
In the given conformation, ${C_2}$ is rotated about ${C_2} - {C_3}$ bond anticlockwise by an angle of ${120^o}$, then the conformation obtained is:
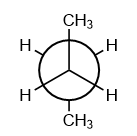
(A) Fully eclipsed conformation
(B) Partially eclipsed conformation
(C) Gauche conformation
(D) Staggered conformation
Answer
232.8k+ views
Hint: The conformation discussed in the question is of Newman projection which visualises the chemical bond conformation from front to back with respect to the relative position of groups attached to the two carbon atoms. The carbon at the front which is represented by a line is known as proximal while the carbon atom at the back which is represented by a circle is known as distal.
Complete Step by Step Solution:
Before comparing the stages of different conformations, let's discuss the different types of conformations shown in Newman projection as follows:
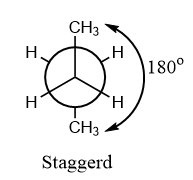
Staggered conformation: When all the groups of different axes in the conformation are at an angle of ${180^o}$ to each other, then the conformation is known as staggered conformation and it is the most stable conformation among all the conformations formed.
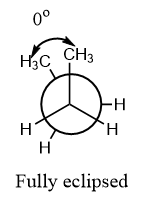
Fully eclipsed: When there is an angle of ${0^o}$ between the similar groups on different axes, i.e., the groups overlap each other, then the conformation is known as a fully eclipsed conformation. It is the most unstable conformation because a repulsion is experienced by the atoms when they overlap.
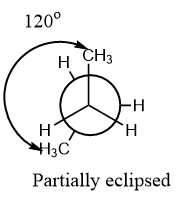
Partially eclipsed: When there is an angle of ${120^o}$ between the similar groups on different axes then the conformation is known as a partially eclipsed conformation.
Gauche conformation: This is a special kind of conformation in which there is an angle of ${60^o}$ between the similar groups on different axes. The Gauche conformation is unstable than the staggered conformation due to the steric hindrance between the two methyl groups but is comparatively stable than the partially and fully eclipsed conformations.
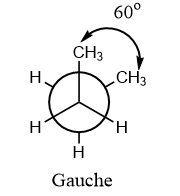
In the given question, the compound is given in staggered conformation and as per the given rotation, the following conformation will be formed:
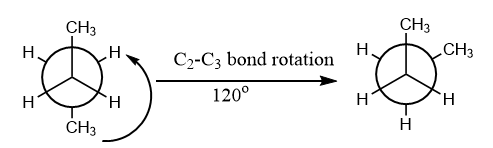
Hence, the formation of gauche conformation will take place on an anti-clock rotation of ${C_2}$ about ${C_2} - {C_3}$ bond by ${120^o}$. Therefore, option (C) is the correct answer.
Note: There are 2 special types of angular momentum of an object: the spin angular momentum is the angular momentum about the object centre of mass while the orbital angular momentum is the angular momentum about the chosen centre of rotation.
Complete Step by Step Solution:
Before comparing the stages of different conformations, let's discuss the different types of conformations shown in Newman projection as follows:
Staggered conformation: When all the groups of different axes in the conformation are at an angle of ${180^o}$ to each other, then the conformation is known as staggered conformation and it is the most stable conformation among all the conformations formed.

Fully eclipsed: When there is an angle of ${0^o}$ between the similar groups on different axes, i.e., the groups overlap each other, then the conformation is known as a fully eclipsed conformation. It is the most unstable conformation because a repulsion is experienced by the atoms when they overlap.

Partially eclipsed: When there is an angle of ${120^o}$ between the similar groups on different axes then the conformation is known as a partially eclipsed conformation.

Gauche conformation: This is a special kind of conformation in which there is an angle of ${60^o}$ between the similar groups on different axes. The Gauche conformation is unstable than the staggered conformation due to the steric hindrance between the two methyl groups but is comparatively stable than the partially and fully eclipsed conformations.

In the given question, the compound is given in staggered conformation and as per the given rotation, the following conformation will be formed:

Hence, the formation of gauche conformation will take place on an anti-clock rotation of ${C_2}$ about ${C_2} - {C_3}$ bond by ${120^o}$. Therefore, option (C) is the correct answer.
Note: There are 2 special types of angular momentum of an object: the spin angular momentum is the angular momentum about the object centre of mass while the orbital angular momentum is the angular momentum about the chosen centre of rotation.
Recently Updated Pages
JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 (January 31 Evening Shift) Question Paper with Solutions [PDF]

JEE Main 2023 January 30 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 25 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 24 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

Trending doubts
JEE Main 2026: Session 2 Registration Open, City Intimation Slip, Exam Dates, Syllabus & Eligibility

JEE Main 2026 Application Login: Direct Link, Registration, Form Fill, and Steps

Understanding the Angle of Deviation in a Prism

Hybridisation in Chemistry – Concept, Types & Applications

How to Convert a Galvanometer into an Ammeter or Voltmeter

Understanding the Electric Field of a Uniformly Charged Ring

Other Pages
JEE Advanced Marks vs Ranks 2025: Understanding Category-wise Qualifying Marks and Previous Year Cut-offs

Hydrocarbons Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 9 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Thermodynamics Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 5 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Equilibrium Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 6 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Organic Chemistry Some Basic Principles And Techniques Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 8 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

NCERT Solutions For Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 7 Redox Reactions (2025-26)




