C{{H}_{3}}COC{{H}_{3}}$ ).
Correct Option: (B) Acetone.
Note: The Grignard reagent ($RMgX$) on treatment with carbon dioxide ($CO_{2}^{{}}$) can form a carboxylic acid ($RCOOH$ ). Also, on treatment of acyl chlorides with dialkyl cadmium, prepared by the reaction of cadmium chloride with Grignard reagent, gives ketones.
Complete Step by Step Solution:
The reaction involves the reaction between the nitrile group and the Grignard reagent.
Firstly, we should understand the nature of the nitrile group. The nitrile group (or cyano group) is electron-withdrawing in nature. The nitrile ($-CN$) group is less basic than other nitrogen-containing compounds such as amines. It is polar in nature. The Grignard reagent ($RMgX$) is prepared by the reaction of an alkyl halide ($RX$) with magnesium ($Mg$). The Grignard reagent helps in the formation of carbon-carbon bonds.
The first step of the reaction is the nucleophilic attack of the Grignard reagent. The reaction between nitrile and Grignard reagent proceeds through the formation of imines. This will get hydrolysed to yield a ketone. So, as in the given reaction, methyl cyanide ($C{{H}_{3}}CN$) is treated with methyl magnesium iodide ($RMgI$), and an imines is formed. This will get hydrolysed and yield acetone ($C{{H}_{3}}COC{{H}_{3}}$ )
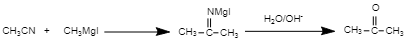
Hence, in the above reaction, the compound ‘B’ is acetone ($C{{H}_{3}}COC{{H}_{3}}$ ).
Correct Option: (B) Acetone.
Note: The Grignard reagent ($RMgX$) on treatment with carbon dioxide ($CO_{2}^{{}}$) can form a carboxylic acid ($RCOOH$ ). Also, on treatment of acyl chlorides with dialkyl cadmium, prepared by the reaction of cadmium chloride with Grignard reagent, gives ketones.
Recently Updated Pages
Types of Solutions in Chemistry: Explained Simply

JEE General Topics in Chemistry Important Concepts and Tips

JEE Extractive Metallurgy Important Concepts and Tips for Exam Preparation

JEE Amino Acids and Peptides Important Concepts and Tips for Exam Preparation

JEE Atomic Structure and Chemical Bonding important Concepts and Tips

Electricity and Magnetism Explained: Key Concepts & Applications

Trending doubts
JEE Main 2026: Session 2 Registration Open, City Intimation Slip, Exam Dates, Syllabus & Eligibility

JEE Main 2026 Application Login: Direct Link, Registration, Form Fill, and Steps

JEE Main Marking Scheme 2026- Paper-Wise Marks Distribution and Negative Marking Details

Understanding the Angle of Deviation in a Prism

Hybridisation in Chemistry – Concept, Types & Applications

How to Convert a Galvanometer into an Ammeter or Voltmeter

Other Pages
JEE Advanced Marks vs Ranks 2025: Understanding Category-wise Qualifying Marks and Previous Year Cut-offs

NCERT Solutions For Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 1 Solutions (2025-26)

Solutions Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 1 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

NCERT Solutions For Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 4 The d and f Block Elements (2025-26)

Biomolecules Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 10 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

NCERT Solutions For Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 10 Biomolecules (2025-26)




