
In the compound\[C{H_3}COCl\], which type of orbitals have been used by the doubly bonded carbon in bond formation
A. \[s{p^3}\]
B.\[s{p^2}\]
C. sp
D. p
Answer
233.1k+ views
Hint: \[C{H_3}COCl\] is called acetyl chloride which is derived from acetic acid. In this molecule, one carbon is doubly bonded to an oxygen atom. This atom is also bonded to a methyl group and a chlorine atom.
Complete step by step solution:Here in this question, the type of orbitals has been used by the doubly bonded carbon in the bond formation of acetyl chloride.
For this, we have to know the hybridization of this carbon atom. This can be done by using the VSEPR model.
We have learned that the structure and hybridization of a molecule are indicated by the VSEPR model.
This model can be described briefly as follows:-
VSEPR or valence shell electron pair repulsion model says that the shape of the molecule relies on the no.of valence shell electron pairs around the main atom and doesn't matter if they are not bonded.
Pairs of electrons in the valence shell are negatively charged and repulse each other and remain distant from each other.
Lone pair-lone pair repulsion is the highest followed by lone pair-bond pair repulsion and bond pair-bond pair repulsion.
In this molecule, one carbon is doubly bonded to an oxygen atom. This atom is also bonded to a methyl group and a chlorine atom.
There are five bond pairs of electrons and no lone pairs.
There are three sigma bonds and one pi-bond.
Thus, there is \[s{p^2}\] hybridization.
During finding the geometry, we can think that there are 3 bond pairs as multiple bonds are accepted as one electron group.
Using VSEPR theory, we can declare that the geometry is a trigonal planar.
The structure is as follows:-
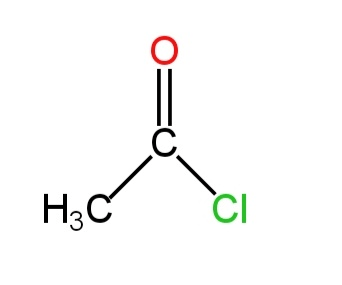
Image: Acetyl chloride
So, option B is correct.
Note: A molecule having four electron groups around the central atom puts the four groups in the direction of a tetrahedron.
If there are four atoms connected to these electron groups the molecular shape is tetrahedral. For instance, methane
Complete step by step solution:Here in this question, the type of orbitals has been used by the doubly bonded carbon in the bond formation of acetyl chloride.
For this, we have to know the hybridization of this carbon atom. This can be done by using the VSEPR model.
We have learned that the structure and hybridization of a molecule are indicated by the VSEPR model.
This model can be described briefly as follows:-
VSEPR or valence shell electron pair repulsion model says that the shape of the molecule relies on the no.of valence shell electron pairs around the main atom and doesn't matter if they are not bonded.
Pairs of electrons in the valence shell are negatively charged and repulse each other and remain distant from each other.
Lone pair-lone pair repulsion is the highest followed by lone pair-bond pair repulsion and bond pair-bond pair repulsion.
In this molecule, one carbon is doubly bonded to an oxygen atom. This atom is also bonded to a methyl group and a chlorine atom.
There are five bond pairs of electrons and no lone pairs.
There are three sigma bonds and one pi-bond.
Thus, there is \[s{p^2}\] hybridization.
During finding the geometry, we can think that there are 3 bond pairs as multiple bonds are accepted as one electron group.
Using VSEPR theory, we can declare that the geometry is a trigonal planar.
The structure is as follows:-

Image: Acetyl chloride
So, option B is correct.
Note: A molecule having four electron groups around the central atom puts the four groups in the direction of a tetrahedron.
If there are four atoms connected to these electron groups the molecular shape is tetrahedral. For instance, methane
Recently Updated Pages
JEE Main 2026 Session 2 Registration Open, Exam Dates, Syllabus & Eligibility

JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 (January 31 Evening Shift) Question Paper with Solutions [PDF]

JEE Main 2023 January 30 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 25 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

Trending doubts
JEE Main Marking Scheme 2026- Paper-Wise Marks Distribution and Negative Marking Details

In Carius method of estimation of halogens 015g of class 11 chemistry JEE_Main

Understanding Average and RMS Value in Electrical Circuits

Understanding Collisions: Types and Examples for Students

Ideal and Non-Ideal Solutions Explained for Class 12 Chemistry

Understanding Atomic Structure for Beginners

Other Pages
JEE Advanced Weightage 2025 Chapter-Wise for Physics, Maths and Chemistry

NCERT Solutions For Class 11 Chemistry in Hindi Chapter 1 Some Basic Concepts of Chemistry (2025-26)

NCERT Solutions For Class 11 Chemistry in Hindi Chapter 8 Redox Reactions (2025-26)

An ideal gas is at pressure P and temperature T in class 11 chemistry JEE_Main

Inductive Effect and Its Role in Acidic Strength

Degree of Dissociation: Meaning, Formula, Calculation & Uses




