
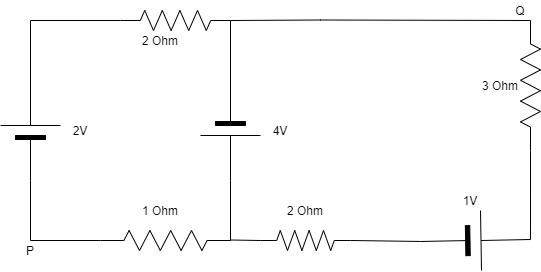
In the circuit shown, what is the potential difference ${V_{PQ}}$?
A) +3V
B) +2V
C) -2V
D) None of these
Answer
233.4k+ views
Hint: Kirchhoff’s proposed two laws that help in solving complex electronics circuits one is KCL (Kirchhoff’s current Law) and another one is KVL (Kirchhoff’s voltage law). These two laws are used for finding the equivalent resistance.
Complete step by step solution:
We will be using KVL, Kirchhoff has defined the voltage loop law as: In any loop network that is closed the net total voltage in the entire loop is equivalent to the sum of all the voltage drops which is within the loop and is also equal to zero.
Here, consider two loops in the clockwise direction for the two areas. Here the current “I” flowing in the 4V and current ${I_1}$ is flowing in 2V and current $\left( {I - {I_1}} \right)$ is flowing in 1V. Apply KVL in the first loop:
$2 - 2{I_1} + 4 - {I_1} = 0$ ;
$ \Rightarrow 6 - 3{I_1} = 0$;
Do the needed calculation:
$ \Rightarrow {I_1} = \dfrac{6}{3}$;
$ \Rightarrow {I_1} = 2A$;
Now,
${V_{PQ}} = {V_p} - {V_Q}$;
Now, we know that:
V = IR;
Put the above relation in the above equation:
$\Rightarrow {V_{PQ}} = 2 - {I_1}R$;
$\Rightarrow {V_{PQ}} = 2 - \left( 2 \right)\left( 2 \right)$;
The value of ${V_{PQ}}$is:
$ \Rightarrow {V_{PQ}} = + 2V$;
Option (B) is the correct option. Therefore, the potential difference ${V_{PQ}}$ is +2V.
Note: Here, there is no electronic device between the midpoint in the circuit and the point Q, so there is no need to choose a long path in calculating the potential difference, instead choose the shortest path between the point P and Q but before that calculate the current in the circuit by using Kirchhoff’s voltage loop law.
Complete step by step solution:
We will be using KVL, Kirchhoff has defined the voltage loop law as: In any loop network that is closed the net total voltage in the entire loop is equivalent to the sum of all the voltage drops which is within the loop and is also equal to zero.
Here, consider two loops in the clockwise direction for the two areas. Here the current “I” flowing in the 4V and current ${I_1}$ is flowing in 2V and current $\left( {I - {I_1}} \right)$ is flowing in 1V. Apply KVL in the first loop:
$2 - 2{I_1} + 4 - {I_1} = 0$ ;
$ \Rightarrow 6 - 3{I_1} = 0$;
Do the needed calculation:
$ \Rightarrow {I_1} = \dfrac{6}{3}$;
$ \Rightarrow {I_1} = 2A$;
Now,
${V_{PQ}} = {V_p} - {V_Q}$;
Now, we know that:
V = IR;
Put the above relation in the above equation:
$\Rightarrow {V_{PQ}} = 2 - {I_1}R$;
$\Rightarrow {V_{PQ}} = 2 - \left( 2 \right)\left( 2 \right)$;
The value of ${V_{PQ}}$is:
$ \Rightarrow {V_{PQ}} = + 2V$;
Option (B) is the correct option. Therefore, the potential difference ${V_{PQ}}$ is +2V.
Note: Here, there is no electronic device between the midpoint in the circuit and the point Q, so there is no need to choose a long path in calculating the potential difference, instead choose the shortest path between the point P and Q but before that calculate the current in the circuit by using Kirchhoff’s voltage loop law.
Recently Updated Pages
JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 (January 31 Evening Shift) Question Paper with Solutions [PDF]

JEE Main 2023 January 30 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 25 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 24 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

Trending doubts
JEE Main 2026: Session 2 Registration Open, City Intimation Slip, Exam Dates, Syllabus & Eligibility

JEE Main 2026 Application Login: Direct Link, Registration, Form Fill, and Steps

Understanding the Angle of Deviation in a Prism

Hybridisation in Chemistry – Concept, Types & Applications

How to Convert a Galvanometer into an Ammeter or Voltmeter

Understanding Uniform Acceleration in Physics

Other Pages
JEE Advanced Marks vs Ranks 2025: Understanding Category-wise Qualifying Marks and Previous Year Cut-offs

Dual Nature of Radiation and Matter Class 12 Physics Chapter 11 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Understanding the Electric Field of a Uniformly Charged Ring

JEE Advanced Weightage 2025 Chapter-Wise for Physics, Maths and Chemistry

Derivation of Equation of Trajectory Explained for Students

Understanding Electromagnetic Waves and Their Importance




